—D. Thiebaut (talk) 11:51, 19 September 2014 (EDT)
The tutorials below are intended for instructors teaching programming languages, and interested in setting up Moodle VPL modules to automatically test student programs.
The modules are listed in chronological order, most recent at the end. Because VPL is a complex system to master, the
early tutorials may not be built using the best approach, but provide functionality. The later modules use more sophisticated features of VPL.
Feel freel to send me your own modules or discoveries, at dthiebaut@smith.edu, and I will be happy to include them here.
Reference Material
- A video I created to help explain how I use VPL for my courses.
(Supporting Files for Video )
- Juan Carlos Rodríguez-del-Pino, Enrique Rubio-Royo, Zenón, and J. HernándezFigueroa, A Virtual Programming Lab for Moodle with automatic assessment and anti-plagiarism features, Proc. WorldComp12, July 2012, Las Vegas, USA. (pdf)
- Automatic Evaluation of Computer Programs using Moodle’s Virtual Programming Lab (VPL) Module, D. Thiebaut, accepted for presentation at CCSCNE 2015.
- YouTube video 1: setting up a simple VPL module Part 1 (for use at CCSCNE2015)
- YouTube video 2: setting up a simple VPL module, Part 2 (for use at CCSCNE2015)
Setting up a VPL module for Python
Moodle Virtual-Programming-Lab (VPL)
| Tutorial | Language | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Moodle/VPL Server Setup |
This tutorial provides rough directions for setting up two virtual servers that will host Moodle on one of them, and the VPL jail server on the other. This setup is used by the tutorials below on the use of VPL to test student programs. |
|
|
Moodle VPL Example 1: Hello World! |
Python |
This tutorial illustrates how to setup VPL to test a simple Python 3 program that prints the string «Hello World!» to the console. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 2: Min of 3 Numbers |
Python |
This tutorial illustrates how to setup VPL to test a simple Python 3 program that receives 3 numbers from the console and prints the smallest of the 3. The program is tested 3 times, with 3 different sets of input numbers. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 3: Rock-Paper-Scissors |
Python |
This tutorial shows the settings for a VPL activity that would test a Python program that plays the game of Rock-Paper-Scissors. The program tested is expected to get its input as pairs of letters (PP, RS, PS, etc), indicates the winner of each round, and stops when one player is 3 points above the other. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 4: Gremlins in my File! |
Python |
This tutorial illustrates how to setup a VPL activity that tests a student program that reads a text file, modifies it, and stores the new content back in the original file. This requires an additional python program that sets up the environment for the first one to run, provides it the information it needs, and captures its output. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 5: Print a 2D chessboard |
Python |
This tutorial illustrates how to setup a VPL activity that tests a student program that asks the user for an integer and then prints a 2D chessboard (alternating black & white cells) with that dimension. The size of a cell is a 3×3 character on the screen. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 6: Display a rectangle of stars |
Assembly |
This tutorial illustrates the setup of a VPL activity to test an assembly language program that displays a fixed string (rectangle of stars). |
|
Moodle VPL Example 7: Assign a grade inversely proportional to the size of the executable |
Assembly |
This tutorial illustrates how to setup a VPL activity that will test the size of the executable version of an assembly language program. This can easily be adapted to other languages. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 8: A Hello World Program in Java |
Java |
This tutorial illustrates how to setup a VPL activity to test a simple Hello World program in Java. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 9: A Multi-File Java Program with A Data File |
Java |
This tutorial illustrates the setting of a VPL activity that evaluates a 2-class Java project that gets its input from a data file. The project is tested with 4 different data files; one provided by the students, 3 provided by the instructor. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 10: Evaluation Using A Custom Python Program |
Python |
This tutorial illustrates how to evaluate student work using a custom Python program. Such evaluation allows for more complex testing than enabled by the VPL .cases file. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 11: Testing a Java Class Using another Class as Tester. |
Java |
This tutorial sets up an environment to test different methods of a Java class provided by the students, and uses a derived class provided by the instructor to activate the student classes. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 12: Using a Java Tester for testing Student Java Program. |
Java |
This tutorial shows how to setup a more sophisticated testing environment for evaluating and grading Java program. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 13: Testing 2 classes, one Holding a Data Structure, the Other Holding a Test Class. |
Java |
This VPL module tests two Java classes, one inherited from the other. The test checks that one class does not access directly a member array of the super class (look for presence of [ ] brackets in code). Different grades are given depending on various stages of success. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 14: Testing Student List Class and Verifying Functionality. |
Java |
This VPL module tests a data structure provided by the student using a class provided by the instructor. The instructor class tests various methods. The grade is proportional to the number of correct output lines. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 15: Looping through Tests in vpl_evaluate.sh. Testing Exceptions. |
Java |
This VPL module tests how a program uses exceptions to parse a simple text file containing numbers. The vpl_evaluate.sh script generates 3 tests, and runs through all 3 of them. Vpl_evaluate.sh skips non digits and non minus characters when comparing the output of the submitted program to the expected output. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 16: Catching Programs Stuck in Infinite Loops. |
Java |
This VPL module is an extension of the previous module (#15), and catches java programs that hang in infinite loops. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 17: Verifying that ASM Program Contains Key Functions. |
Assembly |
This VPL module tests that an assembly program actually declares and calls 3 key functions. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 18: Test Function of Student Program Multiple Times. |
Assembly |
This VPL module tests a function in the student program and calls it several times to see if it performs correctly. The _start label of the student program is invalidated, and the student program is linked with a test program that calls the student function as an extern. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 19: Feed Different Tests on Command Line. |
Java |
This VPL module tests a Java program that outputs 0, 1, or several numbers depending on an input provided on the program’s command line. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 20: Test Elapsed Time of Student Program |
Java |
This VPL module tests a Java program and verify that its execution is greater than some predefined amount of time. Otherwise the program may be short-circuiting the execution and outputting a preprocessed answer. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 21: A Java Test Program that Evaluates Student’s Submitted Class and Methods |
Java |
This VPL module uses a Java test program that energizes the student’s submitted class, activating various methods, and generates OK or FAIL strings for each test given. The vpl_evaluate.sh script simply counts the # of OK strings generated and gives grade proportional to it. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 22: Test functions in the student programs, checks stack and register invariance, and verifies that solution provided is recursive. |
Assembly |
This VPL module requires the student to submit a program that contains only global assembly language functions. The module uses a test program in assembly that calls the functions with a given set of parameters, and tests whether the returned values are correct or not. The test program also verifies that none of the Pentium registers are modified. The testing script also ensures that the student program uses recursion for his/her solution. |
|
Moodle VPL Example 23: Test a Python program that performs basic input/output operations. |
Python |
This VPL module is written mostly in Python. vpl_evaluates simply calls a python program that tests the student’s python code. The python test first attempts to run the student program as a subprocess to catch possible errors or crash. If this is successful, then the student code is imported and run, with its stdin and stdout redirected from and to files controlled by the test program. |
|
Testing a Bash script |
Bash |
This setup tests a bash script submitted by students. The script acts as a teller machine, getting an integer on the command line and printing 4 integers out, corresponding to the number of $20-bills, number of $10-bills, number of $5-bills, and number of $1-bills. |
|
Testing an Assembly Program with Time-Out |
Assembly |
This setup tests a recursive program in assembly (binary search) that may time-out (possibly because of weird recursive coding.) The evaluate script will abort if the program takes longer than a specified amount of time. This uses a bash script for vpl_evaluate.sh and vpl_run.sh. |
|
Testing a C Program |
C |
This setup tests a C program that is supposed to replicate some of the functionality of the Linux grep command. In particular, the C program should get its input from the command line and support the «-i» switch, for case-insensitive searching. |
|
Tips & Tricks |
A collection of notes, recommendations, tips, tricks, and modifications. For example, we describe how to strip comments from java or assembly language comments. |
|
|
Testing a C Program and Setting the Grade Depending on Number of Correct Output Lines |
C & Bash |
A collection of notes, recommendations, tips, tricks, and modifications. For example, we describe how to strip comments from java or assembly language comments. |
|
Testing a C-Sharp «Hello World» program |
C#, Bash |
This is just a rough tutorial assuming that you already know how to setup a VPL module. |
Virtual Programming Lab can be a little intimidating to use, but once you get the swing of things, it’s pretty good. So, let’s get you started with the simplest possible working example. We assume that:
- you have Moodle working at your institution
- someone has installed VPL on Moodle and
- you don’t need or have access to a local VPL server that connects to Moodle.
