1
Написано
lex6630
,
24 May 2014
·
34260 Просмотров
PicKit3_RUS
Доброго Времени Суток! Всем!
Качаем и Тестируем ! Прогу PicKIT3_RUS!
ИНСТРУКЦИЯ Для установки !
1 Скачиваем
2 Копируем В Папку С Установленной Английской Версией Проги
3 Запускаем PICkit3_ru И Улыбаемся!
И Сообщаем О Багах Перевода ! ТАК КАК переводил в основном ГУГЛЕ ТРАНСЛЕЙТОМ.
С Пециально для Сайта BEZKZ.SU
C Уважением Жека
Прикрепленные файлы
-
PICkit3_ru.rar (176.1К)
Количество загрузок:: 16292
- Nikolai4, kroxx, jody и 4 другим это нравится
Для данной записи нет trackbacks.
Многие разработчики в своей работе используют оболочку PICkit2 Programming.
Внутренняя идеология PICkit3 отличается от PICkit2, поэтому по протоколам работы PICkit2 и PICkit3 не совместимы и PICkit3 не может работать с оболочкой PICkit2 Programming.
Microchip выпустила ПО «PICkit3 Programmer Application and Scripting Tool», которое позволяет использовать PICkit3 в режиме совместимости c PICkit2.
ВАЖНО!
Прошивки PICkit3 для работы в «PICkit3 Programmer Application and Scripting Tool» и MPLAB IDE отличаются. Вернуть PICkit3 в режим совместимости с MPLAB IDE можно только из программы «PICkit3 Programmer Application and Scripting Tool».
«PICkit3 Programmer Application and Scripting Tool» поставляется в исходных кодах:
PICkit3 Programmer Application and Scripting Tool v3.10
После установки «PICkit3 Programmer Application and Scripting Tool» необходимо загрузить специальную прошивку в PICkit3.


Выбираем файл прошивки:

Загрузка прошивки в PICkit3

Теперь PICkit3 может работать в аналогичной программатору PICkit2 оболочке.

Работает автоопределение микроконтроллеров в рамках семейств

Логический анализатор аналогичен (см. Утилиты UART & Logic Tool )

Однако инструмент UART Tool еще не реализован.
Возврат в режим совместимости с MPLAB IDE
Для возврата в режим совместимости с MPLAB IDE предусмотрен специальный пункт:



