В этом году Kali Linux исполняется 10 лет, и чтобы отпраздновать это событие, дистрибутив Linux для тестирования на проникновение добавил средства защиты в свой арсенал инструментов безопасности с открытым исходным кодом.
Ещё неизвестно, сделает ли Kali Purple для защитных инструментов то, что Kali Linux сделала для пентеста с открытым исходным кодом, но добавление более 100 инструментов для SIEM , реагирования на инциденты , обнаружения вторжений и многого другого должно поднять профиль из этих защитных инструментов.
На данный момент Kali в первую очередь известна своими примерно 600 инструментами для пентестинга с открытым исходным кодом, что позволяет пентестерам легко устанавливать полный спектр наступательных инструментов безопасности.
В этой статье мы сосредоточимся в первую очередь на том, как использовать эту мощную ОС для проведения пентеста и избежать ошибок. Мы дадим вам обзор того, чего можно достичь с помощью Kali Linux, используя краткий набор предустановленных инструментов. Хотя это руководство служит введением в общие этапы пентестинга с практическими примерами, демонстрирующими передовой опыт, оно не заменяет полную профессиональную методологию пентестинга.
Что такое Kali Linux?
Kali Linux — популярный дистрибутив для пентестинга, поддерживаемый Offensive Security (OffSec), частной охранной компанией с 15-летней историей. Kali содержит сканеры, снифферы и многие другие инструменты для атак.
ОС может обеспечить полный сеанс пентеста или более конкретные атаки. Несмотря на то, что существует множество других дистрибутивов для пентестинга, Kali является лучшим, рекомендованным профессионалами.
Действительно, большинство предустановленных пакетов доступны как отдельные пакеты, но Kali включает и поддерживает высококачественные решения, предназначенные для профессионального использования.
Идея операционной системы состоит в том, чтобы иметь всеобъемлющий набор инструментов, который относительно легко обновлять, следуя лучшим стандартам в отрасли.
Kali создан только для пентестинга. Вот почему вы не захотите устанавливать его в качестве основной ОС, если только ваша машина не предназначена для пентестинга или это виртуальная машина.
Что нового в Kali 2023.1?
Kali 2023.1 представляет новую версию ядра и восемь новых пакетов, включая CyberChef , который является довольно удобным интерфейсом для расшифровки и декодирования различных строк и хэшей с точностью и детализацией.
Новые важные изменения Python (3.11.2) ожидаются в предстоящем стабильном выпуске Debian, что вызывает некоторые проблемы с PIP, менеджером пакетов для Python. Команда Kali говорит, что это повлияет на все дистрибутивы на основе Debian, включая Kali, поэтому они сделали временное исправление, чтобы смягчить проблему.
Команда Kali также предупредила, что на все дистрибутивы Linux может повлиять ошибка с драйверами Nvidia и некоторыми конкретными моделями графических процессоров. Затронутые устройства могут работать медленно или зависать. В таких случаях вы мало что можете сделать, кроме как удалить драйверы Nvidia и дождаться исправления.
Другим важным дополнением в этом выпуске является Purple Edition для обеспечения безопасности, о котором мы расскажем ниже.
Также стоит упомянуть изменения в рабочем столе Xfce и добавление плазменного рабочего стола KDE. Пользователям Kali также понравятся новые обои, экраны загрузки и входа в систему.
Вы можете просмотреть полный журнал изменений , чтобы получить все подробности об этом выпуске.
Подходит ли Kali для начинающих?
Kali доступен для всех. Это бесплатный дистрибутив с открытым исходным кодом, так что каждый может скачать его. Это хорошая идея, чтобы попробовать что-то самостоятельно, а затем прочитать документацию или учебные пособия.
Тем не менее, хорошее ли это место для новичков, чтобы начать? Хотя Kali удобен для начинающих, профессиональное пентестирование — это не то, где вы можете импровизировать. Чтобы быть эффективным, необходимы знания и планирование.
Вот некоторые требования для того, чтобы стать хорошим пентестером:
- Владение основами пентестинга: юридические аспекты, области применения, основные этапы (такие как пассивная разведка, обнаружение сети, перечисление, повышение привилегий), пост-эксплуатация и постоянство.
- Владение сетевыми уровнями (модель OSI, IP, подсети и т. д.)
- Владение системами Windows и Linux
- Знание Python и некоторых языков программирования (например, Go, C, C++, Ruby); на мой взгляд, это необязательно, но некоторые специалисты по безопасности могут сказать иначе
Некоторые люди учатся быстрее, чем другие, но существует огромное количество инструментов и концепций, которые нужно знать, поэтому это займет время, независимо от ваших навыков или скорости обучения.
Начало работы: как установить Kali Linux
Kali Linux удивительно прост в установке. На странице «Get Kali» перечислены различные режимы установки с предварительно настроенными образами и готовыми к использованию виртуальными машинами.
Виртуальные машины идеально подходят для быстрого ознакомления. Не стесняйтесь тестировать их, даже с целью просто посмотреть, как выглядит ОС.
Поддерживается большинство операционных систем, вы найдёте контейнеры Docker и даже поддержку Android и Raspberry Pi. Пользователи Windows могут установить Kali, например, с помощью подсистемы Windows (WSL2).
Однако установка на «голое железо» не рекомендуется для начинающих.
Вы можете прошить ISO-образы на внешнем диске, чтобы установить Kali на выбранное вами устройство, загрузившись с этого диска.
Вы также можете запустить Kali в режиме реального времени с живыми дистрибутивами, не устанавливая его на свое устройство.
Ошибки, которых следует избегать с Kali Linux
Без надлежащих знаний ваш пентест, скорее всего, провалится, так как нет волшебного рецепта, который вы могли бы применить вслепую, независимо от того, насколько хороши ваши инструменты.
Кроме того, атакующие инструменты могут отправлять несколько зондов или заголовков вместе со своими запросами (например, при сканировании и обнаружении), которые могут быть обнаружены и заблокированы средствами безопасности. Обратите внимание, что Kali не будет автоматически скрывать ваш IP-адрес или отпечатки пальцев. Вы можете использовать VPN или установить утилиты для захвата и пересылки трафика в другие подсети или настроить цепочки прокси.
Вы также можете использовать внешние платформы, такие как Linode, для настройки и работы.
Однако, если вы полный новичок, мой совет — не спешить с инструментами и начать с бесплатных проектов с открытым исходным кодом для атаки, таких как Juice Shop или многих других уязвимых приложений, которые призваны помочь вам изучить кибербезопасность.
Тогда вы, возможно, захотите изучить более продвинутые методы или инвестировать в специальные онлайн-программы обучения (см. последний раздел этой статьи).
Пентестинг — это не только серверы и веб-приложения.
Тест на проникновение направлен на имитацию реальной атаки на целевую систему. На самом деле это широкий термин, который охватывает широкий спектр тестов и процедур не только для веб-приложений, и организации могут использовать регулярные пентесты для повышения своей безопасности и устранения критических уязвимостей.
В отличие от оценок уязвимостей , пентесты предполагают эксплуатацию, что означает, что вы, как злоумышленник, взламываете систему по-настоящему, в соответствии с правилами, определёнными перед тестом. Конечная цель — написать хороший отчёт с рекомендациями.
Обратите внимание, что ваш пентест не является исчерпывающим анализом, так как у вас, скорее всего, будет ограниченное время и вам понадобится только один работающий эксплойт для достижения вашей цели.
Важно помнить, что пентестинг не ограничивается взломом уязвимых серверов, на которых размещены приложения и базы данных. Есть несколько других углов атаки для тестирования, в том числе:
- Сетевые компрометации
- Социальная инженерия (например, фишинг)
- Повреждения памяти
- Wi-Fi атаки
Kali — прекрасный набор инструментов, потому что в нём есть инструменты для широкого спектра пентестов. Веб-приложения хороши для обучения, потому что многие веб-серверы уязвимы и открывают большую поверхность для злоумышленников, поскольку организациям приходится открывать свою сеть для общественности.
Однако при необходимости (и в договоре) пентестер может проводить и физические атаки.
Не пренебрегайте юридическими аспектами
Законы не везде одинаковы, а это означает, что одни и те же процедуры могут быть законными в одних странах и незаконными в других. Это особенно верно, если вы сравниваете ЕС с США.
Насколько я знаю, «Этический взлом» не является охраняемым законом статусом. На законных исследователей безопасности подали в суд после демонстрации критических уязвимостей.
Масштаб необходим для того, чтобы отличить пентест от реальной атаки. Конечно, вам нужно явное согласие, которое обычно является юридическим соглашением, чтобы запустить пентест, но вы также должны очень точно определить область действия перед операцией .
И последнее, но не менее важное: установка Kali Linux на работе без разрешения также повлечет за собой дополнительные обязательства. Дистрибутив содержит конфиденциальные программы, которые могут подвергнуть риску вашу организацию, не говоря уже о вашей занятости.
Использование Kali Linux: поиск инструментов
Существуют буквально сотни инструментов Kali Linux для различных целей. Новички могут начать с очень популярных пакетов для классических и повторяющихся задач, или они могут обратиться к специалистам по безопасности за своими любимыми инструментами.
Хотя список инструментов может дать некоторые подсказки, он может сбить с толку новичков. Вот ряд задач пентеста и соответствующие инструменты Kali Linux:
- OSINT : используйте Maltego для сбора информации
- Социальная инженерия : используйте SET (инструментарий социального инженера)
- База знаний : Используйте эксплуатируемую базу данных
- Платформа пентестинга : используйте Metasploit Framework
- Сканирование портов : используйте Nmap для сканирования целевой сети и Ndiff для сравнения сканирований Nmap (например, чтобы увидеть, какие порты закрываются/открываются).
- Беспроводное пентестирование : используйте Aircrack-ng для взлома Wi-Fi, Bettercap для разведки и атак MitM на устройства Wi-Fi и BLE (Bluetooth с низким энергопотреблением).
- Packet sniffing: используйте Scapy для манипулирования пакетами, Ettercap также отлично подходит для выполнения атак MitM, а Wireshark обязателен.
- Перебор URL-адресов : используйте Gobuster или DirBuster для сканирования URL-адресов (каталогов, файлов и DNS) и Nikto для обнаружения уязвимостей сервера.
- Веб-фаззинг : используйте Wfuzz
- Веб-взлом : используйте BeEF для использования XSS и других уязвимостей в браузере или Burp Suite для перехвата запросов.
- SQL-инъекции : используйте sqlmap для взлома уязвимых баз данных
- Сканирование WordPress : используйте WPscan
- Удалённый вход в систему методом грубой силы : используйте Hydra (Hydra GTK для графического интерфейса)
- Перебор паролей : используйте John The Ripper
- Active Directory : используйте Mimikatz, Impacket
Списки не расскажут вам, как использовать каждый инструмент или правильную комбинацию для достижения вашей цели. Однако после установки Kali Linux сортирует пакеты по категориям, что добавляет полезный контекст и метки.
Категория обычно соответствует типичным этапам пентеста, таким как «сбор информации» или «постэксплуатация», а также повторяющимся задачам, таким как «атаки на пароли».
Просто откройте интерактивное меню:
Использование фреймворка для пентестинга
Metasploit Framework может поддерживать многие этапы вашей работы, от сканирования и обнаружения до эксплуатации и даже пост-эксплуатации.
В Kali просто откройте интерактивное меню или введите «msfconsole» в терминале, чтобы запустить консоль.
Консоль многословна, поэтому вы быстро узнаете, удалось ли использовать эксплойт. По моему опыту, интерфейс предоставляет расширенные возможности полезной нагрузки и стандартизированный способ использования очень разных хакерских модулей.
Обратите внимание, что вам не обязательно использовать фреймворк, но вам придётся объединить несколько других предустановленных ресурсов для достижения аналогичных результатов. Если вам не нравятся ручные настройки и другие повторяющиеся процедуры, консоль — отличный вариант.
Конечно, в некоторых случаях могут потребоваться другие инструменты.
Шаг 1: Определение масштаба и целей
Чёткие цели и объём имеют решающее значение для успеха вашего пентеста. Вы и организация определяете объём и правила, которые будут применяться во время теста, что гарантирует отсутствие недопонимания и наличие чётких целей.
Вашему клиенту, скорее всего, придётся выбирать между тремя распространёнными подходами к тесту:
- Черный ящик : вы действуете без какого-либо предварительного доступа или информации о цели и обычно сосредотачиваетесь на получении первоначального доступа.
- Серый ящик: промежуточный подход, при котором вам могут предоставить некоторые учётные данные или внутреннюю информацию только для того, чтобы ускорить ваш прогресс и обеспечить более глубокое тестирование.
- Белый ящик : эти тесты обычно длиннее и сосредоточены на более поздних этапах, таких как пост-эксплуатация или сохранение, чтобы бросить вызов системе и посмотреть, насколько она устойчива к эскалации привилегий, инсайдерским заданиям или боковым перемещениям.
Не всем организациям понадобится тест «белого ящика», требующий значительного времени и бюджета, но иногда он необходим.
На этом этапе вы также должны обсудить сроки и другие юридические условия. Для ваших клиентов очень важно подробно объяснить, что разрешено, а что нет в документе, который будет подписан вами и ими.
Дикие атаки могут показаться более реалистичными для новичков, но на практике нередко заносят в белый список определенные IP-адреса, которые будут использоваться пентестерами. Вам нужно определить методологию.
Шаг 2: Разведка и OSINT
Разведка, или «рекогносцировка», может быть как пассивной, так и активной.
Например, OSINT (разведка с открытым исходным кодом) — это непрямой способ сбора информации, тогда как Nmap включает активное сканирование, когда вы отправляете зонды в целевую сеть.
Kali имеет мощные инструменты OSINT, такие как Maltego (версия для сообщества бесплатна). Эти программы могут помочь вам организовать и автоматизировать ваши исследования.
В любом случае во время пентеста вам, как правило, потребуется как пассивная, так и активная разведка.
Шаг 3: Сканирование и обнаружение
Допустим, у нас есть IP/URL для сканирования. Мы можем использовать классические команды Nmap для обнаружения сервисов и потенциальных хостов для атаки, например:
nmap -oN nmapscan.txt -v -A {IP/URL}
Опция -v предназначена для «подробного», а -A для «агрессивного сканирования», которое выполняется медленнее и отправляет больше зондов к цели. Параметр -oN предназначен для экспорта вывода в текстовый файл с важными результатами.
Если мы обнаружим, что на сервере находится уязвимая система баз данных, мы атакуем её.
Шаг 4. Получение несанкционированного доступа
Внедрение SQL в уязвимую базу данных может привести к удалённому выполнению кода (RCE).
Если нам удастся внедрить вредоносные SQL-запросы в целевую базу данных с помощью sqlmap , мы можем использовать типичную уязвимость, которая позволяет записывать файлы для передачи произвольных команд на сервер.
Многие эксплойты заключаются в загрузке обратной оболочки, которая, по сути, является каналом «обратного подключения» между вашей машиной и целевым сервером.
Если такую оболочку можно открыть от имени привилегированного пользователя (например, администратора), мы получим такие же привилегии для нашего сеанса!
Учётная запись root предоставляет самые высокие привилегии, позволяя выполнять практически любые операции, оставаясь незамеченной, что идеально подходит для постэксплуатации.
Шаг 5: Пост-эксплуатация
После использования уязвимости и компрометации сети вы можете показать своим клиентам, что вы можете сделать с ней, чтобы доказать влияние и риски, связанные с нарушением.
В Metasploit есть множество модулей для этой цели, но вы можете открыть интерактивное меню Kali Linux, чтобы получить полный список доступных инструментов постэксплуатации:
Если это среда каталога Windows/Active, у Kali есть несколько пакетов для этого, например, Mimikatz , небольшая, но мощная утилита для Kerberoasting и дампа паролей, или Impacket, набор сценариев для атаки.
В зависимости от задания и размера организации вам, возможно, придётся получить дополнительный доступ и перейти от системы, которую вы только что скомпрометировали, к другой.
Эта техника называется поворотом. Возможно, вам придется продемонстрировать, что вы можете поддерживать доступ и глубже проникать в целевую инфраструктуру.
Шаг 6: Наведение порядка
Целевая сеть должна быть восстановлена до исходного состояния до того, как вы начнёте свою операцию, что означает удаление всех временных учётных записей, сценариев и любых других изменений, внесённых вами в систему.
Этот этап обычно пропускается во время CTF (события «Захват флага»), потому что цель состоит в том, чтобы отработать атакующие приёмы, но в реальных условиях пентестер должен пройти все дорожки.
Шаг 7: Отчёт и рекомендации
На этом этапе вы напишете отчёт, содержащий только что использованные вами уязвимости, потенциальные украденные данные и рекомендации по исправлению ситуации, включая технические советы.
Отчёт — это сердце пентеста и критический документ, который буквально определяет ценность вашей работы. Он должен быть осмысленным и удобочитаемым, чтобы организация могла принимать конкретные решения для защиты своей сети.
Он может содержать следующие пункты:
- Методы, используемые для сбора разведданных
- Методы, используемые для получения несанкционированного доступа
- Модель угроз и уровень рисков
- Оценочная стоимость украденных и учётных данных
Вы должны отдавать приоритет наиболее важным мерам. Посмотрите это руководство от Hackersploit, чтобы узнать больше.
Альтернативы Kali Linux с открытым исходным кодом
Есть несколько альтернатив Kali Linux, которые стоит рассмотреть.
Parrot OS Security Edition
Parrot OS Security должна быть очень удобной для новичков, так как имеет множество конфигураций по умолчанию. Однако будьте осторожны при загрузке архива, так как Parrot предоставляет «домашнюю версию», которая не предназначена для пентестинга.
Вам понадобится версия «Security». После этого по-прежнему можно установить домашнюю версию и инструменты для пентестинга, но версия для безопасности более проста.
Что мне нравится в Parrot, так это простота использования и подход, ориентированный на конфиденциальность (без телеметрии, анонимного серфинга, прокси).
Также стоит упомянуть «Hack The Box Edition». Он призван помочь новичкам быстро настроить компьютер для CTF (например, на платформе HTB), но вы можете использовать его и для создания лаборатории или обучающей среды для других целей.
Black Arch Linux
Возможно, вы читали, что Arch предназначен для опытных пентестеров (а не для новичков), так как установка считается более технической по сравнению со многими другими дистрибутивами Linux.
Это не совсем так, так как последние версии установить намного проще, чем самые старые. Теперь вы также можете скачать «тонкую» версию.
Если вы уже используете Arch, вы можете «обновить» свою установку до Black Arch с помощью специального установщика за считанные минуты.
Пользователи Linux могут оценить основную философию, которая сильно отличается от других дистрибутивов, таких как Ubuntu или Debian, и возможность получать последние версии пакетов безопасности.
Kali Purple Edition
Версия Kali «Purple» была выпущена недавно и содержит множество популярных пакетов для обеспечения безопасности, включая Yara и DefectDojo. Существует также большой спектр криминалистических и реверсивных инструментов.
Команда добавила специальные меню, которые следуют принципам NIST Cybersecurity Framework: идентификация, защита, обнаружение, реагирование, восстановление.
Пользователи должны знать, что эта инициатива находится на ранней стадии, поэтому вы не получите предварительно настроенные виртуальные машины и большую поддержку, предоставляемую стандартной версией.
Конечно, вы не должны переносить свою текущую рабочую среду на Purple прямо сейчас. Это было бы довольно сумасшедшим шагом, так как это издание ещё довольно сырое.
Тем не менее, он достаточно стабилен, чтобы его можно было протестировать, и защитники наверняка оценят этот новый вариант, несмотря на неизбежные ошибки и недочёты.
Интересно наблюдать, как OffSec исследует новые области. Издание Purple предназначено для команд Blue и Purple для обеспечения безопасности, а это означает, что это сочетание обоих миров, красного и синего.
Вы можете получить более подробную информацию о Kali Purple в официальной вики.
Ресурсы для обучения Kali Linux
Kali Linux требует усилий и времени. Ключ в том, чтобы регулярно практиковаться и учиться у профессионалов в этой области, если вы хотите сделать карьеру. Сертификат этического взлома также может помочь.
Следующие ссылки могут помочь вам разблокировать многие навыки:
- Kali документация
- Kali обучение
- Hackersploit: туториалы по тестированию на проникновение
- OffSec: сертификация OSCP
Заключение
Kali Linux заслуживает своей прекрасной репутации как критически важный инструментарий для пентестеров и всех, кто надеется ими стать. Если ваша организация содержит критически важные данные, будь то веб-интерфейс или внутренние данные, пентестирование — это передовой метод кибербезопасности, который вы должны использовать, чтобы найти уязвимости до того, как это сделают злоумышленники. Kali Linux — отличное место для начала.
Время на прочтение
5 мин
Количество просмотров 55K
Приветствую тебя, дорогой читатель в самой первой вводной части серии статей «Приручение черного дракона. Этичный хакинг с Kali Linux».
Полный список статей прилагается ниже, и будет дополняться по мере появления новых.
Приручение черного дракона. Этичный хакинг с Kali Linux:
Часть 1. Вводная часть. Подготовка рабочего стенда.
Часть 2. Фазы атаки.
Часть 3. Footprinting. Разведка и сбор информации.
Часть 4. Сканирование и типы сканирования. Погружение в nmap.
Часть 5. Методы получения доступа к системе.
Часть 6. Пост-эксплуатация. Способы повышения привилегий.
Часть 7. Пост-эксплуатация. Закрепление в системе.
Часть 8. Методы и средства внешней разведки.
Идеей, побудившей меня к написанию данной серии статей является мое желание поделиться собственным опытом в области тестирования на проникновение в рамках проводимых мной аудитов информационной безопасности финансовых организаций, и попытаться осветить важные, на мой взгляд, ключевые моменты касаемо подхода, инструментов, приемов и методов. Конечно же в сети очень много статей и книг посвященных данной теме (например, замечательная книга Дениела Г. Грэма «Этичный хакинг. Практическое руководство по взлому» или «Kali Linux. Тестирование на проникновение и безопасность» — труд целого коллектива высококлассных специалистов), программы курсов от Offensive Security, EC-Council, но далеко не у всех есть материальные возможности оплачивать дорогостоящие курсы, а в дополнение к учебникам хотелось бы больше практических примеров основанных на чьем-то опыте.
Я искренне надеюсь, дорогой читатель, что в этой серии статей мне удастся охватить большую часть интересующих тебя тем, и ответить на большую часть вопросов возникающих у тебя по мере погружения в таинственный мир информационной безопасности и пентестинга в частности.
Мы будем использовать подход максимально приближенный к сценариям атак проводимых злоумышленниками, а также вдоволь попрактикуемся на отдельных примерах и разберем такие темы как разведка и сбор информации (footprinting), сканирование ресурсов с целью обнаружения известных уязвимостей, применение эксплоитов из базы Metasploit framework для получения доступа к системе, повышение привилегий до уровня root-пользователя за счет уязвимого ПО (privilege escalation), рассмотрим методы социальной инженерии, сетевые атаки канального уровня (MAC-spoofing, ARP-spoofing, DHCP starvation), способы атак на веб-сервера, перехват и анализ трафика с помощью сетевых снифферов и многое другое.
В качестве примеров я буду использовать атаки на специально подготовленные уязвимые машины. Мы рассмотрим и проанализируем в деталях каждый метод, а так же поговорим о том как защитить свои устройства и сетевую инфраструктуру, от подобного рода атак.
Во избежание нарушения каких-либо законов (ведь наша серия статей посвящена именно ЭТИЧНОМУ хакингу), все наши эксперименты мы будем проводить в специально подготовленной виртуальной лаборатории. Ниже я опишу пошагово все действия необходимые для подготовки этой самой лаборатории. Для комфортной работы нам понадобится ПК либо ноутбук с объемом оперативной памяти не менее 6-8 Гигабайтов и любым современным 2-х ядерным процессором с поддержкой технологии виртуализации.
И так, после недолгого вступления, перейдем к практической части и начнем собирать нашу лабораторию.
Первым делом, нам необходимо будет скачать гипервизор, на котором и будем в дальнейшем разворачивать нашу виртуальную лабораторию.
Если сильно не вдаваться в подробности виртуализации, то гипервизор — это специальная программа, которая позволяет нам параллельно запускать на нашем компьютере операционные системы/программы с различной архитектурой (Windows, Linux, FreeBSD).
Для работы я буду использовать бесплатную версию гипервизора VMware Workstation Player, который доступен для скачивания на официальном сайте компании vmware по ссылке.
Гипервизор доступен для платформ Windows и Linux
Процесс установки очень простой и быстрый. Несколько нажатий кнопки NEXT, принятие условий лицензионного соглашения и наш гипервизор готов к работе.
Следующим шагом, нам необходимо скачать виртуальную машину Kali Linux.
Это специально разработанная компанией Offensive Security операционная система для тестирования на взлом и проникновение, которая просто до отказа нафарширована различными инструментами под любые типы проверок и атак.
Скачать ее можно совершенно бесплатно c официального сайта по ссылке.
Версий дистрибутива несколько, нам нужна именно виртуальная машина (Virtual Machines) для платформы VMware.
После того, как архив с образом системы скачается, разархивируем его в заранее подготовленную папку (например VMs).
После завершения распаковки папки с образом Kali Linux, запускаем VMware Workstation Player и открываем в нем существующую машину (при желании, можно скачать образ дистрибутива Kali и установить самому, однако, разворачивать готовый преднастроенный образ куда быстрее).
При первом запуске наш гипервизор выдаст окно с предложением продолжить использовать бесплатную версию, либо ввести лицензионный ключ. Оставляем первый вариант
После чего уже откроется основное окно программы, где мы открываем нашу машину
Заходим в папку VMs – kali-linux-2022.3-vmware-amd64 и открываем файл образа (он единственный отобразится в списке)
Буквально через несколько секунд, в списке у нас появится готовая к работе машина Kali Linux. Но прежде чем ее запустить, зайдем в настройки и кое-что изменим
Здесь мы видим настройки касающиеся самой виртуальной машины и ее виртуальных устройств (сетевые адаптеры, жесткие диски, выделенный объем ОЗУ и т. д.)
Для улучшения производительности добавим ей оперативной памяти (опять же, если на нашей физической машине ее достаточно), а также убедимся, что тип адаптера стоит NAT (такой же тип будет настроен на наших уязвимых машинах, которые желательно изолировать за NAT-ом от вашей физической сети).
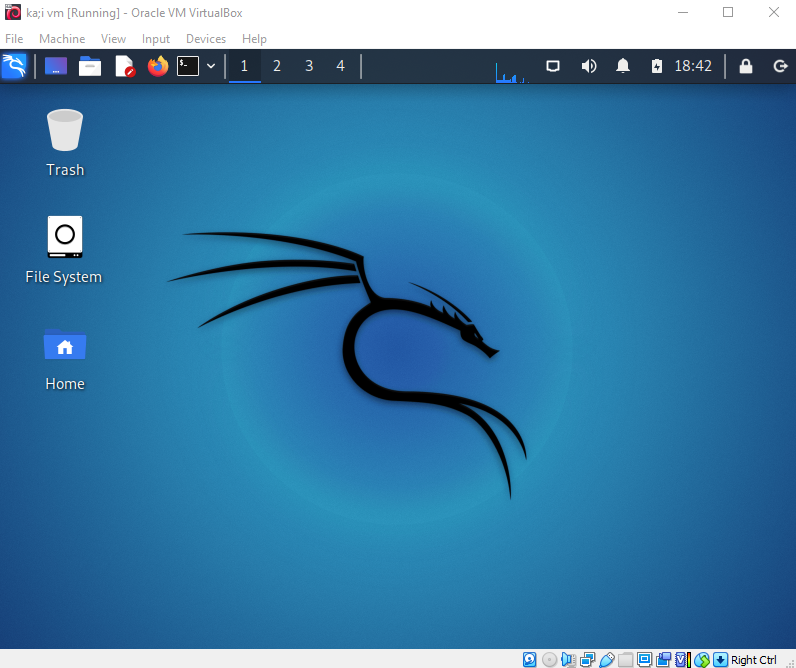
Запускаем виртуальную машину Kali и, при открытии окна с запросом ввода логина и пароля вводим kali/kali.
После успешного входа нас приветствует стильный рабочий стол Kali Linux с черным драконом в центре. Заострять внимание на интерфейсе рабочего стола мы сейчас не будем, поскольку большую часть времени нам придется работать в терминале.
Его и откроем для начала.
С учетом того, что все операции в большинстве своем требуют для выполнения наличия прав суперпользователя, введем команду sudo -s пароль kali и перейдем в режим с правами root.
Далее, первым делом, синхронизируем все списки пакетов в системе, а также обновим их следующей командой:
apt update -y && apt upgrade -y
По завершению выполнения всех обновлений пакетов можно перейти к загрузке уязвимых машин для нашего киберполигона.
Для дальнейшей работы нам понадобятся:
1) Машина Metasploitable2 на базе Linux, представляющая собой уязвимую машину специально подготовленную для обучения этичному хакингу.
Скачиваем ее тут
2) Несколько машин с ресурса Vulnhub подготовленных для соревнований типа CaptureTheFlag (CTF). Ими будут: HappyCorp1, CyberSploit1, CyberSploit2, Mr-Robot.
Прямые ссылки для скачивания:
https://www.vulnhub.com/entry/happycorp-1,296/
https://www.vulnhub.com/entry/cybersploit-1,506/
https://www.vulnhub.com/entry/cybersploit-2,511/
https://www.vulnhub.com/entry/mr-robot-1,151/
Процедура скачивания и установки машин из образов не отличается от вышеописанной и не должна вызвать сложностей.
ВАЖНО! У всех установленных виртуальных машин в разделе интерфейсов должен стоять тот же тип, что и у машины Kali Linux (NAT).
На этом первая вводная часть подошла к концу, и мы полностью готовы к тому, чтобы начать постигать тайны этичного хакинга. В следующей части мы рассмотрим такую важную тему, как фазы атаки. Спасибо за внимание и до новых встреч! 