By default, the VPL Moodle activities are set to set data to a server in Spain that hosts compilers and development tools that can be used to evaluate student submissions. We’ll use that server for this example.
Step 1: Set up a VPL Assignment on eClass (Moodle)
In eClass (Moodle), add a VPL assignment.
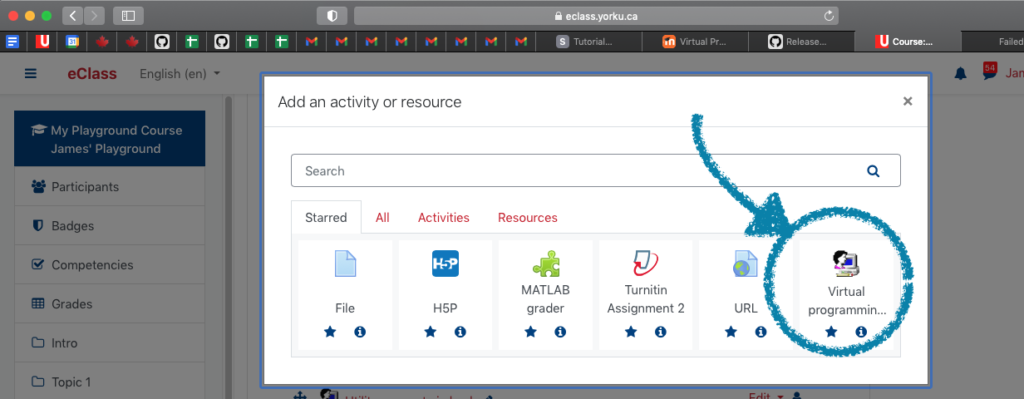
Note, the VPL icon may be in a different location in the «Add an activity» menu. Try «Activities» or «All» if you don’t see it immediately. Now, describe the assignment. Skip all the «Submission period», «Grade», «Tags», etc. settings. Then, «save and display.»
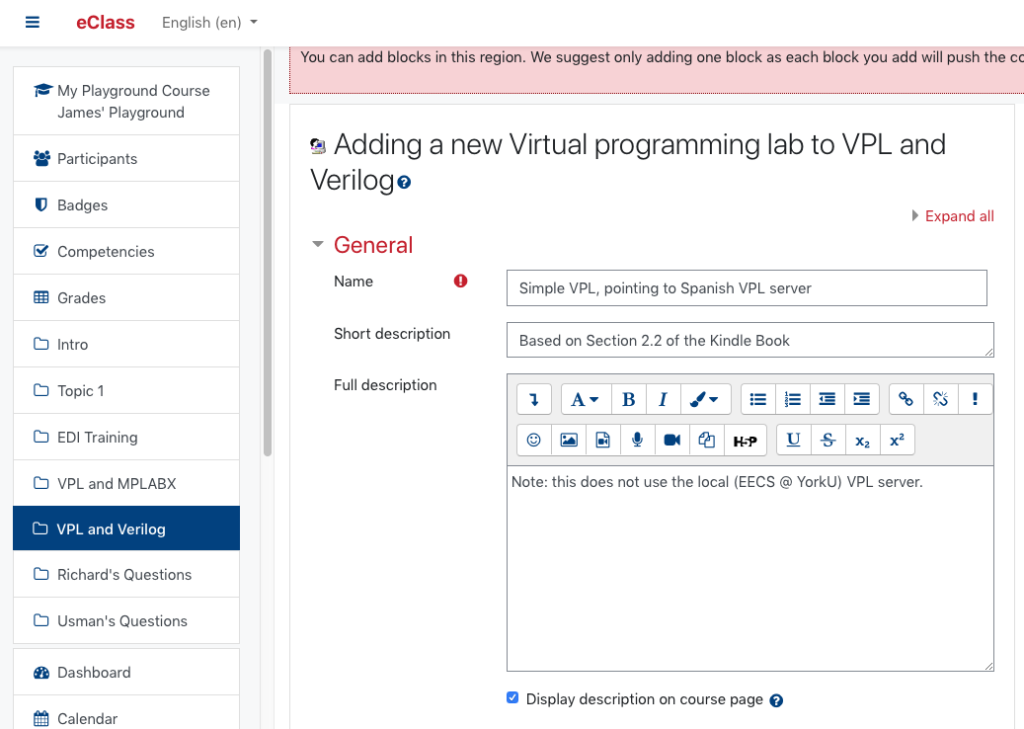
Step 2: Access the Editor via the Edit tab
We’re going to create a simple file for testing within this VPL activity. Now that you’ve set up the assignment and displayed it, click on the Test activity tab, shown below.