-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
PICkit™ 3 Starter Kit
User’s Guide
2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS41628B
Related Manuals for Microchip Technology PICkit 3
Summary of Contents for Microchip Technology PICkit 3
-
Page 1
PICkit™ 3 Starter Kit User’s Guide 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B… -
Page 2
Total Endurance, TSHARC, UniWinDriver, WiperLock, ZENA and Z-Scale are trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries. SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. GestIC and ULPP are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Germany II GmbH &… -
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Data EEPROM Memory …………….. 34 2.16 Programming Basics …………….34 2.16.1 MPASM™ Assembler Operation …………34 2.16.2 XC8 Operation ………………34 2.16.3 Numbers in the Assembler …………..36 2.16.4 Numbers in the XC8 Compiler …………… 36 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 3…
-
Page 4
C Language ……………….57 Lesson 5: Variable Speed Rotate …………59 3.6.1 Introduction ………………..59 3.6.2 Hardware Effects ……………….59 3.6.3 Summary ………………..59 3.6.4 New Registers ………………59 3.6.5 New Instructions ………………59 3.6.6 Assembly ………………..61 3.6.7 C Language ……………….61 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 4… -
Page 5
3.12.5 New Instructions ………………80 3.12.6 Assembly Language …………….81 3.12.7 C language ……………….. 82 3.13 Lesson 12: Look-up Table …………..83 3.13.1 Intro ………………….. 83 3.13.2 Hardware Effects ………………. 83 3.13.3 Summary ………………..83 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 5… -
Page 6
3.14.6 Assembly Language …………….93 3.14.7 C Language ……………….94 Appendix A. Block Diagram and MPLAB® X Shortcuts ® Useful MPLAB X Shortcuts …………..96 Finding Register Names …………….. 96 PIC MCU Assembly Coding Practices: ……….. 96 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 6… -
Page 7: Introduction
The manual layout is as follows: • Section Chapter 1. “Overview” • Section Chapter 2. “PIC® MCU Architecture” • Section Chapter 3. “Lessons” • Appendix A. “Block Diagram and MPLAB® X Shortcuts” 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 7…
-
Page 8: Conventions Used In This Guide
Curly brackets and pipe Choice of mutually exclusive errorlevel {0|1} character: { | } arguments; an OR selection Ellipses… Replaces repeated text var_name [, var_name…] Represents code supplied by void main (void) user { … 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 8…
-
Page 9: Warranty Registration
For the latest information on using other tools, read the tool-specific Readme files in the Readmes subdirectory of the MPLAB IDE installation directory. The Readme files contain update information and known issues that may not be included in this user’s guide. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 9…
-
Page 10
MPLAB IDE, MPLAB SIM simulator, MPLAB IDE Project Manager and general editing and debugging features. • Programmers – The latest information on Microchip programmers. These include the MPLAB PM3 device programmers and PICkit™ 3 development programmers. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 10… -
Page 11: Customer Support
Technical support is available through the web site at: http://support.microchip.com DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY Revision A (October 2012) • Initial Release of this Document. Revision B (November 2012) • Revised Sections 3.5.3, 3.5.4.1.1, 3.11.3.2, Table 3-15. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 11…
-
Page 12
PICkit™ 3 Starter Kit User’s Guide NOTES: 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 12… -
Page 13: Highlights
This new LPC board is still backwards compatible. Bridging the old pins to the new pins will restore functionality. INCLUDED ITEMS 1. 1x PICkit 3 Programmer 2. 1x Micro USB cable 3. 1x LPC Board (Part Number : DM164130-9) 4. 1x PIC16F1829-I/P 5.
-
Page 14: The Low Pin Count Board
PIC devices that come with the board. TABLE 1-1: PIN ASSIGNMENTS Device LEDs <DS4:DS1> Switch – SW1 Potentiometer – RP1 PIC16F1829 <RC4:RC0> PIC18F14K22 <RC4:RC0> 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 14…
-
Page 15: Software Overview
LEDs in succession. Press the push button (SW1), and the sequence will reverse. Rotate the potentiometer (RP1), and the light sequence will blink at a different rate. This demo program is developed through the first seven lessons in this guide. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 15…
-
Page 16
PICkit™ 3 Starter Kit User’s Guide NOTES: 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 16… -
Page 17: Chapter 2. Pic ® Mcu Architecture
Decode & Decode & Start-up Timer Control Control Control Power-on OSC1/CLKIN Reset Timing Timing Timing Watchdog W Reg OSC2/CLKOUT Generation Generation Generation Timer Brown-out Reset Internal Internal Internal Oscillator Oscillator Oscillator Block Block Block 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 17…
-
Page 18
OSC1/CLKIN INTRC Oscillator Figure 2-1 PORTC MCLR PORTD PORTE Timer0 Timer1 Timer2 Timer4 Comparators Timer6 Latch 10-Bit MSSP ECCP1 ECCP2 ECCP3 CCP4 CCP5 EUSART Note See applicable chapters for more information on peripherals. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 18… -