Kali Linux Guide
A guide on setting up your Kali Linux Desktop with all the essential Applications, Tools, and Games to make your experience with kali Linux great! This may not be perfect guide for everyone but I feel there is at least one or more perfect solutions for New and Advanced Kali Linux users.
Note: You can easily convert this markdown file to a PDF in VSCode using this handy extension Markdown PDF.
Table of Contents
-
Getting Started
-
Getting Software
-
Gaming
-
Game Development
-
Setting up a macOS Workspace
-
Setting up a Windows 10 Workspace
-
Using Android and Android Apps on Linux
-
Professional Audio/Video Editing
-
Kubernetes
-
Machine Learning
-
Robotics
-
Open Source Security
-
Differential Privacy
-
Cloud Native Development
-
DevOps Development
-
Networking
-
Databases
Getting Started
Kali Linux is an open-source, Debian-based Linux distribution geared towards various information security tasks, such as Penetration Testing, Security Research, Computer Forensics and Reverse Engineering developed by Offensive Security.
Kali Linux Tools
Kali Linux Documentation
Kali Linux Community Forum
Kali Linux Training Courses
Kali Linux GitLab
Kali Linux Bug Tracker
Kali Linux Package Tracker
Etcher is an open source, cross-platform software that makes it easy to flash operating system images to a microSD card or USB device.
Rufus is a small application that creates bootable USB drives, which can then be used to install or run Microsoft Windows, Linux or DOS.

Kali Linux Desktop
Enable Firewall
sudo ufw enable //enables firewall
sudo ufw status //checks status of firewall
Getting Software
Back to the Top
Software Center
Note 1: All this software is also available in other popular Linux distributions such as Debian, Linux Mint, elementary OS, Pop!_OS, Fedora, Manjaro Linux, EndeavourOS and Arch Linux.
Note 2: For new users not comfortable with using the command-line checkout the Essential Apps section to get started. Also, if you scroll down further you’ll see other easy ways to get software applications through Flathub, Snap Store, and AppImages.
Setting up GNOME Software Center(for those that don’t want to use Ubuntu Software Center)
sudo apt install gnome-software sudo apt install snapd sudo apt install gnome-software-plugin-snap sudo apt install flatpak sudo apt install gnome-software-plugin-flatpak
Essential Apps(depending on your workflow)
Google Chrome browser
Microsoft Edge browser
Visual Studio Code or VSCodium
Microsoft Teams
Microsoft 365 with Office apps(formerly Office Online)
Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)
Zoom
How to install iCloud on Ubuntu
pCloud is the secure cloud storage(like GoogleDrive), where you can store, share and work on all your files. You can access them on any device, anywhere you go.
Jitsi Meet is a fully encrypted, 100% open source video conferencing solution.
Cisco Webex Web App is the web based version of Cisco Webex video conferencing solution.
Slack
Trello Web App
Skype
Discord
TeamViewer
Spotify
Apple Music(Web) is the web app version of Apple Music that runs in Safari, Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox.
MATLAB Online allows to users to uilitize MATLAB and Simulink through a web browser such as Google Chrome.
Adobe Lighroom Online photo editor is an online web version of Adobe Photoshop Lightroom. Adobe account required to sign-in to app.
Adobe Spark(Web) is an applications let you make cool Social Graphics, Short Videos, and Web Pages. Adobe account required to sign-in to app.
Photopea is an advanced online image editor supporting PSD, XCF, Sketch, XD and CDR formats. (Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, Sketch App, Adobe XD, CorelDRAW).
Master PDF Editor is straightforward, easy to use application for working with PDF documents equipped with powerful multi-purpose functionality. With Master PDF Editor you can easily view, create and modify PDF documents.
CrossOver Linux® is a Microsoft Windows compatibility layer(based on WINE(Wine Is Not an Emulator)). The CrossOver compatibility layer enables thousands of Windows-based applications to run on Linux, macOS, or Chrome OS.
WinApps for Linux is a program that runs Windows apps such as Microsoft Office & Adobe in Linux (Ubuntu/Fedora) and GNOME/KDE as if they were a part of the native OS, including Nautilus integration for right clicking on files of specific mime types to open them.
DaVinci Resolve video editor is complete video editing solution that combines professional 8K editing, color correction, visual effects and audio post production all in one software tool.
Reaper Audio editor is a complete digital audio production application for computers, offering a full multitrack audio and MIDI recording, editing, processing, mixing and mastering toolset.
Flameshot is a powerful yet simple to use screenshot software.
Timeshift for Linux is an application that provides functionality similar to the System Restore feature in Windows and the Time Machine tool in Mac OS. Timeshift protects your system by taking incremental snapshots of the file system at regular intervals. These snapshots can be restored at a later date to undo all changes to the system.
Stacer is an open source system optimizer and application monitor that helps users to manage their entire system. Also available as an AppImage.
Nativefier is a command-line tool to easily create a desktop app for any web site with minimal configuration. Apps are wrapped by Electron (which uses Chromium under the hood) in an OS executable (.app, .exe, etc) for use on Windows, macOS and Linux.
App Outlet
App Outlet is a Universal application store(Flatpaks, Snaps, and AppImages) inspired by the Linux App Store online service.
Snaps
Snap Store is a build and distribution service for Snap applications.
Snapcraft Forum
Flatpaks
FlatHub is a build and distribution service for Flatpak applications.
FlatHub Forum
AppImages
AppImageHub is a build and distribution service for AppImage applications.
AppImage Manager is a package manager for AppImages.
AppImage Forum
Gaming
Back to the Top
Steam
Get Steam
Or
wget https://steamcdn-a.akamaihd.net/client/installer/steam.deb
Proton is a tool for use with the Steam client which allows games which are exclusive to Windows to run on the Linux operating system. It uses Wine to facilitate this.
Enable Proton in Steam
- Click on “Steam” then “Settings” to open the Settings window at the far-left corner.
- On the “Settings” window, click on “Steam Play.” Ensure you check the “Enable Steam Play for supported files” and “Enable Steam Play for all other titles” checkboxes. Lastly, select the Proton version you wish to use from the drop-down menu.
ProtonDB
ProtonDB is a collection of over 100,000 gaming reports from other gamers as they test games with Proton on Linux and provide aggregate scores of how well games perform. A growing pool of suggestions provides tweaks that you can try to get games working while Proton continues development. In addition to this, you may explore the Steam game catalog on this site to browse and discover a wide range of titles that were previously unavailable for use on Linux.