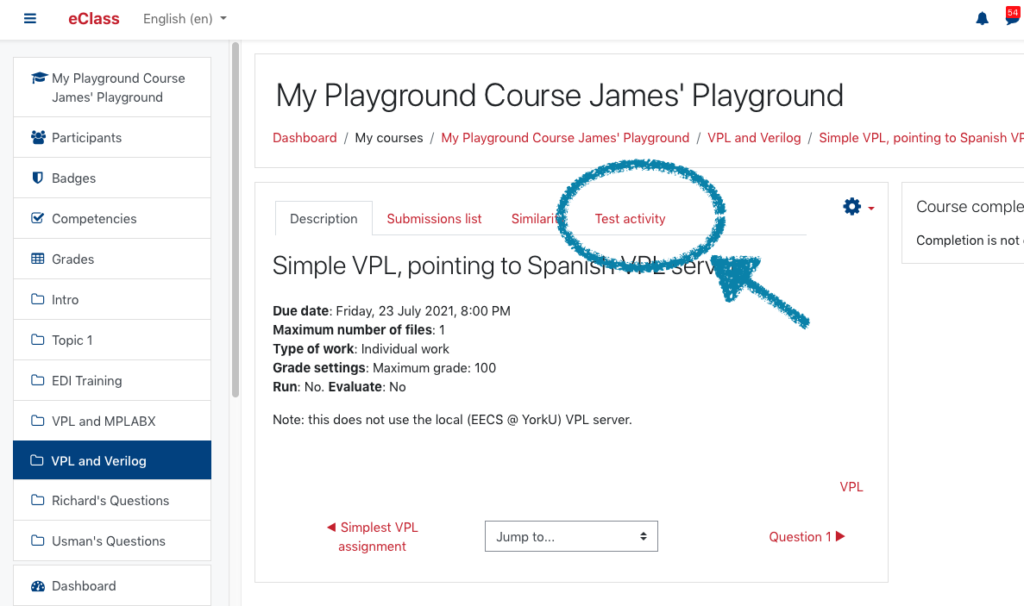
You will now see the «Edit» tab. Click on the Edit tab. A «Create a new file» window will appear, superimposed over the Editor window.
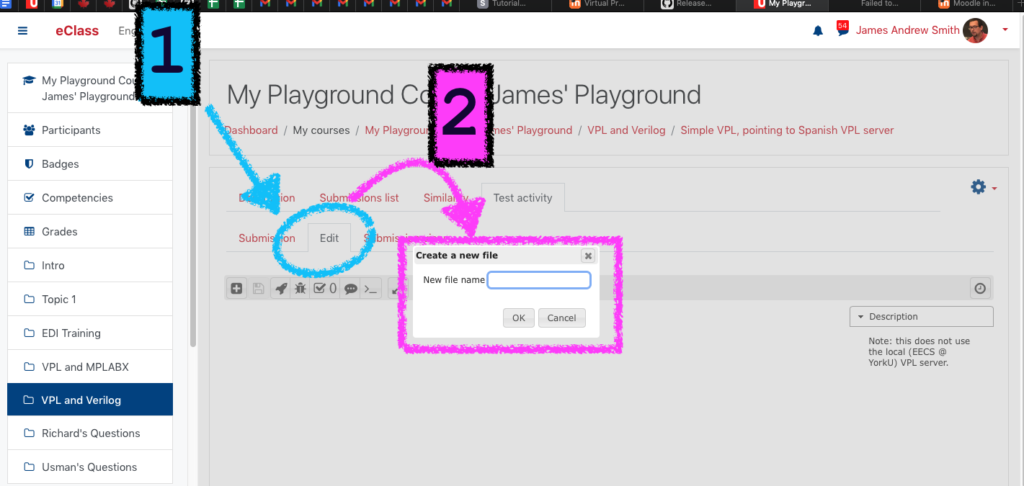
Name your test program file here. The file extension is key as this allows VPL to determine which programming language you intended to use. If it’s a Java program, name it somethingSomething.java. If it’s a Python program, name it blahBlah.py. Me, I’m going to test out a Verilog program and I’ll call it myVerilogProgram.v.
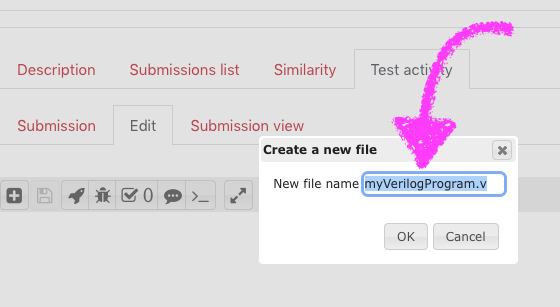
My program is this:
module TestModule;
reg [8:0] x; // an 8-bit registerinitial
begin
$display($time, » «, x);
x = 0;
$display($time, » «, x);
x = x+2;
$display($time, » «, x);
$finish;
end
endmoduleThis is my Verilog test program. Feel free to copy and paste.
Step 3: Run the program
Write it in the editor area and save it using the old-school diskette icon.
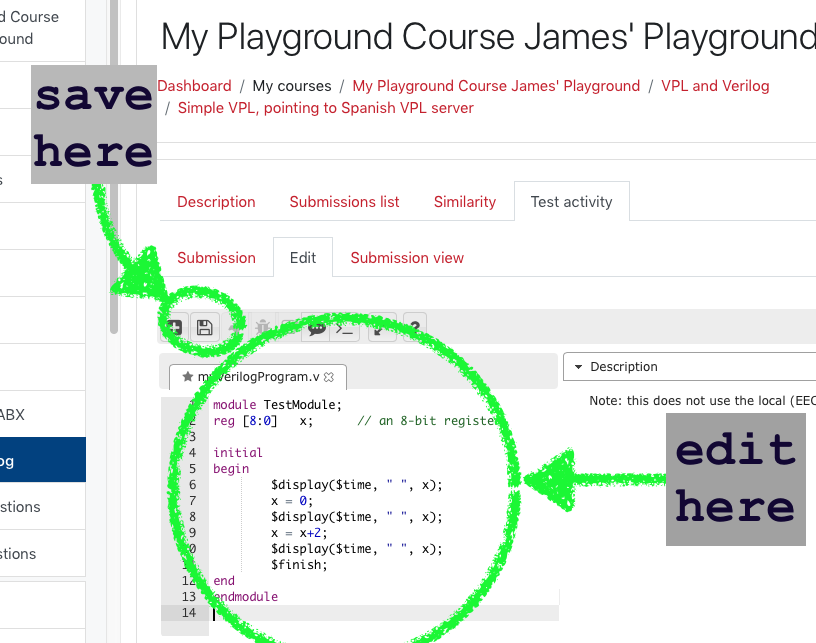
Now it’s time to run your program. Click on the rocket icon to run it.