Page 19
10-bit Note 1: RA3 is only available when MCLR functionality is disabled. OSC1/CLKIN and OSC2/CLKOUT are only available in select oscillator modes and when these pins are not being used as digital I/O. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 19… -
Page 20: Data/Program Bus
The enhanced PIC16 has a 14-bit wide word. An opcode is interpreted by the processor and is unique to each instruction. The opcodes are broken into four formats: 1. Byte oriented 2. Bit oriented 3. Literal 4. Control 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 20…
-
Page 21: Byte
Literal operations contain the data operand within the instruction. Both architectures use an 8-bit intermediate value. The rest of the bits are reserved for the opcode. EXAMPLE 2-4: MOVLW ‘A’ This moves the ASCII value of ‘A’ (0x41) into WREG. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 21…
-
Page 22: Control
Instructions that dictate what address the PC will select in program memory are called control instructions. This would include call, goto, and branch. Each has a unique word length. Please refer to the “Instruction Set Summary” chapter in any PIC device data sheet for more information. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 22…
-
Page 23
= appropriate FSR k = 6-bit immediate value FSR Increment instructions OPCODE n m (mode) ADDFSR FSR1, 3 n = appropriate FSR m = 2-bit mode value OPCODE only OPCODE MOVIW ++FSR0 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 23… -
Page 24
OPCODE n<10:0> (literal) BC MYFUNC OPCODE n<7:0> (literal) There are some subtle differences between the block diagrams in Figure 2-1 Figure 2-3. This document will point out a few of the important ones. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 24… -
Page 25: Stack Level
Configuration bits are programmed in a special way, as seen in the lesson source files. 2.12.3 Device ID The Device ID contains the read-only manufacture’s ID for the PIC MCU. The PIC16F1829 ID is stored in DEVICEID and the PIC18F14K22 is stored in DEVID1 and DEVID2. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 25…
-
Page 26: Revision Id
2-7. PIC18 devices also have two interrupt vectors, whereas the enhanced PIC devices only have one. A stark difference is that the PIC18 has no concept of pages, whereas the enhanced core has its program memory split into different pages. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 26…
-
Page 27: User Id
The data memory layout of the two device families is perhaps the most significant. Data memory on both families can be split into four types: 1. Core Registers 2. Special Function Registers 3. General Purpose RAM 4. Common RAM 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 27…
-
Page 28: Core Registers
2. 20 Special Function Registers (SFR) 3. Up to 80 bytes of General Purpose RAM (GPR) 4. 16 bytes of shared RAM (accessible by any bank) Figure 2-8 shows the above information on the enhanced PIC16. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 28…
-
Page 29
RAM without the need to switch banks each time the byte is used. Figure 2-9 shows the first eight banks on the PIC16F1829. Notice how the top 12 core registers are accessible from every bank, as are the 16 bytes of common RAM. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 29… -
Page 30
FIGURE 2-9: PIC16F1829 MEMORY MAP – THE CORRECT BANK MUST BE SELECTED BEFORE WRITING/READING FROM A REGISTER BANK 0 BANK 1 BANK 2 BANK 3 BANK 4 BANK 5 BANK 6 BANK 7 000h INDF0 080h INDF0 100h INDF0 180h INDF0 200h INDF0… -
Page 31
“Access RAM” and is composed of GPRs. The upper half is where the device’s SFRs are mapped (Bank 15). When going through the assembly lessons, the reader will notice the absence of bank switching. Figure 2-10 Figure 2-11 show this improved mapping scheme. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 31… -
Page 32
Bank 13 DFFh E00h = 1110 Bank 14 EFFh F00h Unused = 1111 F53h Bank 15 F5Fh F60h FFFh Note 1: SFRs occupying F53h to F5Fh address space are not in the virtual bank. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 32… -
Page 33
Bank 15 and do not require banking since this bank is covered by the Access Bank. Switching banks in the enhanced mid-range core requires two instructions, so this could potentially save a great number of instructions in the overall program. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 33… -
Page 34: Data Eeprom Memory
The compiler does all of the translation involved, which is needed to take the high-level code down to a level in which the PIC device understands. Figure 2-13 explains how this is done. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 34…
-
Page 35
The assembly underneath it contains twice as much code, and includes the PIC MCU specific instructions to achieve the desired result of the ‘C’ above it. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 35… -
Page 36: Numbers In The Assembler
BSR directly, to avoid the possi- bility of human error. 2.17.2 cblock EXAMPLE 2-5: cblock [address] Variable endc This is used to define a block of variables starting at address address. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 36…
-
Page 37: Org (Addr)