Lutris
Lutris is a gaming client for Linux. It gives you access to all your video games with the exception of the current console generation. Also, integrates nicely with other stores like GOG, Steam, Battle.net, Origin, Uplay and many other sources that allow you to import your existing game library and community maintained install scripts give you a completely automated setup.
Add Epic Games Store
GameHub
GameHub is a unified library for all your games. It allows you to store your games from different platforms into one program to make it easier for you to manage your games.
GameHub supports:
-
native games for Linux
-
multiple compatibility layers:
- Wine
- Proton
- DOSBox
- RetroArch
- ScummVM
- WineWrap — a set of preconfigured wrappers for supported games;
- custom emulators
-
multiple game platforms:
- Steam
- GOG
- Humble Bundle (including Humble Trove)
- itch.io
Game Streaming
Geforce NOW use the Chromebook version to play all your games in Google Chrome or any Chromium-based web browser such as Brave, Vivaldi, and Microsoft Edge. Also, available as a Electron Desktop App in the Snap store Geforce NOW.
Moonlight Game Streaming is a program that let you stream from your PC games over the Internet with no configuration required. Stream from almost any device, whether you’re in another room or miles away from your gaming rig.
Chiaki is a Free and Open Source Software Client for PlayStation 4 and PlayStation 5 Remote Play for Linux, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, Android, macOS, Windows, Nintendo Switch and potentially even more platforms.
Xbox Project xCloud is Microsoft’s cloud-based Xbox game-streaming technology (currently in Beta). Play games like Forza Horizon 4, Halo 5: Guardians, Gears of War 4, Sea of Thieves, Cuphead, Red Dead Redemption 2, and 100+ other games on your mobile device or Chrome web browser. Microsoft’s Xbox Project xCloud does require an Xbox Game Pass Ultimate subscription.
Game Emulators
RetroArch is a frontend for emulators, game engines and media players. It enables you to run classic games on a wide range of computers and consoles through its slick graphical interface. Settings are also unified so configuration is done once and for all.
Dolphin is an emulator for two recent Nintendo video game consoles: the GameCube and the Wii. It allows PC gamers to enjoy games for these two consoles in full HD (1080p) with several enhancements: compatibility with all PC controllers, turbo speed, networked multiplayer, and even more.
Citra is an open-source emulator for the Nintendo 3DS capable of playing many of your favorite games.
yuzu is an experimental open-source emulator for the Nintendo Switch from the creators of Citra.
DOSBox is an open-source DOS emulator which primarily focuses on running DOS Games.
MAME is a Arcade Machine Emulator.
xemu is an original Xbox emulator.
Graphics Performance
GreenWithEnvy (GWE) is a GTK system utility designed by Roberto Leinardi to provide information, control the fans and overclock your NVIDIA video card for better performance. Available in the Pop Shop as a Flatpak.
CoreCtrl is a free and open source Linux application that allows you to control your computer hardware with ease using application profiles for native and Windows applications, has basic CPU controls and full AMD GPUs controls (for both old and new models).
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ernstp/mesarc sudo apt install corectrl
Performance Benchmarks
Geekbench 5 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures your system’s performance with the press of a button.
Phoronix Test Suite
UNIGINE Superposition is an extreme performance and stability test for PC hardware: video card, power supply, cooling system.
Wine
WINE(Wine Is Not an Emulator) is a compatibility layer capable of running Windows applications on several POSIX-compliant operating systems, such as Linux, macOS, & BSD. Instead of simulating internal Windows logic like a virtual machine or emulator, Wine translates Windows API calls into POSIX calls on-the-fly, eliminating the performance and memory penalties of other methods and allowing you to cleanly integrate Windows applications into your desktop.
Winetricks
Winetricks is an easy way to work around problems in Wine.
this is needed to avoid adobeair error
sudo sed -i 's|echo "\${arg%%=\*}"=\\""${arg### \*=}"\\"|echo \${arg%%=\*}=\\"\${arg### \*=}\\"|g' /usr/local/bin/winetricks
sudo apt install cabextract libncurses5:armhf
Game Development
Back to the Top
Game Engines
Unity is a cross-platform game development platform. Use Unity to build high-quality 3D and 2D games, deploy them across mobile, desktop, VR/AR, consoles or the Web, and connect with loyal and enthusiastic players and customers.
Unity Hub
Unreal Engine 4 is a game engine developed by Epic Games with the world’s most open and advanced real-time 3D creation tool. Continuously evolving to serve not only its original purpose as a state-of-the-art game engine, today it gives creators across industries the freedom and control to deliver cutting-edge content, interactive experiences, and immersive virtual worlds.
Linux Game Development on Unreal Engine 4
Godot Engine is a feature-packed, cross-platform game engine to create 2D and 3D games from a unified interface. It provides a comprehensive set of common tools, so that users can focus on making games without having to reinvent the wheel. Games can be exported in one click to a number of platforms, including the major desktop platforms (Linux, Mac OSX, Windows) as well as mobile (Android, iOS) and web-based (HTML5) platforms.
If you would like to Donate to the Godot Project
Blender is the free and open source 3D creation suite. It supports the entirety of the 3D pipeline—modeling, rigging, animation, simulation, rendering, compositing and motion tracking, video editing and 2D animation pipeline.
If you would like to Donate to the Blender Project
Unigine is a cross-platform game engine designed for development teams (C++/C# programmers, 3D artists) working on interactive 3D apps.
GameMaker Studio 2 is the latest and greatest incarnation of GameMaker. It has everything you need to take your idea from concept to finished game. With no barriers to entry and powerful functionality, GameMaker Studio 2 is the ultimate 2D development environment.
Setting Up GameMaker Studio For Ubuntu
Tools
Panda3D is a game engine, a framework for 3D rendering and game development for Python and C++ programs, developed by Disney and CMU. Panda3D is open-source and free for any purpose, including commercial ventures.
Source 2 is a 3D video game engine in development by Valve as a successor to Source. It is used in Dota 2, Artifact, Dota Underlords, parts of The Lab, SteamVR Home, and Half-Life: Alyx.
Open Graphics Library(OpenGL) is an API used acrossed mulitple programming languages and platforms for hardware-accelerated rendering of 2D/3D vector graphics currently developed by the Khronos Group.
Open Computing Language (OpenCL) is an open standard for parallel programming of heterogeneous platforms consisting of CPUs, GPUs, and other hardware accelerators found in supercomputers, cloud servers, personal computers, mobile devices and embedded platforms.
OpenGL Shading Language(GLSL) is a High Level Shading Language based on the C-style language, so it covers most of the features a user would expect with such a language. Such as control structures (for-loops, if-else statements, etc) exist in GLSL, including the switch statement.
High Level Shading Language(HLSL) is the High Level Shading Language for DirectX. Using HLSL, the user can create C-like programmable shaders for the Direct3D pipeline. HLSL was first created with DirectX 9 to set up the programmable 3D pipeline.
Vulkan is a modern cross-platform graphics and compute API that provides high-efficiency, cross-platform access to modern GPUs used in a wide variety of devices from PCs and consoles to mobile phones and embedded platforms. Vulkan is currently in development by the Khronos consortium.
MoltenVK is an implementation of Vulkan running on iOS and macOS using Apple’s Metal graphics framework.
MoltenGL is an implementation of the OpenGL ES 2.0 API that runs on Apple’s Metal graphics framework.
NVIDIA Omniverse is a powerful, multi-GPU, real-time simulation and collaboration platform for 3D production pipelines based on Pixar’s Universal Scene Description and NVIDIA RTX.
HGIG is a volunteer group of companies from the game and TV display industries that meet to specify and make available for the public guidelines to improve consumer gaming experiences in HDR.
Three.js is a cross-browser JavaScript library and application programming interface used to create and display animated 3D computer graphics in a web browser using WebGL.
Superpowers is a downloadable HTML5 app for real-time collaborative projects . You can use it solo like a regular offline game maker, or setup a password and let friends join in on your project through their Web browser.
Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR)
SteamVR for Linux is the ultimate tool for experiencing VR content on the hardware of your choice. SteamVR supports the Valve Index, HTC Vive, Oculus Rift, Windows Mixed Reality headsets, and others.
SteamVR Home
OpenVR is an API and runtime that allows access to VR hardware(Steam Index, HTC Vive, and Oculus Rift) from multiple vendors without requiring that applications have specific knowledge of the hardware they are targeting.
OpenVR Benchmark on Steam is the first benchmark tool for reproducibly testing your real VR performance, rendering inside of your VR headset.
OpenHMD is open source API and drivers that supports a wide range of HMD(head-mounted display) devices such as Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, Sony PSVR, and others.
openXR is a free, open standard that provides high-performance access to Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) collectively known as XR—platforms and devices.
Monado is the first OpenXR™ runtime for GNU/Linux. Monado aims to jump-start development of an open source XR ecosystem and provide the fundamental building blocks for device vendors to target the GNU/Linux platform.
Libsurvive is a set of tools and libraries that enable 6 dof tracking on lighthouse and vive based systems that is completely open source and can run on any device. It currently supports both SteamVR 1.0 and SteamVR 2.0 generation of devices and should support any tracked object commercially available.
Simula is a VR window manager for Linux that runs on top of Godot. It takes less than 1 minute to install. Simula is officially compatible with SteamVR headsets equipped with Linux drivers (e.g. HTC Vive, HTC Vive Pro, & Valve Index). We have also added experimental support to OpenXR headsets that have Monado drivers (e.g. North Star, OSVR HDK, and PSVR). Some people have gotten the Oculus Rift S to run Simula via OpenHMD (see here).
Game Development Learning Resources
Unreal Online Learning is a free learning platform that offers hands-on video courses and guided learning paths.
Unreal Engine Authorized Training Program
Unreal Engine for education
Unreal Engine Training & Simulation
Unity Certifications
Getting Started with Vulkan
Game Design Online Courses from Udemy
Game Design Online Courses from Skillshare
Learn Game Design with Online Courses and Classes from edX
Game Design Courses from Coursera
Game Design and Development Specialization Course from Coursera
Setting up a macOS workspace
Back to the Top
REQUIREMENTS
- A modern Linux distribution
- QEMU > 2.11.1
- A CPU with Intel VT-x / AMD SVM support is required
- A CPU with SSE4.1 support is required for >= macOS Sierra
- A CPU with AVX2 support is required for >= macOS Mojave
- Internet access for the installation process
Open the terminal and run: sudo apt install qemu uml-utilities virt-manager dmg2img git wget libguestfs-tools p7zip
Sosumi is a app that let’s you download and install macOS in a VM.
OpenCore for macOS
Setting up a Windows 10 workspace
Back to the Top
REQUIREMENTS
- A modern Linux distribution
- QEMU > 2.11.1
- A CPU with Intel VT-x / AMD SVM support is required
- WindowsGuestDrivers/Download Drivers — KVM
- Internet access for the installation process
Open the terminal and run: sudo apt install qemu uml-utilities virt-manager gnome-boxes
GNOME Boxes is an application that gives you access to virtual machines, running locally or remotely. It also allows you to connect to the display of a remote computer.
OpenCore for Windows 10
Using Android and Android Apps on Linux
Back to the Top
Android Studio is the development suite for Google’s Android Operating System(OS). It’s built on JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA software and designed specifically for Android development. It is available for download on Windows, macOS and Linux.

Android Virtual Device (AVD) is a configuration in Android Studio that defines the characteristics of an Android phone, tablet, Wear OS, Android TV, or Automotive OS device that you want to simulate in the Android Emulator. The Android Emulator simulates Android devices on your computer so that you can test your application on a variety of devices and Android API levels without needing to have each physical device.

LineageOS is a free and open-source operating system for various devices, based on the Android mobile platform.

Anbox is an application that provides a container-based approach to boot a full Android system on a regular GNU/Linux system like Ubuntu, Debian Fedora, and openSUSE.

Anbox Cloud is the mobile cloud computing platform delivered by Canonical. Run Android in the cloud, at high scale and on any type of hardware.

Genymotion is a very fast Android emulator. The program itself is based on VirtualBox and is known for its effectively fast speed and is usefulness for running Android apps on a Windows, Mac and Linux desktop.
Desktop
Local virtual devices with high performances.
- Emulate a wide range of virtual device configurations (Android versions, screen size, hardware capacities, etc.)
- Simulate multiple scenarios thanks to our full set of hardware sensors (GPS, network, multitouch, etc.)
- Cross-platform: Windows, Mac and Linux
- Manipulate easily with ADB
- $412 per year for employees in a company (BUSINESS). All features, advanced support.
- $136 per year for freelancers (INDIE). All features, best effort support.
- Free for personal use only (learning & entertainment). Limited features, no support.

Scrcpy is an application by Genymotion that provides display and control of Android devices connected on USB (or over TCP/IP). It does not require any root access and works on GNU/Linux, Windows and macOS. The Android device requires at least API 21 (Android 5.0).