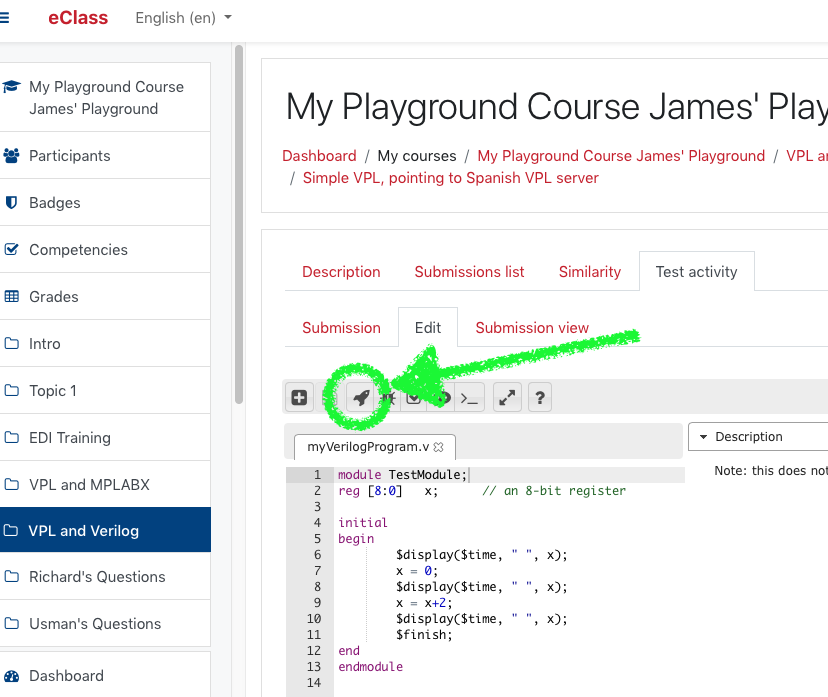
When you run the program a black console will appear superimposed on your editor. If your program prints anything, it will appear here. In my example, three lines appear and show the time (left) and variable value (right).
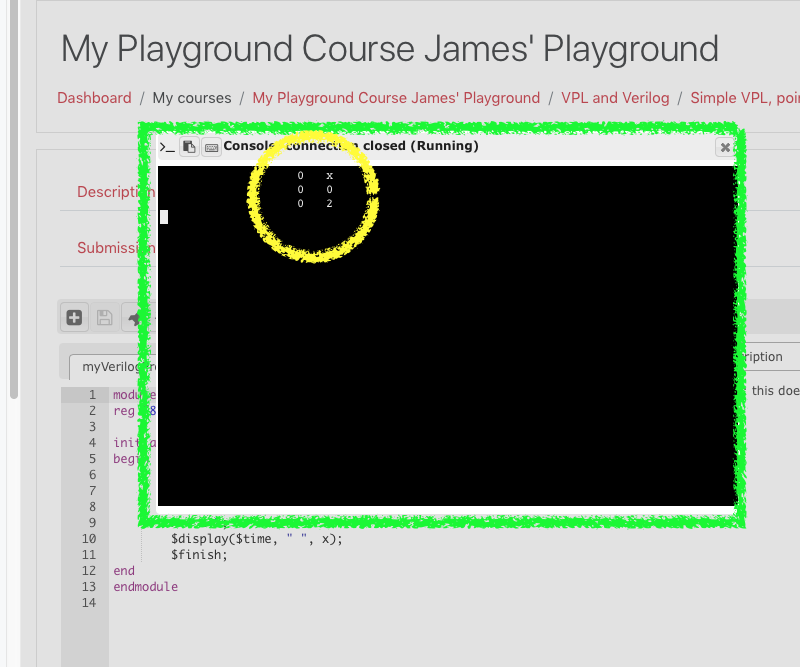
Error? VPL will find it for you!
If you mistype something, VPL will tell you when it tries to run or compile your program.
Next steps: Getting more help
I like looking up things on
- The VPL main website
- The Moodle VPL support page
- A downloaded copy of the VPL source code
- The Kindle book on VPL (it’s inexpensive but could use a good edit to clean it up a bit; however, it’s a decent reference)
- Уроки Информатики
- Учителям
- Учителям информатики

Существенную помощь в организации самостоятельной работы в рамках обучения программированию может оказать использование специальных программных средств, позволяющих в автоматическом режиме проверять корректность разработанной программы. Подобный функционал возможно реализовать на одной из следующих площадках или с использование свободного программного обеспечения:
- Соревнования Уральского федерального университета
- Технокубок от компании mail.ru
- Красноярская школа программиста
- Соревнования по программированию 2.0 (Codeforces)
- Contester 2.4
- Яндекс Контест
- Dudge
- PCMS2
- DOMjudge
- Система Московского центра непрерывного математического образования
Данные системы является самодостаточными и разворачивается на сервере или с ними можно работать зарегистрировавшись в системе. Работа с системой как со стороны администратора, так и со стороны пользователей, в роли которых выступают обучающиеся и преподаватели, осуществляется через веб-интерфейсы. Такая технология обеспечивает дополнительные возможности в организации обучения. Обучаемый может работать с системой из любой точки мира, в которой обеспечен доступ к сети Интернет, и в то же время все действия обучаемого фиксируются на сервере и доступны для преподавателя.
Однако для данных систем есть несколько ограничений и проблем в использовании:
- Дополнительная регистрация
- Отслеживание выполнения
- Оценивание
- Сервер недоступен или медленно проверяет из-за большого количества участников
Среди множества дополнений moodle есть два модуля, схожих по функционалу, а в некоторых моментах и превосходящие указанные выше системы. Первый является полноценным этапом курса с возможностью тонкой настройки и проверки и называется «Virtual Programming lab for Moodle» (сокращенно VPL). Второй является тестовым заданием и может быть включен в состав тестов и называется CodeRunner. Данные дополнения moodle позволяют использовать функционал вышеописанных систем без связанных с ними проблем.
В первую очередь данные дополнения ориентированы на изучение программирования, на работу с классом и использования как автоматически создаваемых, так и настраиваемых вариантов задач, в отличие от тестирующих систем предназначенных прежде всего для проведения олимпиадных соревнований по информатике.
Virtual Programming lab for Moodle
Virtual Programming Lab — это модуль учебного курса moodle, который позволяет создавать и проверять задания на программирование и имеет следующие характерные особенности:
- Редактирование исходного кода программы в браузере с подсветкой кода;
- Запуск интерактивных программ в браузере;
- Тестирование готовых программ;
- Позволяет искать сходство между файлами учащихся;
- Позволяет установить ограничения редактирования, и избежать вставки внешнего текста.
Данный модуль используется для тестирования программ среднего уровня, а также при обучении работы с черепашкой Python.
Метод проверки правильности представленной программы в системе достаточно простой. Создается система тестов, каждый из которых содержит входные данные и выходные данные, которые должны быть выданы правильно работающей программой. Обучаемый через веб-интерфейс пишет текст программы. Программа компилируется на сервере и запускается на выполнение с входными данными, представленными в каждом из тестов. Выходные данные сравниваются с эталоном с помощью специальной подпрограммы, называемой чекером. В системе реализованы компиляторы для подавляющего большинства популярных в настоящее время языков программирования — Ada, Bash script, C, C++, Fortran, Java, Pascal, Prolog, SQL, Scheme, Python и т. д.