Professional Audio & Video Editing
Back to the Top

H.264(AVC) is a video compression standard based on block-oriented and motion-compensated integer-DCT coding that defines multiple profiles (tools) and levels (max bitrates and resolutions) with support up to 8K.
H.265(HEVC) is a video compression standard that is the successor to H.264(AVC). It offers a 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or improved video quality at the same bit-rate.
FFmpeg is a leading multimedia framework that can decode, encode, transcode, mux, demux, stream, filter and play pretty much anything that humans and machines have created. It supports the most obscure ancient formats up to the cutting edge ones on multiple platforms such as Windows, macOS, and Linux.
HandBrake is a tool for transcoding video from almost any format with a selection of widely supported codecs. It is supported on Window, macOS, and Linux.
Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) is an adaptive streaming protocol that allows for a video stream to switch between bit rates on the basis of network performance, in order to keep a video playing.
OpenMAX™ is a cross-platform API that provides comprehensive streaming media codec and application portability by enabling accelerated multimedia components to be developed, integrated and programmed across multiple operating systems and silicon platforms.
DaVinci Resolve is the world’s only solution that combines professional 8K editing, color correction, visual effects and audio post production all in one software tool! You can instantly move between editing, color, effects, and audio with a single click. DaVinci Resolve Studio is also the only solution designed for multi user collaboration so editors, assistants, colorists, VFX artists and sound designers can all work live on the same project at the same time.
Blender comes with a built-in video sequence editor allows you to perform basic actions like video cuts and splicing, as well as more complex tasks like video masking or color grading. The Video Editor includes: Live preview, luma waveform, chroma vectorscope and histogram displays. Audio mixing, syncing, scrubbing and waveform visualization.
Kdenlive is an open source video editing tool that supports unlimited multimedia files. It’s based on the MLT Framework, KDE and Qt. People who are looking for a very versatile video editing tool that comes packed with features. The latest 20.08 release is out with nifty features like Interface Layouts, Multiple Audio Stream support, Cached data management and Zoombars in the Clip Monitor and Effects Panel but one may argue that the highlights of this release are stability and interface improvements.
OpenShot is an open-source video editing tool that’s designed for users new in the editing environment. It has simple features such as a simple drag-and-drop function, it provides an easy-to-use and quick-to-learn user interface. The powerful video editor offers tons of efficient ways to cut and trim down your videos. You can freely utilize the unlimited tracks, video effects engine, title editor, 3D animations, slow motion, and time effects. It supports commonly used video codecs that are supported by FFmpeg like WebM (VP9), AVCHD (libx264), HEVC (libx265) and audio codecs like mp3 (libmp3lame) and aac (libfaac). The program can render MPEG4, ogv, Blu-ray and DVD video, and Full HD videos for uploading to the internet video websites like YouTube.
Lightworks is a non-linear video editing appluication for editing and mastering digital video used by the film industry. Its professional edition has been used for box office hits, such as Shutter Island, Pulp Fiction, and Mission Impossible. Intimidating user interface. Like professional video editors, such as Adobe Premiere Pro, Lightworks is rather complicated to use for new users.
Shotcut is an open source multi-platform video editor. You can perform various actions such as video editing (including 4K video quality), add effects, create new movies, import most image files formats, export to almost any file format and much more.
Olive is a free non-linear video editor aiming to provide a fully-featured alternative to high-end professional video editing software.
Natron is a powerful Digital Compositor that can handle all of your 2D/2.5D needs. Its robust OIIO file formats and OpenFX architecture is what make Natron the most flexible open source compositor for the visual effects community. Its interface and functionally are the same across all platforms such as MacOS, Linux and Windows.
OBS (Open Broadcaster Software) is free and open source software for video recording and live streaming. Stream to Twitch, YouTube and many other providers or record your own videos with high quality H264 / AAC encoding.
REAPER is a complete digital audio production application for computers, offering a full multitrack audio and MIDI recording, editing, processing, mixing and mastering toolset.REAPER supports a vast range of hardware, digital formats and plugins, and can be comprehensively extended, scripted and modified.
JACK Audio Connection Kit AKA JACK is a professional sound server daemon that provides real-time, low-latency connections for both audio and MIDI data between applications that implement its API. JACK can be configured to send audio data over a network to a «master» machine, which then outputs the audio to a physical device. This can be useful to mix audio from a number of «slave» computers without requiring additional cables or hardware mixers, and keeping the audio path digital for as long as possible.
Bitwig Studio is a digital audio workstation that has linear and non-linear workflows for sound design, recording, live performance, and more. Along with 90+ instruments, effects, and other creative tools. It is supported Windows, macOS, and Linux.
PipeWire is a server and user space API to deal with multimedia pipelines.It provides a low-latency, graph based processing engine on top of audio and video devices that can be used to support the use cases currently handled by both pulseaudio and JACK. PipeWire was designed with a powerful security model that makes interacting with audio and video devices from containerized applications easy. Nodes in the graph can be implemented as separate processes, communicating with sockets and exchanging multimedia content using fd passing.
Yabridge is a modern and transparent way to use Windows VST2 and VST3 plugins on Linux. Yabridge seamlessly supports using both 32-bit and 64-bit Windows VST2 and VST3 plugins in a 64-bit Linux VST host as if they were native VST2 and VST3 plugins, with optional support for plugin groups to enable inter-plugin communication for VST2 plugins and quick startup times.
Sonobus is an easy to use application for streaming high-quality, low-latency peer-to-peer audio between devices over the internet or a local network.
Avid Pro Tools is an industry standard audio-production software for songwriters, musicians, producers, and engineers.
LMMS is an open source digital audio workstation application program. When LMMS is pairedr with appropriate computer hardware, it allows music to be produced by arranging samples, synthesizing sounds, playing on a MIDI keyboard, and combining the features of trackers and sequencers. Developed by Paul Giblock and Tobias Junghans, this program stands for «Linux MultiMedia Studio» and supports handy plugins that enables it to work on different operating systems.
Ardour is an open source, collaborative effort of a worldwide team including musicians, programmers, and professional recording engineers. Development is transparent — anyone can watch our work as it happens. Like a good piece of vintage hardware, you can open the box and look inside.
Audacity is an easy-to-use, multi-track audio editor and recorder for Windows, Mac OS X, GNU/Linux and other operating systems. Developed by a group of volunteers as open source and offered free of charge. Amazing support community.
Glimpse is a cross-platform raster graphics editor based on the GNU Image Manipulation Program available for Linux, MacOS, and Windows. A great tool for making YouTube video thumbnails.
Kubernetes
Back to the Top

Kubernetes (K8s) is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.

Building Highly-Availability(HA) Clusters with kubeadm. Source: Kubernetes.io, 2020
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) is a managed, production-ready environment for running containerized applications.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is serverless Kubernetes, with a integrated continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) experience, and enterprise-grade security and governance. Unite your development and operations teams on a single platform to rapidly build, deliver, and scale applications with confidence.
Amazon EKS is a tool that runs Kubernetes control plane instances across multiple Availability Zones to ensure high availability.
AWS Controllers for Kubernetes (ACK) is a new tool that lets you directly manage AWS services from Kubernetes. ACK makes it simple to build scalable and highly-available Kubernetes applications that utilize AWS services.
Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE) is an Oracle-managed container orchestration service that can reduce the time and cost to build modern cloud native applications. Unlike most other vendors, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure provides Container Engine for Kubernetes as a free service that runs on higher-performance, lower-cost compute.
Anthos is a modern application management platform that provides a consistent development and operations experience for cloud and on-premises environments.
Red Hat Openshift is a fully managed Kubernetes platform that provides a foundation for on-premises, hybrid, and multicloud deployments.
OKD is a community distribution of Kubernetes optimized for continuous application development and multi-tenant deployment. OKD adds developer and operations-centric tools on top of Kubernetes to enable rapid application development, easy deployment and scaling, and long-term lifecycle maintenance for small and large teams.
Odo is a fast, iterative, and straightforward CLI tool for developers who write, build, and deploy applications on Kubernetes and OpenShift.
Kata Operator is an operator to perform lifecycle management (install/upgrade/uninstall) of Kata Runtime on Openshift as well as Kubernetes cluster.
Thanos is a set of components that can be composed into a highly available metric system with unlimited storage capacity, which can be added seamlessly on top of existing Prometheus deployments.
OpenShift Hive is an operator which runs as a service on top of Kubernetes/OpenShift. The Hive service can be used to provision and perform initial configuration of OpenShift 4 clusters.
Rook is a tool that turns distributed storage systems into self-managing, self-scaling, self-healing storage services. It automates the tasks of a storage administrator: deployment, bootstrapping, configuration, provisioning, scaling, upgrading, migration, disaster recovery, monitoring, and resource management.
VMware Tanzu is a centralized management platform for consistently operating and securing your Kubernetes infrastructure and modern applications across multiple teams and private/public clouds.
Kubespray is a tool that combines Kubernetes and Ansible to easily install Kubernetes clusters that can be deployed on AWS, GCE, Azure, OpenStack, vSphere, Packet (bare metal), Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (Experimental), or Baremetal.
KubeInit provides Ansible playbooks and roles for the deployment and configuration of multiple Kubernetes distributions.
Rancher is a complete software stack for teams adopting containers. It addresses the operational and security challenges of managing multiple Kubernetes clusters, while providing DevOps teams with integrated tools for running containerized workloads.
K3s is a highly available, certified Kubernetes distribution designed for production workloads in unattended, resource-constrained, remote locations or inside IoT appliances.
Helm is a Kubernetes Package Manager tool that makes it easier to install and manage Kubernetes applications.
Knative is a Kubernetes-based platform to build, deploy, and manage modern serverless workloads. Knative takes care of the operational overhead details of networking, autoscaling (even to zero), and revision tracking.
KubeFlow is a tool dedicated to making deployments of machine learning (ML) workflows on Kubernetes simple, portable and scalable.
Etcd is a distributed key-value store that provides a reliable way to store data that needs to be accessed by a distributed system or cluster of machines. Etcd is used as the backend for service discovery and stores cluster state and configuration for Kubernetes.
OpenEBS is a Kubernetes-based tool to create stateful applications using Container Attached Storage.
Container Storage Interface (CSI) is an API that lets container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes seamlessly communicate with stored data via a plug-in.
MicroK8s is a tool that delivers the full Kubernetes experience. In a Fully containerized deployment with compressed over-the-air updates for ultra-reliable operations. It is supported on Linux, Windows, and MacOS.
Charmed Kubernetes is a well integrated, turn-key, conformant Kubernetes platform, optimized for your multi-cloud environments developed by Canonical.
Grafana Kubernetes App is a toll that allows you to monitor your Kubernetes cluster’s performance. It includes 4 dashboards, Cluster, Node, Pod/Container and Deployment. It allows for the automatic deployment of the required Prometheus exporters and a default scrape config to use with your in cluster Prometheus deployment.
KubeEdge is an open source system for extending native containerized application orchestration capabilities to hosts at Edge.It is built upon kubernetes and provides fundamental infrastructure support for network, app. deployment and metadata synchronization between cloud and edge.
Lens is the most powerful IDE for people who need to deal with Kubernetes clusters on a daily basis. It has support for MacOS, Windows and Linux operating systems.
kind is a tool for running local Kubernetes clusters using Docker container “nodes”. It was primarily designed for testing Kubernetes itself, but may be used for local development or CI.
Flux CD is a tool that automatically ensures that the state of your Kubernetes cluster matches the configuration you’ve supplied in Git. It uses an operator in the cluster to trigger deployments inside Kubernetes, which means that you don’t need a separate continuous delivery tool.
Kubernetes Learning Resources
Getting Kubernetes Certifications
Getting started with Kubernetes on AWS
Kubernetes on Microsoft Azure
Intro to Azure Kubernetes Service
Getting started with Google Cloud
Getting started with Kubernetes on Red Hat
Getting started with Kubernetes on IBM
YAML basics in Kubernetes
Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes
Docker and Kubernetes
Deploy a model to an Azure Kubernetes Service cluster
Simplify Machine Learning Inference on Kubernetes with Amazon SageMaker Operators
Running Apache Spark on Kubernetes
Kubernetes Across VMware vRealize Automation
VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid
All the Ways VMware Tanzu Works with AWS
VMware Tanzu Education
Using Ansible in a Cloud-Native Kubernetes Environment
Managing Kubernetes (K8s) objects with Ansible
Setting up a Kubernetes cluster using Vagrant and Ansible
Running MongoDB with Kubernetes
Kubernetes Fluentd
Understanding the new GitLab Kubernetes Agent
Kubernetes Contributors
KubeAcademy from VMware
Machine Learning
Back to the Top
ML frameworks & applications
TensorFlow is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
Tensorman is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by System76.Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
Keras is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
PyTorch is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook’s AI Research lab.
Amazon SageMaker is a fully managed service that provides every developer and data scientist with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly. SageMaker removes the heavy lifting from each step of the machine learning process to make it easier to develop high quality models.
Azure Databricks is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
Apache Airflow is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
Apache MXNet is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
AutoGluon is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
Anaconda is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
PlaidML is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
OpenCV is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
Scikit-Learn is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
Weka is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
Caffe is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
Theano is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
nGraph is an open source C++ library, compiler and runtime for Deep Learning. The nGraph Compiler aims to accelerate developing AI workloads using any deep learning framework and deploying to a variety of hardware targets.It provides the freedom, performance, and ease-of-use to AI developers.
NVIDIA cuDNN is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for deep neural networks. cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including Caffe2, Chainer, Keras, MATLAB, MxNet, PyTorch, and TensorFlow.
Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
Apache Spark is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
Apache PredictionIO is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK) is a tool for managing Apache Kafka clusters.
BigDL is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
Koalas is project makes data scientists more productive when interacting with big data, by implementing the pandas DataFrame API on top of Apache Spark.
Apache Spark™ MLflow is an open source platform to manage the ML lifecycle, including experimentation, reproducibility, deployment, and a central model registry. MLflow currently offers four components:
MLflow Tracking: Record and query experiments: code, data, config, and results.
MLflow Projects: Package data science code in a format to reproduce runs on any platform.
MLflow Models: Deploy machine learning models in diverse serving environments.
Model Registry: Store, annotate, discover, and manage models in a central repository.
Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
Numba is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
Chainer is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using CuPy for high performance training and inference.
cuML is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML’s Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
Online ML Learning Resources
Machine Learning by Stanford University from Coursera
Machine Learning Courses Online from Coursera
Machine Learning Courses Online from Udemy
Learn Machine Learning with Online Courses and Classes from edX
Robotics
Back to the Top

Tools for Robotics
ROS is robotics middleware. Although ROS is not an operating system, it provides services designed for a heterogeneous computer cluster such as hardware abstraction, low-level device control, implementation of commonly used functionality, message-passing between processes, and package management.
ROS2 is a set of software libraries and tools that help you build robot applications. From drivers to state-of-the-art algorithms, and with powerful developer tools, ROS has what you need for your next robotics project. And it’s all open source.
Robot Framework is a generic open source automation framework. It can be used for test automation and robotic process automation. It has easy syntax, utilizing human-readable keywords. Its capabilities can be extended by libraries implemented with Python or Java.
The Robotics Library (RL) is a self-contained C++ library for robot kinematics, motion planning and control. It covers mathematics, kinematics and dynamics, hardware abstraction, motion planning, collision detection, and visualization.RL runs on many different systems, including Linux, macOS, and Windows. It uses CMake as a build system and can be compiled with Clang, GCC, and Visual Studio.
MoveIt is the most widely used software for manipulation and has been used on over 100 robots. It provides an easy-to-use robotics platform for developing advanced applications, evaluating new designs and building integrated products for industrial, commercial, R&D, and other domains.
AutoGluon is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
Gazebo accurately and efficiently simulates indoor and outdoor robots. You get a robust physics engine, high-quality graphics, and programmatic and graphical interfaces.
Robotics System Toolbox provides tools and algorithms for designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots. For manipulators and humanoid robots, the toolbox includes algorithms for collision checking, trajectory generation, forward and inverse kinematics, and dynamics using a rigid body tree representation.
For mobile robots, it includes algorithms for mapping, localization, path planning, path following, and motion control. The toolbox provides reference examples of common industrial robot applications. It also includes a library of
commercially available industrial robot models that you can import, visualize, and simulate.
Intel Robot DevKit is the tool to generate Robotics Software Development Kit (RDK) designed for autonomous devices, including the ROS2 core and capacibilities packages like perception, planning, control driver etc. It provides flexible build/runtime configurations to meet different autonomous requirement on top of diversity hardware choices, for example use different hareware engine CPU/GPU/VPU to accelerate AI related features.
Arduino is an open-source platform used for building electronics projects. Arduino consists of both a physical programmable circuit board (often referred to as a microcontroller) and a piece of software, or IDE (Integrated Development Environment) that runs on your computer, used to write and upload computer code to the physical board.
ArduPilot enables the creation and use of trusted, autonomous, unmanned vehicle systems for the peaceful benefit of all. ArduPilot provides a comprehensive suite of tools suitable for almost any vehicle and application.
AirSim is a simulator for drones, cars and more, built on Unreal Engine (we now also have an experimental Unity release). It is open-source, cross platform, and supports hardware-in-loop with popular flight controllers such as PX4 for physically and visually realistic simulations.
F´ (F Prime) is a component-driven framework that enables rapid development and deployment of spaceflight and other embedded software applications. Originally developed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, F´ has been successfully deployed on several space applications.
The JPL Open Source Rover is an open source, build it yourself, scaled down version of the 6 wheel rover design that JPL uses to explore the surface of Mars. The Open Source Rover is designed almost entirely out of consumer off the shelf (COTS) parts. This project is intended to be a teaching and learning experience for those who want to get involved in mechanical engineering, software, electronics, or robotics.
Light Detection and Ranging(LiDAR) is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser at an object, and uses the time and wavelength of the reflected beam of light to estimate the distance and in some applications (Laser Imaging), to create a 3D representation of the object and its surface characteristics. This technology is commonly used in aircraft and self-driving vehicles.
AliceVision is a Photogrammetric Computer Vision Framework which provides a 3D Reconstruction and Camera Tracking algorithms. AliceVision aims to provide strong software basis with state-of-the-art computer vision algorithms that can be tested, analyzed and reused. The project is a result of collaboration between academia and industry to provide cutting-edge algorithms with the robustness and the quality required for production usage.
CARLA is an open-source simulator for autonomous driving research. CARLA has been developed from the ground up to support development, training, and validation of autonomous driving systems. In addition to open-source code and protocols, CARLA provides open digital assets (urban layouts, buildings, vehicles) that were created for this purpose and can be used freely. The simulation platform supports flexible specification of sensor suites and environmental conditions.
ROS bridge is a package to bridge ROS for CARLA Simulator.
ROS-Industrial is an open source project that extends the advanced capabilities of ROS software to manufacturing.
AWS RoboMaker is the most complete cloud solution for robotic developers to simulate, test and securely deploy robotic applications at scale. RoboMaker provides a fully-managed, scalable infrastructure for simulation that customers use for multi-robot simulation and CI/CD integration with regression testing in simulation.
Microsoft Robotics Developer Studio is a free .NET-based programming environment for building robotics applications.
Visual Studio Code Extension for ROS is an extension provides support for Robot Operating System (ROS) development.
Azure Kinect ROS Driver is a node which publishes sensor data from the Azure Kinect Developer Kit to the Robot Operating System (ROS). Developers working with ROS can use this node to connect an Azure Kinect Developer Kit to an existing ROS installation.
Azure IoT Hub for ROS is a ROS package works with the Microsoft Azure IoT Hub service to relay telemetry messages from the Robot to Azure IoT Hub or reflect properties from the Digital Twin to the robot using dynamic reconfigure.
ROS 2 with ONNX Runtime is a program that uses ROS 2 to run on different hardware platforms using their respective AI acceleration libraries for optimized execution of the ONNX model.
Azure Cognitive Services LUIS ROS Node is a ROS node that bridges between ROS and the Azure Language Understanding Service. it can be configured to process audio directly from a microphone, or can subscribe to a ROS audio topic, then processes speech and generates «intent» ROS messages which can be processed by another ROS node to generate ROS commands.
Robotics Learning Resources
Robotics courses from Coursera
Learn Robotics with Online Courses and Classes from edX
Top Robotics Courses Online from Udemy
Free Online AI & Robotics Courses
REC Foundation Robotics Industry Certification
Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy
RIA Robotic Integrator Certification Program
AWS RoboMaker – Develop, Test, Deploy, and Manage Intelligent Robotics Apps
Microsoft AI School
Language Understanding (LUIS) for Azure Cognitive Services
Azure VM templates to bootstrap ROS and ROS 2 environments
Google Robotics Research
Open Source Security
Back to the Top

Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF) is a cross-industry collaboration that brings together leaders to improve the security of open source software by building a broader community, targeted initiatives, and best practices. The OpenSSF brings together open source security initiatives under one foundation to accelerate work through cross-industry support. Along with the Core Infrastructure Initiative and the Open Source Security Coalition, and will include new working groups that address vulnerability disclosures, security tooling and more.
Security Standards, Frameworks and Benchmarks
STIGs Benchmarks — Security Technical Implementation Guides
CIS Benchmarks — CIS Center for Internet Security
NIST — Current FIPS
ISO Standards Catalogue
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (CC) is an international standard (ISO / IEC 15408) for computer security. It allows an objective evaluation to validate that a particular product satisfies a defined set of security requirements.
ISO 22301 is the international standard that provides a best-practice framework for implementing an optimised BCMS (business continuity management system).
ISO27001 is the international standard that describes the requirements for an ISMS (information security management system). The framework is designed to help organizations manage their security practices in one place, consistently and cost-effectively.
ISO 27701 specifies the requirements for a PIMS (privacy information management system) based on the requirements of ISO 27001.
It is extended by a set of privacy-specific requirements, control objectives and controls. Companies that have implemented ISO 27001 will be able to use ISO 27701 to extend their security efforts to cover privacy management.
EU GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is a privacy and data protection law that supersedes existing national data protection laws across the EU, bringing uniformity by introducing just one main data protection law for companies/organizations to comply with.
CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is a data privacy law that took effect on January 1, 2020 in the State of California. It applies to businesses that collect California residents’ personal information, and its privacy requirements are similar to those of the EU’s GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standards (DSS) is a global information security standard designed to prevent fraud through increased control of credit card data.
SOC 2 is an auditing procedure that ensures your service providers securely manage your data to protect the interests of your comapny/organization and the privacy of their clients.
NIST CSF is a voluntary framework primarily intended for critical infrastructure organizations to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risk based on existing best practice.
Security Tools
AppArmor is an effective and easy-to-use Linux application security system. AppArmor proactively protects the operating system and applications from external or internal threats, even zero-day attacks, by enforcing good behavior and preventing both known and unknown application flaws from being exploited. AppArmor supplements the traditional Unix discretionary access control (DAC) model by providing mandatory access control (MAC). It has been included in the mainline Linux kernel since version 2.6.36 and its development has been supported by Canonical since 2009.
SELinux is a security enhancement to Linux which allows users and administrators more control over access control. Access can be constrained on such variables as which users and applications can access which resources. These resources may take the form of files. Standard Linux access controls, such as file modes (-rwxr-xr-x) are modifiable by the user and the applications which the user runs. Conversely, SELinux access controls are determined by a policy loaded on the system which may not be changed by careless users or misbehaving applications.
Control Groups(Cgroups) is a Linux kernel feature that allows you to allocate resources such as CPU time, system memory, network bandwidth, or any combination of these resources for user-defined groups of tasks (processes) running on a system.
EarlyOOM is a daemon for Linux that enables users to more quickly recover and regain control over their system in low-memory situations with heavy swap usage.
Libgcrypt is a general purpose cryptographic library originally based on code from GnuPG.
Kali Linux is an open source project that is maintained and funded by Offensive Security, a provider of world-class information security training and penetration testing services.
Pi-hole is a DNS sinkhole that protects your devices from unwanted content, without installing any client-side software, intended for use on a private network. It is designed for use on embedded devices with network capability, such as the Raspberry Pi, but it can be used on other machines running Linux and cloud implementations.
Aircrack-ng is a network software suite consisting of a detector, packet sniffer, WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis tool for 802.11 wireless LANs. It works with any wireless network interface controller whose driver supports raw monitoring mode and can sniff 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g traffic.
Burp Suite is a leading range of cybersecurity tools.
KernelCI is a community-based open source distributed test automation system focused on upstream kernel development. The primary goal of KernelCI is to use an open testing philosophy to ensure the quality, stability and long-term maintenance of the Linux kernel.
Continuous Kernel Integration project helps find bugs in kernel patches before they are commited to an upstram kernel tree. We are team of kernel developers, kernel testers, and automation engineers.
eBPF is a revolutionary technology that can run sandboxed programs in the Linux kernel without changing kernel source code or loading kernel modules. By making the Linux kernel programmable, infrastructure software can leverage existing layers, making them more intelligent and feature-rich without continuing to add additional layers of complexity to the system.
Cilium uses eBPF to accelerate getting data in and out of L7 proxies such as Envoy, enabling efficient visibility into API protocols like HTTP, gRPC, and Kafka.
Hubble is a Network, Service & Security Observability for Kubernetes using eBPF.
Istio is an open platform to connect, manage, and secure microservices. Istio’s control plane provides an abstraction layer over the underlying cluster management platform, such as Kubernetes and Mesos.
Certgen is a convenience tool to generate and store certificates for Hubble Relay mTLS.
Scapy is a python-based interactive packet manipulation program & library.
syzkaller is an unsupervised, coverage-guided kernel fuzzer.
SchedViz is a tool for gathering and visualizing kernel scheduling traces on Linux machines.
oss-fuzz aims to make common open source software more secure and stable by combining modern fuzzing techniques with scalable, distributed execution.
OSSEC is a free, open-source host-based intrusion detection system. It performs log analysis, integrity checking, Windows registry monitoring, rootkit detection, time-based alerting, and active response.
Metasploit Project is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development.
Wfuzz was created to facilitate the task in web applications assessments and it is based on a simple concept: it replaces any reference to the FUZZ keyword by the value of a given payload.
Nmap is a security scanner used to discover hosts and services on a computer network, thus building a «map» of the network.
Patchwork is a web-based patch tracking system designed to facilitate the contribution and management of contributions to an open-source project.
pfSense is a free and open source firewall and router that also features unified threat management, load balancing, multi WAN, and more.
Snowpatch is a continuous integration tool for projects using a patch-based, mailing-list-centric git workflow. This workflow is used by a number of well-known open source projects such as the Linux kernel.
Snort is an open-source, free and lightweight network intrusion detection system (NIDS) software for Linux and Windows to detect emerging threats.
Wireshark is a free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education.
OpenSCAP is U.S. standard maintained by National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). It provides multiple tools to assist administrators and auditors with assessment, measurement, and enforcement of security baselines. OpenSCAP maintains great flexibility and interoperability by reducing the costs of performing security audits. Whether you want to evaluate DISA STIGs, NIST‘s USGCB, or Red Hat’s Security Response Team’s content, all are supported by OpenSCAP.
Tink is a multi-language, cross-platform, open source library that provides cryptographic APIs that are secure, easy to use correctly, and harder to misuse.
OWASP is an online community, produces freely-available articles, methodologies, documentation, tools, and technologies in the field of web application security.
Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language is a community effort to standardize how to assess and report upon the machine state of computer systems. OVAL includes a language to encode system details, and community repositories of content. Tools and services that use OVAL provide enterprises with accurate, consistent, and actionable information to improve their security.
ClamAV is an open source antivirus engine for detecting trojans, viruses, malware & other malicious threats.
Open Source Security Learning Resources
Microsoft Open Source Software Security
Cloudflare Open Source Security
The Seven Properties of Highly Secure Devices
How Layer 7 of the Internet Works
The 7 Kinds of Security
The Libgcrypt Reference Manual
The Open Web Application Security Project(OWASP) Foundation Top 10
Best Practices for Using Open Source Code from The Linux Foundation
AWS Certified Security — Specialty Certification
Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate
Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Security Engineer
Cisco Security Certifications
The Red Hat Certified Specialist in Security: Linux
Linux Professional Institute LPIC-3 Enterprise Security Certification
Cybersecurity Training and Courses from IBM Skills
Cybersecurity Courses and Certifications by Offensive Security
RSA Certification Program
Check Point Certified Security Expert(CCSE) Certification
Check Point Certified Security Administrator(CCSA) Certification
Check Point Certified Security Master (CCSM) Certification
Certified Cloud Security Professional(CCSP) Certification
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Certification
CCNP Routing and Switching
Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)
Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)
Security Training Certifications and Courses from Udemy
Security Training Certifications and Courses from Coursera
Security Certifications Training from Pluarlsight
Differential Privacy
Back to the Top
Differential Privacy is a system that simultaneously enables researchers and analysts to extract useful insights from datasets containing personal information and offers stronger privacy protections. This is achieved by introducing «statistical noise».
Statistical Noise is a process that small aletrations to masked datasets. The statistical noise hides identifiable characteristics of individuals, ensuring that the privacy of personal information is protected, but it’s small enough to not materially impact the accuracy of the answers extracted by analysts and researchers.
Laplacian Noise is a mechanism that adds Laplacian-distributed noise to a function.
Above is a simple diagram of how Differential Privacy-Preserving Data Sharing and Data Mining protects a User’s Data
Tools
PySyft is a Python library for secure and private Deep Learning. PySyft decouples private data from model training, using Federated Learning, Differential Privacy, and Encrypted Computation (like Multi-Party Computation (MPC) and Homomorphic Encryption (HE) within the main Deep Learning frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow.
TensorFlow Privacy is a Python library that includes implementations of TensorFlow optimizers for training machine learning models with differential privacy. The library comes with tutorials and analysis tools for computing the privacy guarantees provided.
TensorFlow Federated (TFF) is an open-source framework for machine learning and other computations on decentralized data. TFF has been developed to facilitate open research and experimentation with Federated Learning (FL), an approach to machine learning where a shared global model is trained across many participating clients that keep their training data locally.
Privacy on Beam is an end-to-end differential privacy solution built on Apache Beam. It is intended to be usable by all developers, regardless of their differential privacy expertise.
PyDP is a Python wrapper for Google’s Differential Privacy project.
PennyLane is a cross-platform Python library for differentiable programming of quantum computers. By training a quantum computer the same way as a neural network.
BoTorch is a library for Bayesian Optimization built on PyTorch.
PyTorch Geometric (PyG) is a geometric deep learning extension library for PyTorch.
Skorch is a scikit-learn compatible neural network library that wraps PyTorch.
Diffprivlib is the IBM Differential Privacy Library for experimenting with, investigating and developing applications in, differential privacy.
Opacus is a library that enables training PyTorch models with differential privacy. It supports training with minimal code changes required on the client, has little impact on training performance and allows the client to online track the privacy budget expended at any given moment.
Smart Noise is a toolkit that uses state-of-the-art differential privacy (DP) techniques to inject noise into data, to prevent disclosure of sensitive information and manage exposure risk.
Privacy Learning Resources
Differential Privacy Blog Series by the National Institute of Standards and Technology(NIST)
Apple’s Differential Privacy Overview
Learning with Privacy at Scale with Apple Machine Learning
Microsoft Research Differential Privacy Overview
Responsible Machine Learning with Microsoft Azure
Responsible AI Resources with Microsoft AI
Preserve data privacy by using differential privacy and the SmartNoise package
Open Differential Privacy(OpenDP) Initiative by Microsoft and Harvard
Google’s Differential Privacy Library
Computing Private Statistics with Privacy on Beam from Google Codelabs
Introducing TensorFlow Privacy: Learning with Differential Privacy for Training Data
TensorFlow Federated: Machine Learning on Decentralized Data
Federated Analytics: Collaborative Data Science without Data Collection
Differentially-Private Stochastic Gradient Descent(DP-SGD)
Learning Differential Privacy from Harvard University Privacy Tools Project
Harvard University Privacy Tools Project Courses & Educational Materials
The Weaknesses of Differential Privacy course on Coursera
The Differential Privacy of Bayesian Inference
Simultaneous private learning of multiple concepts
The Complexity of Computing the Optimal Composition of Differential Privacy
Order revealing encryption and the hardness of private learning
SAP HANA data anonymization using SAP Software Solutions
SAP HANA Security using their In-Memory Database
DEFCON Differential Privacy Training Launch
Secure and Private AI course on Udacity
Differential Privacy — Security and Privacy for Big Data — Part 1 course on Coursera
Differential Privacy — Security and Privacy for Big Data — Part 2 course on Coursera
Certified Ethical Emerging Technologist Professional Certificate course on Coursera
Cloud Native Development
Back to the Top

Cloud Native Learning Resources
CNCF Cloud Native Interactive Landscape
Build Cloud-Native applications in Microsoft Azure
Cloud-Native application development for Google Cloud
Cloud-Native development for Amazon Web Services
Cloud Native Applications with VMware Tanzu
Cloud Native Computing Foundation Training and Certification Program
Cloud Foundry Developer Training and Certification Program
Cloud-Native Architecture Course on Pluralsight
AWS Fundamentals: Going Cloud-Native on Coursera
Developing Cloud-Native Apps w/ Microservices Architectures course on Udemy
How load balancing works for cloud native applications with Azure Application Gateway on Linkedin Learning
Developing Cloud Native Applications course on edX
Cloud Native courses from IBM

Cloud Native Architecture
DevOps
Application Framework
Spring Boot is an open-source micro framework maintained by Pivotal, which was acquired by VMware in 2019. It provides Java developers with a platform to get started with an auto configurable production-grade Spring application.
Apache Mesos is a cluster manager that provides efficient resource isolation and sharing across distributed applications, or frameworks. It can run Hadoop, Jenkins, Spark, Aurora, and other frameworks on a dynamically shared pool of nodes.
Apache Spark is a unified analytics engine for big data processing, with built-in modules for streaming, SQL, machine learning and graph processing.
Apache Hadoop is a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. It is designed to scale up from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage. Rather than rely on hardware to deliver high-availability, the library itself is designed to detect and handle failures at the application layer, so delivering a highly-available service on top of a cluster of computers, each of which may be prone to failures.
Runtime Platform
BOSH is a tool that prepares your infrastructure for what needs to be managed. BOSH espouses software engineering best practices, such as continuous delivery, by making it easy to create software releases that automatically update complex distributed systems with simple commands.Due to the flexibility and power of BOSH, Google and VMware made it the heart of the Kubo project, now called the Cloud Foundry Container Runtime, based on Kubernetes.
Infrastructure Automatation
Maven is a build automation tool used primarily for Java projects. Maven can also be used to build and manage projects written in C#, Ruby, Scala, and other languages. The Maven project is hosted by the Apache Software Foundation.
Gradle is an open-source build-automation system that builds upon the concepts of Apache Ant and Apache Maven and introduces a Groovy-based domain-specific language instead of the XML form used by Apache Maven for declaring the project configuration.
Chef is an effortless Infrastructure Suite offers visibility into security and compliance status across all infrastructure and makes it easy to detect and correct issues long before they reach production.
Puppet is an open source tool that makes continuous integration and delivery of your software on traditional or containerized infrastructure easy by pulling together all your existing tools and giving you flexibility to deploy your way.
Ansible is an open-source software provisioning, configuration management, and application-deployment tool. It runs on many Unix-like systems, and can configure both Unix-like systems as well as Microsoft Windows.
Salt is Python-based, open-source software for event-driven IT automation, remote task execution, and configuration management. Supporting the «Infrastructure as Code» approach to data center system and network deployment and management, configuration automation, SecOps orchestration, vulnerability remediation, and hybrid cloud control.
Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code software tool created by HashiCorp.It enables users to define and provision a datacenter infrastructure using a high-level configuration language known as Hashicorp Configuration Language (HCL), or optionally JSON.
Cloud Infrastructure
Amazon web service(AWS) is a platform that offers flexible, reliable, scalable, easy-to-use and cost-effective cloud computing solutions. The AWS platform is developed with a combination of infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and packaged software as a service (SaaS) offerings.
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service created by Microsoft for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications and services through Microsoft-managed data centers.
Azure DevOps is a set of services for teams to share code, track work, and ship software; CLIs Build, deploy, diagnose, and manage multi-platform, scalable apps and services; Azure Pipelines Continuously build, test, and deploy to any platform and cloud; Azure Lab Services Set up labs for classrooms, trials, development and testing, and other scenarios.
Azure Draft is a tool for developers to create cloud-native applications on Kubernetes.
Google Cloud Platform integrates industry-leading tools(data management, hybrid & multi-cloud, and AI & ML) with Cloud Storage for enhanced support with everything from security and data transfer, to data backup and archive. Expand all . Backup, archival, and disaster recovery. Along with File systems and gateways.
OpenStack is a free and open-source software platform for cloud computing, mostly deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service that controls large pools of compute, storage, and networking resources throughout a datacenter, managed through a dashboard or via the OpenStack API. OpenStack works with popular enterprise and open source technologies making it ideal for heterogeneous infrastructure.
Cloud Foundry is an open source, multi cloud application platform as a service that makes it faster and easier to build, test, deploy and scale applications, providing a choice of clouds, developer frameworks, and application services. It is an open source project and is available through a variety of private cloud distributions and public cloud instances.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery
Bamboo is a continuous integration (CI) server that can be used to automate the release management for a software application, creating a continuous delivery pipeline.
Drone is a Continuous Delivery system built on container technology. Drone uses a simple YAML configuration file, a superset of docker-compose, to define and execute Pipelines inside Docker containers.
Travis CI is a hosted continuous integration service used to build and test software projects hosted at GitHub.
Circle CI is a continuous integration and continuous delivery platform that helps software teams work smarter, faster.
Team City is a build management and continuous integration server from JetBrains.
Shippable simplifies DevOps and makes it systematic with an Assembly Line platform that is heterogeneous, flexible, and provides complete visibility across your DevOps workflows.
Spinnaker is an open source, multi-cloud continuous delivery platform for releasing software changes with high velocity and confidence.
Prow is a Kubernetes based CI/CD system. Jobs can be triggered by various types of events and report their status to many different services. In addition to job execution, Prow provides GitHub automation in the form of policy enforcement, chat-ops via /foo style commands, and automatic PR merging. Prow has a microservice architecture implemented as a collection of container images that run as Kubernetes deployments.
Microservices
AWS ECS is a highly scalable, high-performance container orchestration service that supports Docker containers and allows you to easily run and scale containerized applications on AWS. Amazon ECS eliminates the need for you to install and operate your own container orchestration software, manage and scale a cluster of virtual machines, or schedule containers on those virtual machines.
AWS CodeBuild is a fully managed continuous integration service that compiles source code, runs tests, and produces software packages that are ready to deploy. With CodeBuild, you don’t need to provision, manage, and scale your own build servers.
CFEngine is an open-source configuration management system, written by Mark Burgess.Its primary function is to provide automated configuration and maintenance of large-scale computer systems, including the unified management of servers, desktops, consumer and industrial devices, embedded networked devices, mobile smartphones, and tablet computers.
Octpus Deploy is the deployment automation server for your entire team, designed to make it easy to orchestrate releases and deploy applications, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
AWS CodeDeploy is a fully managed deployment service that automates software deployments to a variety of compute services such as Amazon EC2, AWS Fargate, AWS Lambda, and your on-premises servers. AWS CodeDeploy makes it easier for you to rapidly release new features, helps you avoid downtime during application deployment, and handles the complexity of updating your applications.
AWS Lambda is an event-driven, serverless computing platform provided by Amazon as a part of the Amazon Web Services. It is a computing service that runs code in response to events and automatically manages the computing resources required by that code.
Traefik is an open-source Edge Router that makes publishing your services a fun and easy experience. It receives requests on behalf of your system and finds out which components are responsible for handling them. What sets Traefik apart, besides its many features, is that it automatically discovers the right configuration for your services.
Containers
Kubernetes is an open-source container-orchestration system for automating application deployment, scaling, and management. It was originally designed by Google, and is now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation.
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) is a managed, production-ready environment for deploying containerized applications.
OpenShift is focused on security at every level of the container stack and throughout the application lifecycle. It includes long-term, enterprise support from one of the leading Kubernetes contributors and open source software companies.
Rancher is a complete software stack for teams adopting containers. It addresses the operational and security challenges of managing multiple Kubernetes clusters, while providing DevOps teams with integrated tools for running containerized workloads.
Docker is a set of platform as a service products that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. Containers are isolated from one another and bundle their own software, libraries and configuration files; they can communicate with each other through well-defined channels. All containers are run by a single operating-system kernel and are thus more lightweight than virtual machines.
Rook is an open source cloud-native storage orchestrator for Kubernetes that turns distributed storage systems into self-managing, self-scaling, self-healing storage services. It automates the tasks of a storage administrator: deployment, bootstrapping, configuration, provisioning, scaling, upgrading, migration, disaster recovery, monitoring, and resource management.
Podman(the POD MANager) is a tool for managing OCI containers and pods.
Rkt is a pod-native container engine for Linux. It is composable, secure, and built on standards.
DevOps Development
Back to the Top