Есть возможность установки ограничений на время исполнения и используемую память. Есть возможность создания заданий с несколькими вариантами, а также настройки позволяющие открывать или скрывать от учеников входные и выходные данные тестовых заданий на валидацию программы учащегося с эталонной. Проверка работоспособности программы учащегося возможна в браузере. Это достаточно компактная IDE работающая на любом компьютере с выходом в интернет.
Пример из практики
Условие Задачи 1
В файле files.csv записаны сведения о файлах. Всего в списке 280 записей, каждая из которых содержит
- имя файла;
- размер файла в Кбайтах;
- тип файла (аудио, видео, изображение, презентация, текстовый, электронная таблица);
- дату создания файла;
- дату последнего изменения файла;
- и уровень доступа.
Все элементы в каждой строке разделены запятыми.
Напишите программу, которая читает данные из файла в массив структур (записей) и выводит на экран
а) количество файлов каждого типа;
б) список 10 самых больших файлов, отсортированный по именам файлов (для каждого вывести имя файла и размер);
в) список презентаций ограниченного доступа, которые изменялись в 2012 году; список нужно отсортировать в алфавитном порядке по именам файлов;
г) список видео размером больше 100 Мбайт, созданных во второй половине 2011 года; список нужно отсортировать по убыванию размеров файлов.
Файл files прикреплен к заданию, но учащийся его не видит.
Проверка производится с помощью специальной программы:
import os
from subprocess import Popen, PIPE
checkGrade = 0
answerData = {}
answer = {"а:":"20 23 83 31 94 29",
"б:":"addition.avi 872791 earthquake.avi 394928 flesh.avi 657246 garden.avi 585151 head.avi 687945 kitten.avi 877704 quartz.avi 439667 rhythm.avi 314300 route.avi 338731 stem.avi 865410",
"в:":"eyes.ppt fall.ppt good-bye.ppt month.ppt rod.ppt tray.ppt",
"г:":"kitten.avi route.avi rhythm.avi face.avi"
}
def comment(s):
#s=s.decode('utf-8')
'''formats strings to create VPL comments'''
if len(s.split("\n"))>2:
for d in s.split("\n"):
print('Comment :=>> ' + str(d))
else:
print('Comment :=>> ' + str(s))
def grade(num):
'''formats a number to create a VPL grade'''
print('Grade :=>> ' + str(num))
with Popen('python3 main.py', shell=True, stdout=PIPE,stderr=PIPE) as proc:
res=proc.communicate()
if proc.returncode:
comment(res[1])
else:
for d in res[0].decode('utf-8').strip().split("\n"):
listD = d.split()
ans = " ".join(listD[1:])
key = listD[0]
answerData[key] = ans
for key in answerData:
if key in answer:
if answer[key].replace(' ','') == answerData[key].strip().replace(' ',''):
checkGrade += 1
print('Comment :=>> ' + 'Выполнено задание '+key)
moodle_max_grade = float(os.environ["VPL_GRADEMAX"])
check = int(checkGrade/4*100)
print('Comment :=>> ' + "Вы выполнили задание на " + str(check)+ "%")
check = moodle_max_grade*(check/100)
grade(check)Которая так же не видна учащимся.
Условие Задачи 2.
В одной фирме решили организовать локальную сеть, но инженер Вася не ходил на лекции по основам организации сети и забыли купить маршрутизатор. Однако его дедушка, знающий военный инженер связист, рассказал ему что 30 лет назад они соединяли все компьютеры в одну сеть используя один кабель. Такая топология сети называлась «Шина». Вася решил организовать сеть по топологии Шина, а для этого ему нужно проложить как можно меньше кабеля, чтобы уложиться в бюджет и организовать сеть без маршрутизатора. Помогите Васе рассчитать минимальную длину кабеля, которую нужно заказать в магазине.
Проверка производится на основе стандартных средств модуля по параметрам заданным в специальном файле:
ase=#1
grade reduction=100%
input=3 3
1 2 1
2 3 2
3 1 3
output=3
....
Case=#4
grade reduction=100%
input=8 8
1 2 1
2 4 3
4 3 7
3 6 9
5 6 6
6 7 4
7 8 2
8 1 1
output=24Есть небольшая возможность указывать учащимся варианты, но она достаточно простая и требует дополнительно описывать программу теста. Вариант теста храниться в глобальной переменной VPL_VARIATION0
CodeRunner
CodeRunner — это бесплатный модуль с открытым исходным кодом для Moodle, который может запускать программный код на разных языках программирования, представленный учащимися в качестве ответа. Он предназначен главным образом для использования в курсах компьютерного программирования, хотя он может использоваться для оценки любого вопроса, ответ на который является текстом. Обычно используется в адаптивном режиме тестов Moodle; учащиеся пишут свой код на каждый вопрос по программированию и сразу же получают результаты тестирования кода. Затем они могут исправить свой код и отправить повторно, как правило, с небольшим штрафом в 10% и есть возможность установки этого значения.
Тестовые задания помеченные светло-зеленым цветом не видны учащемуся.
В настоящее время поддерживает Python2, Python3, C, C++, Java, PHP, JavaScript (NodeJS), Octave и Matlab. Архитектура позволяет добавлять и другие языки программирования, например Pascal.
Данная система уже используется во множестве зарубежных учебных учреждениях, а также в школе 179 г. Москвы и Инженерный лицей НГТУ в г. Санкт Петербург.
Тонкая настройка вопроса позволяет запретить использовать некоторые встроенные функции языка программирования или проверять только определенные функции или процедуры написанные учащимся.
Важной особенностью модуля CodeRunner является возможность встраивать его в тестовое задание как один из вопросов теста, что значительно повышает возможности формирования алгоритмического мышления учащихся.
Тип вопросов CodeRunner поддерживает возможность генерации мультивариантных вопросы для каждого учащегося путем использования механизмов шаблона Twig.
Пример из практики
Условие Задачи 1.