DevOps Tools
GitHub provides hosting for software development version control using Git. It offers all of the distributed version control and source code management functionality of Git as well as adding its own features. It provides access control and several collaboration features such as bug tracking, feature requests, task management, and wikis for every project.
GitHub Codespaces is an integrated development environment(IDE) on GitHub. That allows developers to develop entirely in the cloud using Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code.
GitHub Actions will automate, customize, and execute your software development workflows right in your repository with GitHub Actions. You can discover, create, and share actions to perform any job you’d like, including CI/CD, and combine actions in a completely customized workflow.GitHub Actions for Azure you can create workflows that you can set up in your repository to build, test, package, release and deploy to Azure.Learn more about all other integrations with Azure.
GitLab is a web-based DevOps lifecycle tool that provides a Git-repository manager providing wiki, issue-tracking and CI/CD pipeline features, using an open-source license, developed by GitLab Inc.
Jenkins is a free and open source automation server. Jenkins helps to automate the non-human part of the software development process, with continuous integration and facilitating technical aspects of continuous delivery.
Bitbucket is a web-based version control repository hosting service owned by Atlassian, for source code and development projects that use either Mercurial or Git revision control systems. Bitbucket offers both commercial plans and free accounts. It offers free accounts with an unlimited number of private repositories. Bitbucket integrates with other Atlassian software like Jira, HipChat, Confluence and Bamboo.
Bamboo is a continuous integration (CI) server that can be used to automate the release management for a software application, creating a continuous delivery pipeline.
Codecov is the leading, dedicated code coverage solution. It provides highly integrated tools to group, merge, archive and compare coverage reports. Whether your team is comparing changes in a pull request or reviewing a single commit, Codecov will improve the code review workflow and quality.
Drone is a Continuous Delivery system built on container technology. Drone uses a simple YAML configuration file, a superset of docker-compose, to define and execute Pipelines inside Docker containers.
Travis CI is a hosted continuous integration service used to build and test software projects hosted at GitHub.
Circle CI is a continuous integration and continuous delivery platform that helps software teams work smarter, faster.
Zuul-CI is a program that drives continuous integration, delivery, and deployment systems with a focus on project gating and interrelated projects. Using the same Ansible playbooks to deploy your system and run your tests.
Artifactory is a Universal Artifact Repository Manager developed by JFrog. It supports all major packages, enterprise ready security, clustered, HA, Docker registry, multi-site replication and scalable.
Azure DevOps is a set of services for teams to share code, track work, and ship software; CLIs Build, deploy, diagnose, and manage multi-platform, scalable apps and services; Azure Pipelines Continuously build, test, and deploy to any platform and cloud; Azure Lab Services Set up labs for classrooms, trials, development and testing, and other scenarios.
Team City is a build management and continuous integration server from JetBrains.
Shippable simplifies DevOps and makes it systematic with an Assembly Line platform that is heterogeneous, flexible, and provides complete visibility across your DevOps workflows.
Spinnaker is an open source, multi-cloud continuous delivery platform for releasing software changes with high velocity and confidence.
AWS CodeBuild is a fully managed continuous integration service that compiles source code, runs tests, and produces software packages that are ready to deploy. With CodeBuild, you don’t need to provision, manage, and scale your own build servers.
Selenium is a free (open source) automated testing suite for web applications across different browsers and platforms.
Cucumber is a tool based on Behavior Driven Development (BDD) framework which is used to write acceptance tests for the web application. It allows automation of functional validation in easily readable and understandable format (like plain English) to Business Analysts, Developers, and Testers.
JUnit is a unit testing framework for the Java programming language.
Mocha is a JavaScript test framework for Node.js programs, featuring browser support, asynchronous testing, test coverage reports, and use of any assertion library.
Karma is a simple tool that allows you to execute JavaScript code in multiple real browsers.
Jasmine is an open source testing framework for JavaScript. It aims to run on any JavaScript-enabled platform, to not intrude on the application nor the IDE, and to have easy-to-read syntax.
Maven is a build automation tool used primarily for Java projects. Maven can also be used to build and manage projects written in C#, Ruby, Scala, and other languages. The Maven project is hosted by the Apache Software Foundation.
Gradle is an open-source build-automation system that builds upon the concepts of Apache Ant and Apache Maven and introduces a Groovy-based domain-specific language instead of the XML form used by Apache Maven for declaring the project configuration.
Chef is an effortless Infrastructure Suite offers visibility into security and compliance status across all infrastructure and makes it easy to detect and correct issues long before they reach production.
Puppet is an open source tool that makes continuous integration and delivery of your software on traditional or containerized infrastructure easy by pulling together all your existing tools and giving you flexibility to deploy your way.
Ansible is an open-source software provisioning, configuration management, and application-deployment tool. It runs on many Unix-like systems, and can configure both Unix-like systems as well as Microsoft Windows.
KubeInit provides Ansible playbooks and roles for the deployment and configuration of multiple Kubernetes distributions.
Salt is Python-based, open-source software for event-driven IT automation, remote task execution, and configuration management. Supporting the «Infrastructure as Code» approach to data center system and network deployment and management, configuration automation, SecOps orchestration, vulnerability remediation, and hybrid cloud control.
Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code software tool created by HashiCorp.It enables users to define and provision a datacenter infrastructure using a high-level configuration language known as Hashicorp Configuration Language (HCL), or optionally JSON.
Consul is a service networking solution to connect and secure services across any runtime platform and public or private cloud.
Packer is lightweight, runs on every major operating system, and is highly performant, creating machine images for multiple platforms in parallel. Packer does not replace configuration management like Chef or Puppet. In fact, when building images, Packer is able to use tools like Chef or Puppet to install software onto the image.
Nomad is a highly available, distributed, data-center aware cluster and application scheduler designed to support the modern datacenter with support for long-running services, batch jobs, and much more.
Vagrant is a tool for building and managing virtual machine environments in a single workflow. With an easy-to-use workflow and focus on automation, Vagrant lowers development environment setup time and increases production parity.
Vault is a tool for securely accessing secrets. A secret is anything that you want to tightly control access to, such as API keys, passwords, certificates, and more. Vault provides a unified interface to any secret, while providing tight access control and recording a detailed audit log.
CFEngine is an open-source configuration management system, written by Mark Burgess.Its primary function is to provide automated configuration and maintenance of large-scale computer systems, including the unified management of servers, desktops, consumer and industrial devices, embedded networked devices, mobile smartphones, and tablet computers.
Octpus Deploy is the deployment automation server for your entire team, designed to make it easy to orchestrate releases and deploy applications, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
AWS CodeDeploy is a fully managed deployment service that automates software deployments to a variety of compute services such as Amazon EC2, AWS Fargate, AWS Lambda, and your on-premises servers. AWS CodeDeploy makes it easier for you to rapidly release new features, helps you avoid downtime during application deployment, and handles the complexity of updating your applications.
Kubernetes is an open-source container-orchestration system for automating application deployment, scaling, and management. It was originally designed by Google, and is now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation.
Docker is a set of platform as a service products that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. Containers are isolated from one another and bundle their own software, libraries and configuration files; they can communicate with each other through well-defined channels. All containers are run by a single operating-system kernel and are thus more lightweight than virtual machines.
PowerShell/PowerShell Core is a cross-platform (Windows, Linux, and macOS) automation and configuration tool/framework that works well with your existing tools and is optimized for dealing with structured data (e.g. JSON, CSV, XML, etc.), REST APIs, and object models. It includes a command-line shell, an associated scripting language and a framework for processing cmdlets.
Hyper-V creates virtual machines on Windows 10. Hyper-V can be enabled in many ways including using the Windows 10 control panel, PowerShell or using the Deployment Imaging Servicing and Management tool (DISM).
Cloud Hypervisor is an open source Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) that runs on top of KVM. The project focuses on exclusively running modern, cloud workloads, on top of a limited set of hardware architectures and platforms. Cloud workloads refers to those that are usually run by customers inside a cloud provider. Cloud Hypervisor is implemented in Rust and is based on the rust-vmm crates.
VMware vSphere Hypervisor is a bare-metal hypervisor that virtualizes servers; allowing you to consolidate your applications while saving time and money managing your IT infrastructure.
VMware vSphere is the industry-leading compute virtualization platform, and your first step to application modernization. It has been rearchitected with native Kubernetes to allow customers to modernize the 70 million+ workloads now running on vSphere.
VMware Tanzu is a centralized management platform for consistently operating and securing your Kubernetes infrastructure and modern applications across multiple teams and private/public clouds.
Rancher is a complete software stack for teams adopting containers. It addresses the operational and security challenges of managing multiple Kubernetes clusters, while providing DevOps teams with integrated tools for running containerized workloads.
K3s is a highly available, certified Kubernetes distribution designed for production workloads in unattended, resource-constrained, remote locations or inside IoT appliances.
Rook is an open source cloud-native storage orchestrator for Kubernetes that turns distributed storage systems into self-managing, self-scaling, self-healing storage services. It automates the tasks of a storage administrator: deployment, bootstrapping, configuration, provisioning, scaling, upgrading, migration, disaster recovery, monitoring, and resource management.
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) is a managed, production-ready environment for deploying containerized applications.
Anthos is a modern application management platform that provides a consistent development and operations experience for cloud and on-premises environments.
AWS ECS is a highly scalable, high-performance container orchestration service that supports Docker containers and allows you to easily run and scale containerized applications on AWS. Amazon ECS eliminates the need for you to install and operate your own container orchestration software, manage and scale a cluster of virtual machines, or schedule containers on those virtual machines.
Apache Mesos is a cluster manager that provides efficient resource isolation and sharing across distributed applications, or frameworks. It can run Hadoop, Jenkins, Spark, Aurora, and other frameworks on a dynamically shared pool of nodes.
Apache Spark is a unified analytics engine for big data processing, with built-in modules for streaming, SQL, machine learning and graph processing.
Apache Hadoop is a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. It is designed to scale up from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage. Rather than rely on hardware to deliver high-availability, the library itself is designed to detect and handle failures at the application layer, so delivering a highly-available service on top of a cluster of computers, each of which may be prone to failures.
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service created by Microsoft for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications and services through Microsoft-managed data centers.
Azure Functions is a solution for easily running small pieces of code, or «functions,» in the cloud. You can write just the code you need for the problem at hand, without worrying about a whole application or the infrastructure to run it.
Rkt is a pod-native container engine for Linux. It is composable, secure, and built on standards.
AWS Lambda is an event-driven, serverless computing platform provided by Amazon as a part of the Amazon Web Services. It is a computing service that runs code in response to events and automatically manages the computing resources required by that code.
Helm is the Kubernetes Package Manager.
Kubespray is a tool that combines Kubernetes and Ansible to easily install Kubernetes clusters that can be deployed on AWS, GCE, Azure, OpenStack, vSphere, Packet (bare metal), Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (Experimental), or Baremetal
Red Hat OpenShift is focused on security at every level of the container stack and throughout the application lifecycle. It includes long-term, enterprise support from one of the leading Kubernetes contributors and open source software companies.
OpenShift Hive is an operator which runs as a service on top of Kubernetes/OpenShift. The Hive service can be used to provision and perform initial configuration of OpenShift 4 clusters.
OKD is a community distribution of Kubernetes optimized for continuous application development and multi-tenant deployment. OKD adds developer and operations-centric tools on top of Kubernetes to enable rapid application development, easy deployment and scaling, and long-term lifecycle maintenance for small and large teams.
Odo is a fast, iterative, and straightforward CLI tool for developers who write, build, and deploy applications on Kubernetes and OpenShift.
Kata Operator is an operator to perform lifecycle management (install/upgrade/uninstall) of Kata Runtime on Openshift as well as Kubernetes cluster.
Knative is a Kubernetes-based platform to build, deploy, and manage modern serverless workloads. Knative takes care of the operational overhead details of networking, autoscaling (even to zero), and revision tracking.
Etcd is a distributed key-value store that provides a reliable way to store data that needs to be accessed by a distributed system or cluster of machines. Etcd is used as the backend for service discovery and stores cluster state and configuration for Kubernetes.
OpenStack is a free and open-source software platform for cloud computing, mostly deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service that controls large pools of compute, storage, and networking resources throughout a datacenter, managed through a dashboard or via the OpenStack API. OpenStack works with popular enterprise and open source technologies making it ideal for heterogeneous infrastructure.
Cloud Foundry is an open source, multi cloud application platform as a service that makes it faster and easier to build, test, deploy and scale applications, providing a choice of clouds, developer frameworks, and application services. It is an open source project and is available through a variety of private cloud distributions and public cloud instances.
Splunk software is used for searching, monitoring, and analyzing machine-generated big data, via a Web-style interface.
Prometheus is a free software application used for event monitoring and alerting. It records real-time metrics in a time series database (allowing for high dimensionality) built using a HTTP pull model, with flexible queries and real-time alerting.
Loki is a horizontally-scalable, highly-available, multi-tenant log aggregation system inspired by Prometheus. It is designed to be very cost effective and easy to operate. It does not index the contents of the logs, but rather a set of labels for each log stream.
Thanos is a set of components that can be composed into a highly available metric system with unlimited storage capacity, which can be added seamlessly on top of existing Prometheus deployments.
Container Storage Interface (CSI) is an API that lets container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes seamlessly communicate with stored data via a plug-in.
OpenEBS is a Kubernetes-based tool to create stateful applications using Container Attached Storage.
ElasticSearch is a search engine based on the Lucene library. It provides a distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search engine with an HTTP web interface and schema-free JSON documents. Elasticsearch is developed in Java.
Logstash is a tool for managing events and logs. When used generically, the term encompasses a larger system of log collection, processing, storage and searching activities.
Kibana is an open source data visualization plugin for Elasticsearch. It provides visualization capabilities on top of the content indexed on an Elasticsearch cluster. Users can create bar, line and scatter plots, or pie charts and maps on top of large volumes of data.
New Relic is a SaaS-based monitoring tool that fully supports the way DevOps teams work in the modern enterprise by streamlining your workflows with today’s collaboration software and orchestration tools like Puppet, Chef, and Ansible.
Nagios is a free and open source computer-software application that monitors systems, networks and infrastructure. Nagios offers monitoring and alerting services for servers, switches, applications and services. It alerts users when things go wrong and alerts them a second time when the problem has been resolved.
SonarQube is an open-source platform developed by SonarSource for continuous inspection of code quality to perform automatic reviews with static analysis of code to detect bugs, code smells, and security vulnerabilities on 20+ programming languages.
Genie is a federated job orchestration engine developed by Netflix. Genie provides REST APIs to run a variety of big data jobs like Hadoop, Pig, Hive, Spark, Presto, Sqoop and more. It also provides APIs for managing the metadata of many distributed processing clusters and the commands and applications which run on them.
Inviso is a lightweight tool that provides the ability to search for Hadoop jobs, visualize the performance, and view cluster utilization.
Fenzo is a scheduler Java library for Apache Mesos frameworks that supports plugins for scheduling optimizations and facilitates cluster autoscaling.
Dynomite is a thin, distributed dynamo layer for different storage engines and protocols, which includes Redis and Memcached. Dynomite supports multi-datacenter replication and is designed for High Availability(HA).
Dyno is a tool that is used to scale a Java client application utilizing Dynomite.
Raigad is a process/tool that runs alongside Elasticsearch to automate backup/recovery, Deployments and Centralized Configuration management.
Priam is a process/tool that runs alongside Apache Cassandra to automate backup/recovery, Deployments and Centralized Configuration management.