Условие задачи задано шаблоном Twig:
На вход программы поступает неизвестное количество целых чисел, ввод заканчивается нулём. Требуется написать программу, которая подсчитает кол-во чисел оканчивающихся на {{ dN }}
Параметры Twig:
{
{% set index = random(2) %}
"text": "{{ ["двухзначных","трехзначных","четырехзначных"][index] }}",
"uravnen": "{{ ["9<n<100","99<n<1000","999<n<10000"][index] }}",
"nRange1": "{{ ["1","50","800"][index] }}",
"nRange2": "{{ ["200","300","3000"][index] }}",
"dN": "{{ 3 + random(6) }}"
}Программа проверки решения:
import subprocess
import random
import json
random.seed()
student_ans = """{{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }}"""
test_program = """{{ QUESTION.answer | e('py') }}"""
def someStreamCreatingProcess(stream1, stream2):
for i in range(200):
x = str(random.randint({{ nRange1 }}, {{ nRange2 }}))+"\n"
stream1.write(bytes(x, encoding='utf-8'))
stream2.write(bytes(x, encoding='utf-8'))
stream1.write(bytes("0\n", encoding='utf-8'))
stream2.write(bytes("0\n", encoding='utf-8'))
stream1.close()
stream2.close()
with open('student.py', 'w') as fout:
fout.write(student_ans)
with open('test.py', 'w') as fout:
fout.write(test_program)
subpr1 = subprocess.Popen(["python3", "student.py"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
subpr2 = subprocess.Popen(["python3", "test.py"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
someStreamCreatingProcess(stream1=subpr1.stdin, stream2=subpr2.stdin)
chek = subpr1.wait()
err = subpr1.stderr.read()
out1 = subpr1.stdout.read()
out2 = subpr2.stdout.read()
if err:
mark = 0
result = {'got': str(err.strip().decode()), 'fraction': mark}
else:
if out1 == out2:
mark = 1
great = "Супер! У тебя все получилось"
result = {'got': great, 'fraction': mark}
else:
mark = 0
result = {'got': str(out1.strip().decode()), 'expected': str(out2.strip().decode()), 'fraction': mark}
print(json.dumps(result))Эталонная программа:
n = int(input())
g = 0
while n != 0:
if {{ uravnen }} and n%10 == {{ dN }}:
g = g+1
n = int(input())
print(g)Условие Задачи 2.
Известно что список a содержит только целочисленные элементы, количество этих элементов неизвестно. Необходимо написать программу, которая в заданном списке найдет максимальный по значению элемент.
Программа проверки решения:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__saved_input__ = input
def input(prompt=''):
s = __saved_input__(prompt)
print(s)
return s
import sys
import codecs
sys.stdout = codecs.getwriter("utf-8")(sys.stdout.detach())
__student_answer__ = """{{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }}"""
if "max(" not in __student_answer__.replace(' ', ''):
pass
else:
print("Запрещено использовать функцию max")
sys.exit(0)
SEPARATOR = "#<ab@17943918#@>#"
{% for TEST in TESTCASES %}
{{ TEST.extra }}
{{ TEST.testcode }}
{{ STUDENT_ANSWER }}
{% if not loop.last %}
print(SEPARATOR)
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}В данном случае проверка производится путем запуска программы учащегося на нескольких тестовых значениях. Результат программы учащегося сравнивается с эталонным:
Вишенка на торте для инженерных классов. Arduino и CodeRunner.
Возможности Moodle и модуля CodeRunner позволяют также внедрить мини курс по изучению микроконтроллеров на базе платформы Arduino.
Тонкая настройка вопроса позволила описать стандартные функции и операторы Arduino IDE и импортировать их перед запуском программы учащегося. Сопоставление производится путем простого алгоритма, в котором сравниваются данные полученные на эталонном алгоритме и алгоритме учащегося.
В данном примере в вопрос встроена виртуальная плата Arduino с сайта Tincercad, на которой можно испытать свой код даже без наличия реальной платы на руках.
Ответ учащийся заносит в поле ответа, проверка так же автоматическая, как и в случае с задачами на программирование.
Полная документация на английском языке для описанных выше модулей находится тут Coderunner и тут VPL
Все статьи раздела
- Коменты VK
- Анонимные коменты, G+ или Facebook
If you teach computer science and use Moodle as your LMS, good news: you can now have student submit snippets of code easily using the new Virtual Programming Lab created by ULPGC (University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain).
How to assess computer programming skills in Moodle
According to creator Juan Carlos Rodríguez-del-Pino,
“VPL is a activity module that manage programming assignments and whose salient features are:
- Enable to edit the programs source code in the browser
- Students can run interactively programs in the browser
- You can run tests to review the programs
- Allows searching for similarity between files
- Allows setting editing restrictions and avoiding external text pasting“
The module allows code editing, running tests and more, all within Moodle. It appears that the main thrust of the module is also increasing the opportunities for learning within the Moodle classroom, as it pertains to code and software development.
As of writing, VPL supports nearly 20 programming languages, from Java and Python down to Haskell and Prolog. The environment will let you run complete programs, its performance depending on the server resources available. It is able to provide basic automated checks to ensure code submitted by students runs smoothly.
8 Things Every Educator Should Know About Python
Real reasons for virtual environments
Rodríguez-del-Pino expands:
“The programming assignments of the early courses can present particular difficulties for the student and require frequent monitoring by the teacher. Often, until the work is assessed, students don’t know if it is correct or not. This mode of operation meets the evaluative aspect, but does not provide the student to learn from their mistakes, which lost a significant part of the learning potential associated with the making of an assignment. More over, the evaluation may require considerable time and effort by the teacher due to the number of students, the number of submits required and their complexity.
The availability of a teaching tool to facilitate monitoring and personalized guidance in a continuous learning process allows to reduce the initial difficulties faced by the student. For teachers, the possibility of automating much of the assessment allows them to perform other productive tasks.”
The main website has information in both Spanish and English and is a great resource for seeing what the module can do. Demo the module, or check out these screenshots:
Installing VPL on Moodle LMS
To set up VPL on your Moodle site, you need to install the VPL plugin, which you can do in one click from the Moodle Plugin Directory.
Then you will also need a “VPL-Jail-System,” a special application with full server functionality, but outside of the production server scope. This will prevent any “accidental” misconfiguration of the real server from the VPL.
Resources & References
VPL is compatible with Moodle 2.7 to 3.9
- VPL — Main page at the Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain website
- VPL General documentation
- Download the VPL plugin at moodle.org/plugins/mod_vpl and the VPL-Jail-System here
- In addition, the VPL Question plugin lets you embed the environment in the Moodle Quiz activity
- Find installation instructions here
- Try out a demo here
- Submit questions and issues to Rodríguez-del-Pino directly in the Moodle Forum
What Is A Virtual Moodle Development Environment?
Release of VPL 3.4.1
This is a major release of VPL. The release includes improvements a new features.
Prerequisites
- Moodle 3.5 or higher
- PHP 7.3 or higher
New features of VPL 3.4.1
General functionalities
- Supports the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- To protect you from accidentally lost work when saving files, the system now asks for confirmation when you want to save a submission or configuration older than the current saved.
- Adds Chinese (simplified) translation thanks to the Computer Science Education group of Beijing Technology and Business University
- To improve the identification of directories when downloading student’s submissions add the username field to the user directory name.