Chaos Monkey is a resiliency tool used to randomly terminates virtual machine instances and containers that run inside of your production environment. Chaos Monkey should work with any backend that Spinnaker supports (AWS, Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure, Kubernetes, and Cloud Foundry).
Falcor is a JavaScript library for efficient data fetching. Falcor lets you represent all your remote data sources as a single domain model via a virtual JSON graph, whether in memory on the client or over the network on the server.
Restify is a framework, utilizing connect style middleware for building REST APIs.
Traefik is an open source Edge Router that makes publishing your services a fun and easy experience. It receives requests on behalf of your system and finds out which components are responsible for handling them. What sets Traefik apart, besides its many features, is that it automatically discovers the right configuration for your services.
Jira is a proprietary issue tracking product developed by Atlassian that allows bug tracking and agile project management.
Pivotal Tracker is the agile project management tool of choice for developers around the world for real-time collaboration around a shared, prioritized backlog.
Trello is a web-based Kanban-style list-making application that gives you perspective over all your projects, at work and at home.
Microsoft Teams is the hub for team collaboration in Office 365 that integrates the people, content, and tools your team needs to be more engaged and effective.
Slack is a cloud-based proprietary instant messaging platform developed by Slack Technologies.
OpsGenie is a cloud-based service for dev & ops teams, providing reliable alerts, on-call schedule management and escalations. OpsGenie integrates with monitoring tools & services, ensures the right people are notified.
Pagerduty automates processes built on best practices, allowing you to focus on higher value parts of incident response. Granular and scalable permissions enable teams to administer and operate independently while controlling visibility.
Veracode is a leading provider of enterprise-class application security, seamlessly integrating agile security solutions for organizations around the globe. In addition to application security services and secure devops services, Veracode provides a full security assessment to ensure your website and applications are secure, and ensures full enterprise data protection.
DevOps Learning Resources
DevOps Engineering on AWS from AWS Training
AWS Certified DevOps Engineer — Professional from A Cloud Guru
Microsoft Certified: DevOps Engineer Expert Cert.
Introduction to Azure DevOps from A Cloud Guru
Architecting with Google Compute Engine
Architecting with Google Kubernetes Engine in Google Cloud
VMware Training and Certification Program
Cloudera Certification Program
Salesforce Certification Program
Salesforce Superbadges
Red Hat Training and Certification Program
Linux Foundation Training and Certification Program
Linux Professional Institute(LPI) Training and Certification
Learn DevOps with Online Courses and Lessons from edX
Top DevOps Courses Online from Udemy
Devops Courses from Coursera
Networking
Back to the Top
Networking Learning Resources
AWS Certified Security — Specialty Certification
Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate
Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Security Engineer
Cisco Security Certifications
The Red Hat Certified Specialist in Security: Linux
Linux Professional Institute LPIC-3 Enterprise Security Certification
Cybersecurity Training and Courses from IBM Skills
Cybersecurity Courses and Certifications by Offensive Security
Citrix Certified Associate – Networking(CCA-N)
Citrix Certified Professional – Virtualization(CCP-V)
CCNP Routing and Switching
Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)
Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)
Networking courses and specializations from Coursera
Network & Security Courses from Udemy
Network & Security Courses from edX
Tools & Networking Concepts
• Connection: In networking, a connection refers to pieces of related information that are transferred through a network. This generally infers that a connection is built before the data transfer (by following the procedures laid out in a protocol) and then is deconstructed at the at the end of the data transfer.
• Packet: A packet is, generally speaking, the most basic unit that is transferred over a network. When communicating over a network, packets are the envelopes that carry your data (in pieces) from one end point to the other.
Packets have a header portion that contains information about the packet including the source and destination, timestamps, network hops. The main portion of a packet contains the actual data being transferred. It is sometimes called the body or the payload.
• Network Interface: A network interface can refer to any kind of software interface to networking hardware. For instance, if you have two network cards in your computer, you can control and configure each network interface associated with them individually.
A network interface may be associated with a physical device, or it may be a representation of a virtual interface. The «loop-back» device, which is a virtual interface to the local machine, is an example of this.
• LAN: LAN stands for "local area network". It refers to a network or a portion of a network that is not publicly accessible to the greater internet. A home or office network is an example of a LAN.
• WAN: WAN stands for "wide area network". It means a network that is much more extensive than a LAN. While WAN is the relevant term to use to describe large, dispersed networks in general, it is usually meant to mean the internet, as a whole.
If an interface is connected to the WAN, it is generally assumed that it is reachable through the internet.
• Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules and standards that basically define a language that devices can use to communicate. There are a great number of protocols in use extensively in networking, and they are often implemented in different layers.
Some low level protocols are TCP, UDP, IP, and ICMP. Some familiar examples of application layer protocols, built on these lower protocols, are HTTP (for accessing web content), SSH, TLS/SSL, and FTP.
• Port: A port is an address on a single machine that can be tied to a specific piece of software. It is not a physical interface or location, but it allows your server to be able to communicate using more than one application.
• Firewall: A firewall is a program that decides whether traffic coming into a server or going out should be allowed. A firewall usually works by creating rules for which type of traffic is acceptable on which ports. Generally, firewalls block ports that are not used by a specific application on a server.
• NAT: Network address translation is a way to translate requests that are incoming into a routing server to the relevant devices or servers that it knows about in the LAN. This is usually implemented in physical LANs as a way to route requests through one IP address to the necessary backend servers.
• VPN: Virtual private network is a means of connecting separate LANs through the internet, while maintaining privacy. This is used as a means of connecting remote systems as if they were on a local network, often for security reasons.
Network Layers
While networking is often discussed in terms of topology in a horizontal way, between hosts, its implementation is layered in a vertical fashion throughout a computer or network. This means is that there are multiple technologies and protocols that are built on top of each other in order for communication to function more easily. Each successive, higher layer abstracts the raw data a little bit more, and makes it simpler to use for applications and users. It also allows you to leverage lower layers in new ways without having to invest the time and energy to develop the protocols and applications that handle those types of traffic.
As data is sent out of one machine, it begins at the top of the stack and filters downwards. At the lowest level, actual transmission to another machine takes place. At this point, the data travels back up through the layers of the other computer. Each layer has the ability to add its own "wrapper" around the data that it receives from the adjacent layer, which will help the layers that come after decide what to do with the data when it is passed off.
One method of talking about the different layers of network communication is the OSI model. OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnect.This model defines seven separate layers. The layers in this model are:
• Application: The application layer is the layer that the users and user-applications most often interact with. Network communication is discussed in terms of availability of resources, partners to communicate with, and data synchronization.
• Presentation: The presentation layer is responsible for mapping resources and creating context. It is used to translate lower level networking data into data that applications expect to see.
• Session: The session layer is a connection handler. It creates, maintains, and destroys connections between nodes in a persistent way.
• Transport: The transport layer is responsible for handing the layers above it a reliable connection. In this context, reliable refers to the ability to verify that a piece of data was received intact at the other end of the connection. This layer can resend information that has been dropped or corrupted and can acknowledge the receipt of data to remote computers.
• Network: The network layer is used to route data between different nodes on the network. It uses addresses to be able to tell which computer to send information to. This layer can also break apart larger messages into smaller chunks to be reassembled on the opposite end.
• Data Link: This layer is implemented as a method of establishing and maintaining reliable links between different nodes or devices on a network using existing physical connections.
• Physical: The physical layer is responsible for handling the actual physical devices that are used to make a connection. This layer involves the bare software that manages physical connections as well as the hardware itself (like Ethernet).
The TCP/IP model, more commonly known as the Internet protocol suite, is another layering model that is simpler and has been widely adopted.It defines the four separate layers, some of which overlap with the OSI model:
• Application: In this model, the application layer is responsible for creating and transmitting user data between applications. The applications can be on remote systems, and should appear to operate as if locally to the end user.
The communication takes place between peers network.
• Transport: The transport layer is responsible for communication between processes. This level of networking utilizes ports to address different services. It can build up unreliable or reliable connections depending on the type of protocol used.
• Internet: The internet layer is used to transport data from node to node in a network. This layer is aware of the endpoints of the connections, but does not worry about the actual connection needed to get from one place to another. IP addresses are defined in this layer as a way of reaching remote systems in an addressable manner.
• Link: The link layer implements the actual topology of the local network that allows the internet layer to present an addressable interface. It establishes connections between neighboring nodes to send data.
Interfaces
Interfaces are networking communication points for your computer. Each interface is associated with a physical or virtual networking device. Typically, your server will have one configurable network interface for each Ethernet or wireless internet card you have. In addition, it will define a virtual network interface called the «loopback» or localhost interface. This is used as an interface to connect applications and processes on a single computer to other applications and processes. You can see this referenced as the «lo» interface in many tools.
Protocols
Networking works by piggybacks on a number of different protocols on top of each other. In this way, one piece of data can be transmitted using multiple protocols encapsulated within one another.
Media access control is a communications protocol that is used to distinguish specific devices. Each device is supposed to get a unique MAC address during the manufacturing process that differentiates it from every other device on the internet. Addressing hardware by the MAC address allows you to reference a device by a unique value even when the software on top may change the name for that specific device during operation. Media access control is one of the only protocols from the link layer that you are likely to interact with on a regular basis.
The IP protocol is one of the fundamental protocols that allow the internet to work. IP addresses are unique on each network and they allow machines to address each other across a network. It is implemented on the internet layer in the IP/TCP model. Networks can be linked together, but traffic must be routed when crossing network boundaries. This protocol assumes an unreliable network and multiple paths to the same destination that it can dynamically change between. There are a number of different implementations of the protocol. The most common implementation today is IPv4, although IPv6 is growing in popularity as an alternative due to the scarcity of IPv4 addresses available and improvements in the protocols capabilities.
ICMP: internet control message protocol is used to send messages between devices to indicate the availability or error conditions. These packets are used in a variety of network diagnostic tools, such as ping and traceroute. Usually ICMP packets are transmitted when a packet of a different kind meets some kind of a problem. Basically, they are used as a feedback mechanism for network communications.
TCP: Transmission control protocol is implemented in the transport layer of the IP/TCP model and is used to establish reliable connections. TCP is one of the protocols that encapsulates data into packets. It then transfers these to the remote end of the connection using the methods available on the lower layers. On the other end, it can check for errors, request certain pieces to be resent, and reassemble the information into one logical piece to send to the application layer. The protocol builds up a connection prior to data transfer using a system called a three-way handshake. This is a way for the two ends of the communication to acknowledge the request and agree upon a method of ensuring data reliability. After the data has been sent, the connection is torn down using a similar four-way handshake. TCP is the protocol of choice for many of the most popular uses for the internet, including WWW, FTP, SSH, and email. It is safe to say that the internet we know today would not be here without TCP.
UDP: User datagram protocol is a popular companion protocol to TCP and is also implemented in the transport layer. The fundamental difference between UDP and TCP is that UDP offers unreliable data transfer. It does not verify that data has been received on the other end of the connection. This might sound like a bad thing, and for many purposes, it is. However, it is also extremely important for some functions. It’s not required to wait for confirmation that the data was received and forced to resend data, UDP is much faster than TCP. It does not establish a connection with the remote host, it simply fires off the data to that host and doesn’t care if it is accepted or not. Since UDP is a simple transaction, it is useful for simple communications like querying for network resources. It also doesn’t maintain a state, which makes it great for transmitting data from one machine to many real-time clients. This makes it ideal for VOIP, games, and other applications that cannot afford delays.
HTTP: Hypertext transfer protocol is a protocol defined in the application layer that forms the basis for communication on the web. HTTP defines a number of functions that tell the remote system what you are requesting. For instance, GET, POST, and DELETE all interact with the requested data in a different way.
JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact URL-safe means of representing claims to be transferred between two parties. The claims in a JWT are encoded as a JSON object that is digitally signed using JSON Web Signature (JWS).
OAuth 2.0 is an open source authorization framework that enables applications to obtain limited access to user accounts on an HTTP service, such as Amazon, Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Twitter GitHub, and DigitalOcean. It works by delegating user authentication to the service that hosts the user account, and authorizing third-party applications to access the user account.
FTP: File transfer protocol is in the application layer and provides a way of transferring complete files from one host to another. It is inherently insecure, so it is not recommended for any externally facing network unless it is implemented as a public, download-only resource.
DNS: Domain name system is an application layer protocol used to provide a human-friendly naming mechanism for internet resources. It is what ties a domain name to an IP address and allows you to access sites by name in your browser.
SSH: Secure shell is an encrypted protocol implemented in the application layer that can be used to communicate with a remote server in a secure way. Many additional technologies are built around this protocol because of its end-to-end encryption and ubiquity. There are many other protocols that we haven’t covered that are equally important. However, this should give you a good overview of some of the fundamental technologies that make the internet and networking possible.
Virtualization
KVM (for Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a full virtualization solution for Linux on x86 hardware containing virtualization extensions (Intel VT or AMD-V). It consists of a loadable kernel module, kvm.ko, that provides the core virtualization infrastructure and a processor specific module, kvm-intel.ko or kvm-amd.ko.
QEMU is a fast processor emulator using a portable dynamic translator. QEMU emulates a full system, including a processor and various peripherals. It can be used to launch a different Operating System without rebooting the PC or to debug system code.
Hyper-V enables running virtualized computer systems on top of a physical host. These virtualized systems can be used and managed just as if they were physical computer systems, however they exist in virtualized and isolated environment. Special software called a hypervisor manages access between the virtual systems and the physical hardware resources. Virtualization enables quick deployment of computer systems, a way to quickly restore systems to a previously known good state, and the ability to migrate systems between physical hosts.
VirtManager is a graphical tool for managing virtual machines via libvirt. Most usage is with QEMU/KVM virtual machines, but Xen and libvirt LXC containers are well supported. Common operations for any libvirt driver should work.
oVirt is an open-source distributed virtualization solution, designed to manage your entire enterprise infrastructure. oVirt uses the trusted KVM hypervisor and is built upon several other community projects, including libvirt, Gluster, PatternFly, and Ansible.Founded by Red Hat as a community project on which Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization is based allowing for centralized management of virtual machines, compute, storage and networking resources, from an easy-to-use web-based front-end with platform independent access.
Xen is focused on advancing virtualization in a number of different commercial and open source applications, including server virtualization, Infrastructure as a Services (IaaS), desktop virtualization, security applications, embedded and hardware appliances, and automotive/aviation.
Ganeti is a virtual machine cluster management tool built on top of existing virtualization technologies such as Xen or KVM and other open source software. Once installed, the tool assumes management of the virtual instances (Xen DomU).
Packer is an open source tool for creating identical machine images for multiple platforms from a single source configuration. Packer is lightweight, runs on every major operating system, and is highly performant, creating machine images for multiple platforms in parallel. Packer does not replace configuration management like Chef or Puppet. In fact, when building images, Packer is able to use tools like Chef or Puppet to install software onto the image.