Interface
- Icons have been added to easier access to menus and options.
- Users can select themes for the editor and terminal.
- Terminal can be size reduced.
- Edition is available when running.
- The «Submissions list» now includes an «action menu» to the right of each row. The «action menu» of the heading allows accessing «Assessment report», «Download submissions», etc. The «action menu» of each submission allows access to «Submission view», «Previous submissions list», «Grade» and «Copy submission».
- The variation edition interface now allows using the HTML editor.
- Charts are now using the new Moodle API.
Programming languages
- Adds support for Kotlin adding a default run script. Kotlin is detected when using files with the kt file extension. Notice that the Jail servers do not support Snap packages, you must install Kotlin compiler manually or use jail server installer 2.7 or higher.
- Adds support for Minizinc adding a default run script. Minizinc is detected when using files with the mzn file extension.
- Adds support for Groovy adding a default run script. Groovy is detected when using files with the groovy file extension.
- Adds support for error messages from PHP and Perl.
- Adds new indexes to speedup DB access.
- Adds ‘dll’ extension to the list of binary file extensions.
Updating from previous versions to VPL 3.4.1
- VPL 3.4.1 is fully compatible with previous versions.
- Notice that in some cases, after the upgrade, the browser may not show the editor. This is due to the use by the browser of cached JavaScript code instead of the new one. To resolve this issue you must hold the Ctrl key and click the Reload button on the navigation toolbar. This action will instruct the browser to fully reload the page without using cache.
Fixes from 3.4.0
- Fixes a bug that prevents teachers from downloading all students’ submissions as a zip file.
Fixes from 3.3.8
- The teachers with privileges can see the Jail server URL path, now the path is not shown.
- Detects if ws/wss protocol is not available at jail server to selects the correct one.
- Fixes error deleting variations.
- Avoid assigning variations on group activity.
From VPL 3.3.8
- Cron. The cron function is deprecated and has been replaced with a cron task.
- Similarity. This version resolves bugs in the normalization phase of code tokenizer of C, Java, and Python languages. Thanks to LennardF1989 at Github.
- Logs. This version resolves a bug in the URL in Logs. Thanks to Leônidas Brandão at Moodle.
- Submissions. This version resolves a bug in sharing the same files in different submissions that avoid sharing the first file.
From VPL 3.3.7
The bugs fixed and features improve are:
- Gradebook. The patch removes ghost empty grades appearing in the gradebook.
- Navigation. The action menu now appears in many of the activity settings.
- Non-editing teacher role. The patch fixes the allowed functionalities for the «non-editing teacher» role. If you are updating VPL from a previous version to 3.3.6, you must edit the definition of the «non-editing teacher» role setting the «Allow» value at the capability «mod/vpl:submit».
- Activity grade report. The grade reports Improve showing also the automatic evaluation.
- Similarity. The patch fixes the similarity search in group activities.
- Default evaluation program. The patch removes a compilation warning. The warning is harmless but uglies the evaluation output.
- Java. The default java scripts improve by searching and add the jar files to the CLASSPATH. This makes easy the use of java frameworks packed as jar files. The 3.3.7 version fixes a regression bug introduced in V3.3.6 with this feature.
- PHP. The patch fixes the use of the CLI version of PHP. This allows testing PHP programs for the console.
- Python. The patch fixes the detection and use of the tkinter library.
- Scala. The patch fixes a bug running scala programs.
From VPL 3.3.5
The main fixes and small features added are:
- Adds support for MathJax
- Fixes empty grading problem
- Fixes maximum similarity background-color
- Fixes Webservice
- Adds languages scripts from v3.4dev
- Fixes evaluation program
- Improves str i18n with parameter
- Fixes based-on localjailservers order
- Increases default memory to 128Mb (if updating, increase it manually)
- Increases default and maximum number of process to 200 (if updating, increase it manually)
Update notes:
- It is highly recommended to increase default memory to 128Mb
- It is highly recommended to increases the default and maximum number of process to 200 and 400
- If you are getting a hidden menu problem in full window mode. Please, clear your browser cache by doing a hard reload on the editing page. Ctl+Shit+R or Hold Shift and click the Reload button.
From VPL 3.3.4
- The full regular screen mode has been updated to the new standard Boost theme. The new code has been tested on Boost, Clear, More, and Essential themes.
- Fixes an error in background-color of similarity report.
- Tries to reduce terminal high load problem and blinking accuracy.
- Fixes a bug when resetting VPL instances.
- Adds check of directory and file creation. The plugin throws an exception if a file or directory cannot be created.
- Adds PHP file extension to similarity checks. The plugin uses the CPP parser to checks PHP. This is not a full solution, but it is better than nothing.
- The default running and debugging scripts of many programming languages have been fixes to select the first source file of the submission correctly.
Known issues
- Has been found a problem with the change of the grade hide/show state. If you hide the grade in the grade book and then unhide the grade in the VPL plugin, the activity grade state is changed to show, but the state for every student grade is still hidden. As a workaround, you can hide/show grades in the grade book or at the activity setting, do not mix this setting.
- Sometimes the terminal breaks the connection if it receives a huge number of newlines, e.g., running a program with an infinite loop printing newlines.
- There are some minor problems showing source code files using the Essential theme. These problems are about aesthetic decoration and do not reduce the functionalities.
From VPL 3.3.3
This is a bug fix release of VPL3.3.2. The fixes are:
- The evaluation process now asks for accepting certificates if the connection fails.
- Has been fixed a problem with grade form. This problem that appears in some themes and browser combinations leads to a continuous increase in the width of the text area field.
- Has been fixed a bug in the grade setting update. The problem was that VPL does not change the grade hide/show state. As a workaround, the changes would be done in the grade book.
From VPL 3.3.2
VPL 3.3.2 includes fixes for VPL 3.3 and adds a new feature.
This release fixes a bug that prevents the default evaluation program from using a maximum grade value different than the default (10 ).
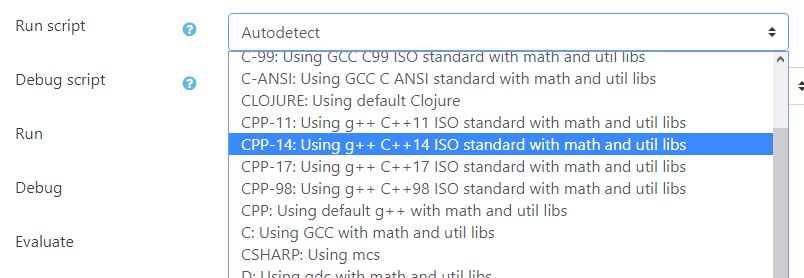
Now you can let the system autodetects the programming language to use based on the filenames extension, or you can select the programming language or debugger to use. For example, you can select from python 2 or python 3, C ANSI or C ISO 11, etc.
From VPL 3.3.1.
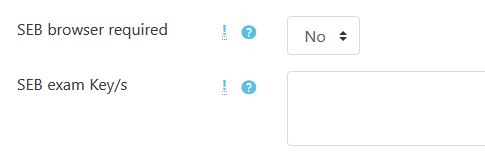
This release includes fixes for VPL 3.3 and support for the Safe Exam Browser.
The Safe Exam Browser (SEB) allows a controlled environment for exams. VPL activities now can require the use of SEB and/or the use of SEB with specific configuration by the «Browser Exam Key». See https://safeexambrowser.org
Has been fixes different bugs in the use of “group work” activities introduced in the V3.3. If you are using V3.3 and “group work” it is recommended to upgrade to V3.3.1.
New and improved features in VPL 3.3
Syntax highlighter
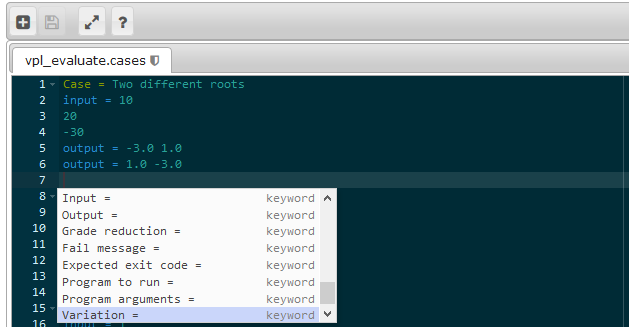
The server-based syntax highlighter has been removed, now all syntax highlighting is done in the browser using the Ace editor. This change extends to more than 50 the number of programming languages supported. This improvement also will reduce the CPU load on the server. It has also been developed the syntax highlighter for the test cases definition file.
Code editor
The editor has been updated using the last Ace code. This update will allow using basic autocompleting in all languages, snipes in many, and syntax checking in a few as PHP, JavaScript, and CSS.
- Now it’s possible to select the editor theme in the plugin setting.
- The menu has now a button to unfold and fold less used options.
- Now, it is possible to delete multiple files using the new multi-delete button.
- Now you can select the code font size. The size selected will be saved as a user preference.
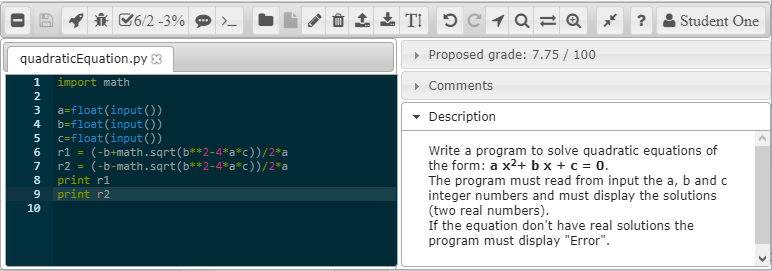
- The activity description is now shown in a “Description” tab. The student can read the activity description while writing code in one window.
- The countdown timer can’t be hidden when the time left is less than five minutes.
- The evaluate button now gives information about the number of automatic evaluations done and the grade reduction definition.
Default evaluation program
The default evaluation program has been improved, trying to accomplish the common requests of the users of VPL. The new instructions are:
- Fail message. This instruction sets the text to show when the case fails. The input and output information is omitted.
- Program to run: This instruction allows to replace, for this case, the student’s program for another one. For example, you can use this instruction to run a static/dynamic analysis of the student code.
- Program arguments. This instruction allows sending information to the student program (or “program to run”) as command-line arguments. Notice that this instruction can be used with the input instruction.
- Expected exit code. This instruction sets the expected exit code of the program case execution. The test case is passed if the exit code match. Notice that the test case can also be passed if an output matches.
Reducing grading marks by the number of automatic evaluations
The grading system has been enhanced with a penalization by automatic evaluation requests. The number of free evaluations can also be configured. Once the student uses free evaluations, the grading system will start to reduce its current mark. The reduction value can be a fixed number or a percent. Every new evaluation will apply a further reduction to the current grade. These reductions are applied to manual and automatic assessments.
Group/team VPL activities redesigned
The pre v3.3 design of the team’s activities has a different drawback that needs to be resolved. The main problem is that if you change a student group after submissions, the submissions may be moved to another group with the student. In the new design, the submissions belong to the group and not to a student. Now it is safe to remove or add students to a group at any moment, and the submissions will remain in the group. The grade is assigned to the members of the group at the moment of been graded.
Check execution servers
Check execution servers now show the actual servers, including the locals, and based on ones. The report now also shows the list of current processes running in the course.
Diff files
The diff files code has been rewritten to support the Ace editor as the way to show files side by side.
Download submissions
The “download submissions” button has been moved to the “submission list” report. It has been added a new button to download all submissions, including old versions. The zip file format has changed to give more information, including the full name of the student, time of submission, and evaluation details.
Reducing the size of space used by submission
Due to how the submitted files are managed: created or deleted but not modified, this version includes the reuse of files of the previous submission. This is achieved by reusing (linking) files of the last submission with the same contents as new ones.
Using GUI programs
If you are planning to use languages with GUI capabilities as Java, C#, PHP, etc. it is highly recommended to use vncaccel to reduce the start time of the programs (see the release of execution server 2.2.2)
Testing VPL
VPL is now tested using travis-ci. The tests include PHP Lint, PHP Mess Detector, Moodle Code Checker, CSS Lint, JSHint, PHPUnit tests, and specific tests for the default Student’s program tester. These tests alone do not correct bugs in the code but are a first step to detect them.
Translations
Has been added the Brazilian translation thanks to Gabriel P. Silva UFRJ
Bug fixes
- Adds timemodified field for compatibility with Moodle.
- Fixes drop and paste problems.
- Uses own copy of Jquery and Jquery-UI, this removes version problems.
- Fixes issues reordering files.
- Removes for students to view the hints of grade reduction at the end of the title line of grader comments. The students could see clues in HTML before JavaScript processes it.
- Fixes the problem that avoids saving new submissions when the name of requested files is changed.
- Has been modified the table vpl_jailservers to remove the key of the server URL. This key with a field of 255 chars generates an error that aborts the installation of VPL due to problems for reaching the limits of key size in MySQL with some charsets.
Updating VPL
If VPL is updated, it is highly recommended to clean the browser’s cache. The cache can mix JavaScript files from the previous version and generate errors for a while.
IMPORTANT NOTE!: If you update or restore activities to VPL 3.3 or higher from a previous version and this action include teams’ activities with submissions, you need to go to the list of “Virtual Programming Lab” activities and click on the “Check all” button (at the bottom of the report). This process will assign groups to the submissions.