Vagrant is a tool for building and managing virtual machine environments in a single workflow. With an easy-to-use workflow and focus on automation, Vagrant lowers development environment setup time, increases production parity, and makes the «works on my machine» excuse a relic of the past. It provides easy to configure, reproducible, and portable work environments built on top of industry-standard technology and controlled by a single consistent workflow to help maximize the productivity and flexibility of you and your team.
VMware Workstation is a hosted hypervisor that runs on x64 versions of Windows and Linux operating systems; it enables users to set up virtual machines on a single physical machine, and use them simultaneously along with the actual machine.
VirtualBox is a powerful x86 and AMD64/Intel64 virtualization product for enterprise as well as home use. Not only is VirtualBox an extremely feature rich, high performance product for enterprise customers.
Databases
Back to the Top
Database Learning Resources
SQL is a standard language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data in relational databases.
SQL Tutorial by W3Schools
Learn SQL Skills Online from Coursera
SQL Courses Online from Udemy
SQL Online Training Courses from LinkedIn Learning
Learn SQL For Free from Codecademy
GitLab’s SQL Style Guide
OracleDB SQL Style Guide Basics
Tableau CRM: BI Software and Tools
Databases on AWS
Best Practices and Recommendations for SQL Server Clustering in AWS EC2.
Connecting from Google Kubernetes Engine to a Cloud SQL instance.
Educational Microsoft Azure SQL resources
MySQL Certifications
SQL vs. NoSQL Databases: What’s the Difference?
What is NoSQL?
Databases and Tools
Azure Data Studio is an open source data management tool that enables working with SQL Server, Azure SQL DB and SQL DW from Windows, macOS and Linux.
Azure SQL Database is the intelligent, scalable, relational database service built for the cloud. It’s evergreen and always up to date, with AI-powered and automated features that optimize performance and durability for you. Serverless compute and Hyperscale storage options automatically scale resources on demand, so you can focus on building new applications without worrying about storage size or resource management.
Azure SQL Managed Instance is a fully managed SQL Server Database engine instance that’s hosted in Azure and placed in your network. This deployment model makes it easy to lift and shift your on-premises applications to the cloud with very few application and database changes. Managed instance has split compute and storage components.
Azure Synapse Analytics is a limitless analytics service that brings together enterprise data warehousing and Big Data analytics. It gives you the freedom to query data on your terms, using either serverless or provisioned resources at scale. It brings together the best of the SQL technologies used in enterprise data warehousing, Spark technologies used in big data analytics, and Pipelines for data integration and ETL/ELT.
MSSQL for Visual Studio Code is an extension for developing Microsoft SQL Server, Azure SQL Database and SQL Data Warehouse everywhere with a rich set of functionalities.
SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT) is a development tool for building SQL Server relational databases, Azure SQL Databases, Analysis Services (AS) data models, Integration Services (IS) packages, and Reporting Services (RS) reports. With SSDT, a developer can design and deploy any SQL Server content type with the same ease as they would develop an application in Visual Studio or Visual Studio Code.
Bulk Copy Program is a command-line tool that comes with Microsoft SQL Server. BCP, allows you to import and export large amounts of data in and out of SQL Server databases quickly snd efficeiently.
SQL Server Migration Assistant is a tool from Microsoft that simplifies database migration process from Oracle to SQL Server, Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Database Managed Instance and Azure SQL Data Warehouse.
SQL Server Integration Services is a development platform for building enterprise-level data integration and data transformations solutions. Use Integration Services to solve complex business problems by copying or downloading files, loading data warehouses, cleansing and mining data, and managing SQL Server objects and data.
SQL Server Business Intelligence(BI) is a collection of tools in Microsoft’s SQL Server for transforming raw data into information businesses can use to make decisions.
Tableau is a Data Visualization software used in relational databases, cloud databases, and spreadsheets. Tableau was acquired by Salesforce in August 2019.
DataGrip is a professional DataBase IDE developed by Jet Brains that provides context-sensitive code completion, helping you to write SQL code faster. Completion is aware of the tables structure, foreign keys, and even database objects created in code you’re editing.
RStudio is an integrated development environment for R and Python, with a console, syntax-highlighting editor that supports direct code execution, and tools for plotting, history, debugging and workspace management.
MySQL is a fully managed database service to deploy cloud-native applications using the world’s most popular open source database.
PostgreSQL is a powerful, open source object-relational database system with over 30 years of active development that has earned it a strong reputation for reliability, feature robustness, and performance.
Amazon DynamoDB is a key-value and document database that delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale. It is a fully managed, multiregion, multimaster, durable database with built-in security, backup and restore, and in-memory caching for internet-scale applications.
FoundationDB is an open source distributed database designed to handle large volumes of structured data across clusters of commodity servers. It organizes data as an ordered key-value store and employs ACID transactions for all operations. It is especially well-suited for read/write workloads but also has excellent performance for write-intensive workloads. FoundationDB was acquired by Apple in 2015.
CouchbaseDB is an open source distributed multi-model NoSQL document-oriented database. It creates a key-value store with managed cache for sub-millisecond data operations, with purpose-built indexers for efficient queries and a powerful query engine for executing SQL queries.
IBM DB2 is a collection of hybrid data management products offering a complete suite of AI-empowered capabilities designed to help you manage both structured and unstructured data on premises as well as in private and public cloud environments. Db2 is built on an intelligent common SQL engine designed for scalability and flexibility.
MongoDB is a document database meaning it stores data in JSON-like documents.
OracleDB is a powerful fully managed database helps developers manage business-critical data with the highest availability, reliability, and security.
MariaDB is an enterprise open source database solution for modern, mission-critical applications.
SQLite is a C-language library that implements a small, fast, self-contained, high-reliability, full-featured, SQL database engine.SQLite is the most used database engine in the world. SQLite is built into all mobile phones and most computers and comes bundled inside countless other applications that people use every day.
SQLite Database Browser is an open source SQL tool that allows users to create, design and edits SQLite database files. It lets users show a log of all the SQL commands that have been issued by them and by the application itself.
dbWatch is a complete database monitoring/management solution for SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, Sybase, MySQL and Azure. Designed for proactive management and automation of routine maintenance in large scale on-premise, hybrid/cloud database environments.
Cosmos DB Profiler is a real-time visual debugger allowing a development team to gain valuable insight and perspective into their usage of Cosmos DB database. It identifies over a dozen suspicious behaviors from your application’s interaction with Cosmos DB.
Adminer is an SQL management client tool for managing databases, tables, relations, indexes, users. Adminer has support for all the popular database management systems such as MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, SQLite, MS SQL, Oracle, Firebird, SimpleDB, Elasticsearch and MongoDB.
DBeaver is an open source database tool for developers and database administrators. It offers supports for JDBC compliant databases such as MySQL, Oracle, IBM DB2, SQL Server, Firebird, SQLite, Sybase, Teradata, Firebird, Apache Hive, Phoenix, and Presto.
DbVisualizer is a SQL management tool that allows users to manage a wide range of databases such as Oracle, Sybase, SQL Server, MySQL, H3, and SQLite.
AppDynamics Database is a management product for Microsoft SQL Server. With AppDynamics you can monitor and trend key performance metrics such as resource consumption, database objects, schema statistics and more, allowing you to proactively tune and fix issues in a High-Volume Production Environment.
Toad is a SQL Server DBMS toolset developed by Quest. It increases productivity by using extensive automation, intuitive workflows, and built-in expertise. This SQL management tool resolve issues, manage change and promote the highest levels of code quality for both relational and non-relational databases.
Lepide SQL Server is an open source storage manager utility to analyse the performance of SQL Servers. It provides a complete overview of all configuration and permission changes being made to your SQL Server environment through an easy-to-use, graphical user interface.
Sequel Pro is a fast MacOS database management tool for working with MySQL. This SQL management tool helpful for interacting with your database by easily to adding new databases, new tables, and new rows.
Contribute
- If would you like to contribute to this guide simply make a Pull Request.
License
Back to the Top
Distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Public License.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим начало работы с Kali Linux, одного из лучших инструментов для тестирования информационной безопасности компьютерных систем. В статье описано как скачать и запустить дистрибутив Kali Linux, типовые сценарии развёртывания, процесс установки и первоначальной настройки.
Содержание:
- Где скачать Kali Linux?
- Запуск Kali Linux из готового OVA образа Virtual Box
- Установка Kali Linux в виртуальную машину с помощью ISO образа
- Базовая настройка Kali Linux
Kali является самым распространенным и одним из лучших Linux дистрибутивов в области тестирования защищенности. Дистрибутив Kali Linux основан на Debian и поставляется с множеством инструментов для тестирования безопасности от Offensive Security. Доступны несколько классов инструментов.
- Sniffing & Spofing
- Анализ уязвимостей
- Анонимность
- Подбор паролей
- Атаки на беспроводные сети
- Веб приложения
- Инструментарий для составления отчетов
- Инструментарий для эксплуатации уязвимостей
- Инструменты для решения задач цифровой криминалистики
- Обратная инженерия
- Инструменты установления и поддержания доступа
- Сбор информации
- Стресс-тестирование
- Уязвимые среды и программы для проведения тестирования
Где скачать Kali Linux?
Дистрибутив Kali Linux для различных аппаратных и виртуальных платформ можно скачать по ссылке: https://www.kali.org/get-kali/#kali-platforms
Доступны следующие виды дистрибутивов:
- Bare Metal версия для полноценной установки на физические компьютеры или сервера. Доступы образы
- x64 с максимальным количеством обновлений (2022-W02)
- x64 offline стабильный инсталлятор (2021-4a)
- x64 NetInstaller сетевая установка (2021-4a)
- Образы виртуальных машин:
- Для Virtual Box x64/x32
- VMware x64/x32
- Vagrant
- Образы для ARM архитектуры (доступны пакеты микро-ПК таких как Raspberry Pi)
- Версия для Android (Kali NetHunter) — полноценная работа возможна только при наличии root-прав у пользователя мобильного устройства.
- Образы для установки в облако (пока поддерживается только Amazon AWS)
- Контейнеры — доступны образы для Docker и LXD
- Использование в рамках Windows subsystem for Linux (WSL) – образы для Windows 10 и 11 доступны для установки через и можно скачать Microsoft Store
- Установка на USB накопитель (в том числе с поддержкой Live Boot) – есть образы для x64/x32/Apple M1
Далее мы покажем, как запустить готовый. ova образ Kali в виртуальной машине Virtual Box, и установить образ в чистую виртуальную машину с помощью ISO образа.
Запуск Kali Linux из готового OVA образа Virtual Box
Самый быстрый способ запустить Kali Linux на вашем компьютере – скачать готовый OVA образ для VirtualBox (не забудьте установить Extension Pack для Virtual Box).
Проверьте, что в BIOS/UEFI вашего компьютера включена виртуализация. Обычно это Intel VT-x или AMD-V.
Скачайте x64 .ova образ Kali Linux для Virtual Box здесь https://www.kali.org/get-kali/#kali-virtual-machines
Импортируйте готовый ova образ в Virtual Box (File -> Import Appliance -> Source – Local File System, File – выбираем ранее загруженный .ova и жмем Import).
Kali готова к запуску, осталось запустить ВМ кнопкой Start и вы увидите экран входа.
Вводим стандартный логин и пароль kali/kali.
Виртуальная машина Kali запущена, можно приступать к дальнейшей работе. Рассмотренный способ является наиболее оптимальным для первого знакомства — занимает меньшее количество времени.
Установка Kali Linux в виртуальную машину с помощью ISO образа
Можно установить Kali Linux в виртуальную машину с помощью установочного ISO образа. Скачайте x64 образ Kali для офлайн установки (https://www.kali.org/get-kali/#kali-bare-metal).
Создайте виртуальную машину со следующими параметрами:
- Type – Linux;
- Version – Debian (64-bit);
- Memory size (RAM) – 2048MB (не менее);
- Hard disk– VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image), Dynamically allocated, размером не менее 80 Гб.
В настройках виртуальной машины Virtual Box измените следующие параметры:
- Включите общий буфер обмена: General – Advanced, Shared Clipboard и Drag’n’Drop на bidirectional;
- Добавьте 2 vCPU, а также в Extended Features опцию Enable PAE/NX;
- Добавьте 128 Мб для видеопамяти (Display –> Screen -> Video Memory)
- Выделяем 128MB видеопамяти: Display – Screen, Video Memory в значение 128 MB;
Для начала установки смонтируйте скачанный ISO образ Kali Linux в виртуальный привод (Storage -> Controller –> IDE /CD).
Запустите виртуальную машину. Для упрощения рассмотрим графическую установку:
- Graphical Install
- Язык English, локация
- Выберите локацию и раскладку
- Имя хоста — vmkali
- Имя домена пропускаем
- Задайте имя пользователя
- Задайте пароль
- Настраиваем временную зону
- Разбивка диска –
Guided – use entire disk
.Для первого знакомства этого достаточно, в будущем разбивку можно выполнять и вручную, в том числе с включением LVM, если требуется.
- Выберите разбиение диска:
All files in one partitio
n - Выберите окружение рабочего стола – если предпочтений нет, не изменяйте.
- Установить загрузчик Grub –
yes - Указываем диск для загрузчика –
/dev/sda
Если все сделано верно, как в случае с использованием готового образа Kali, вы увидите окно входа в учетную запись:
Войдите в Kali с помощью заданных ранее логином и паролем.
Базовая настройка Kali Linux
Теперь можно изменить базовые настройки Kali.
По умолчанию Kali настроена на автоматическое получение IP адреса через DHCP. Можно задать параметры сети вручную в Настройках -> Сеть. Здесь же можно указать адрес прокси-сервер для доступа в Интернет.
Узнать текущий IP адрес:
sudo ifconfig
Можно задать параметры IPv4 адреса вручную из консоли
IP адрес и маска сети:
sudo ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.0
Шлюз по-умолчанию:
sudo route add default gw 192.168.1.2 eth0
Адрес DNS сервера:
sudo echo nameserver %DNS ADDRESS% > /etc/resolv.conf
Если вы используете дистрибутив NetInsall, Kali linux автоматически пропишет актуальное зеркало для устанавливаемого дистрибутива в системных параметрах.
Список депозитариев хранится в файле /etc/apt/source.list. По умолчанию использутся репозиторий:
deb http://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main contrib non-free
Обновите репозитории и установите обновления операционный системы:
apt-get clean && apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y && apt-get dist-upgrade –y
По окончании установки обновлений операционной системы выполните перезагрузку:
sudo systemctl reboot
Для установки группы программ (если она была пропущена при установке) нужно выполнить команду:
sudo apt install kali-tools-wireless
Можно установить PowerShell для Linux:
sudo apt -y install powershell
Список самых распространенных инструментов (если вы установили Kali в минимальной конфигурации):
sudo apt install kali-tools-information-gathering kali-tools-vulnerability kali-tools-web kali-tools-password kali-tools-exploitation
Либо можно установить сразу все:
sudo apt install kali-linux-large
Вывести список программ в пакете:
sudo apt depends kali-tools-wireless
Для удаленного подключения к консоли Kali Linux по SSH нужно включить автоматической запуск службы SSH (по умолчанию установлена, но отключена):
sudo systemctl start ssh.socket
sudo systemctl enable ssh.socket
Проверьте, что служба SSH запущена:
sudo systemctl status ssh.socket
Чтобы разрешить удаленный доступ под Root, нужно в файле
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
найти строку
#PermitRootLogin prohibit-password
и заменить ее на
PermitRootLogin yes
.
В этой статье мы показали, как быстро установить и запустить Kali Linux. Это позволит вам познакомится с ее интерфейсом и терминалом. Попробуйте выполнить простые задачи, описанные в сети Интернет, попытаться при помощи nmap провести первые сканирования, начать можно с личного роутера или аналогично установить на Oracle virtual box операционную систему Metasploitable 2 и отработать первые атаки. В следующих статьях мы рассмотрим использование различных инструментов Kali Linux.
Теги: книги, пентест, тестирование на проникновение, pentest, kali linux, дистрибутив linux
Kali Linux — полезный дистрибутив, включающий в себя более 600 предустановленных программ тестирования проникновения. Это один из самых популярных пентест-дистрибутивов, и причина этому проста, ведь он имеет дружелюбный интерфейс и широкий набор инструментов, распределённых по категориям, что весьма удобно. Ознакомиться с Kali Linux вам помогут следующие книги:
1. «Kali Linux от разработчиков» — Херцог Р., О’Горман Д., Ахарони М.
Не что иное, как официальное руководство по Kali Linux. С помощью этой книги вы научитесь применять и настраивать Kali Linux с нуля. Некоторые темы:
— установка Kali Linux и работа с командной строкой;
— применение менеджера пакетов Debian: установка и настройка, обновление, создание своих настраиваемых пакетов;
— компиляция ядра Linux;
— создание своих ISO-образов;
— обеспечение шифрования и защиты конфиденциальной информации.
2. «Kali Linux. Тестирование на проникновение и безопасность» — авторский коллектив
Эта книга будет полезна этическим хакерам, пентестерам и специалистам по ИТ-безопасности. Для усвоения материала потребуются базовые знания ОС Windows и Linux. Понимание области информационной безопасности будет плюсом.
Чему научитесь:
— выполнять тестирование на проникновение (начальные этапы), понимать сферу его использования;
— выполнять «разведку» и учёт ресурсов в целевых сетях;
— задействовать Kali Linux NetHunter в целях пентеста беспроводных сетей;
— получать и взламывать пароли;
— создавать отчеты о тестировании на проникновение;
— ориентироваться в стандарте PCI-DSS и инструментах, применяемых для сканирования и пентеста.
3. «Linux глазами хакера» — Михаил Фленов
Здесь рассматриваются вопросы настройки Linux с учётом максимальной производительности и безопасности. Вы узнаете про администрирование и управление доступом, разберёте настройки Firewall, познакомитесь с файлообменным сервером, WEB-, FTP– и Proxy-серверами, программами доставки электронной почты. Узнаете про DNS-службы и политику мониторинга системы и архивирование данных.
Рассмотрев потенциальные уязвимости, вы получите рекомендации по предотвращению атак и поймёте, как надо действовать при возможной атаке либо взломе системы, дабы как можно быстрее восстановить работоспособность и предотвратить утерю конфиденциальной информации.
4. «Тестирование на проникновение с Kali Linux»
Подробное электронное пособие, в котором собраны наиболее интересные материалы с сайта codeby.net. Источником являются переводы англоязычных ресурсов и не только. Смысл создания этой книги — систематизация имеющихся знаний. Все материалы бесплатны.