The angled brackets (< >) indicate that the file can be found in the library folder of the assembler. Double quotes ( “ “) indicate that the include file is in the current working directory. The exact locations can be changed in the IDE. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 37…
-
Page 38: Microchip Technology Inc. Ds41628B
PICkit™ 3 Starter Kit User’s Guide NOTES: 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 38…
-
Page 39: Lessons
Please see the getting started videos that are linked to on the Start Page inside of the ® MPLAB X IDE. Refer to the MPLAB IDE Quick Start Guide (DS51281) (http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/51281d.pdf) as a getting started guide for MPLAB 8.XX. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 39…
-
Page 40
LESSONS Lesson New Modules New Concepts New Registers New Instructions 1 Hello World Latch Port Basics of PIC MCU TRISC PORTC LATC CLRF programming 2 Blink Delay OSCCON MOVLW DECFSZ GOTO MOVWF ACCESS RAM Banking Oscillator 3 Rotate Bit Check STATUS BTFSC LSRF… -
Page 41: Lesson 1: Hello World (Turn On An Led)
An easy way to remember this is that the number ‘1’ looks like the letter ‘I’ for input, and the number ‘0’ looks like the letter ‘0’ for output. The reader should always write to the latch and read from the port. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 41…
-
Page 42: New Instructions
This clears an entire register. It is useful during initialization to turn off all attached peripherals such as LEDs. EXAMPLE 3-3: clrf LATC Before Instruction: LATC = b’11011000’ After Instruction: LATC = b’00000000’ 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 42…
-
Page 43: Assembly
This is a label. Labels are assigned the same memory address as the opcode immedi- ately following the label. Labels can, and should be, used in your code to specify the destination for call, goto and branch instructions. Banksel TRISC 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 43…
-
Page 44
Configuration Word does. The most important different distinction here is the lack of having to change banks. All of the SFRs are in the Access Bank and do not require a banksel statement. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 44… -
Page 45: C Language
It will sit here forever. The continue statement is not required for correct operation. Notice how few lines were needed to replicate the same behavior as the assembly version. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 45…
-
Page 46
PICkit™ 3 Starter Kit User’s Guide 3.2.7.2 PIC18 There is nothing different from the PIC16 version, except for the Configuration Words. For more information, see the PIC18F14K22 data sheet. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 46… -
Page 47: Lesson 2: Blink
Makes code modular bra label Unconditional Make code modular goto label 3.3.5.1.1 movlw An 8-bit literal, or rather constant, is loaded into the Working Register (W) movlw 0x5A After instruction: W = 0x5A 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 47…
-
Page 48: Assembly
Purpose Toggle Bit Blink LED 3.3.5.2.1 This will invert the value of a bit in the target register. 3.3.6 Assembly 3.3.6.1 ENHANCED MID-RANGE EXAMPLE 3-8: movlw b’00111000′ ;set cpu clock speed movwf OSCCON 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 48…
-
Page 49
When a program occurs, the already fetched instruction located after the goto or bra is not executed. Instead, a NOP is executed while the instruction located at the des- tination is fetched. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 49… -
Page 50: C Language
XORs the pin with ‘1’ to create the toggling affect. If the optimization of the compiler is heightened or lowered, the delay will increase or decrease since the compiler produces different code for each optimization level. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 50…
-
Page 51: Introduction
If/Else statements btfsc 3.4.5.1.1 BTFSC This tests a specific bit in a specific register. If it is clear (value of ‘0’), then the next instruction is skipped. This is useful for performing IF-ELSE statements. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 51…
-
Page 52: Assembly
;did the bit rotate into the carry (i.e. was DS1 just lit?) LATC, 3 ;yes, it did and now start the sequence over again by turning on DS4 goto MainLoop ;repeat this program forever 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 52…
-
Page 53
MainLoop ;nope, repeat this program forever LATC, 3 ;yes, it did and now start the sequence over again by turning on DS4 STATUS, C ;clear the carry goto MainLoop ;repeat this program forever 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 53… -
Page 54: C Language
‘C’, as described in Example 3-18. EXAMPLE 3-18: LATC >> = 1; This is equivalent as: LATC LATC >> 1; Or rather: lsrf LATC,F ;shift the LEDs and turn on the next LED to the right 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 54…
-
Page 55: Lesson 4: Analog-To-Digital Conversion
TRIS bit must be set to Input mode in order to allow external control of the voltage on the pin. This lesson sets RA4 as an analog input, since the POT will vary the voltage. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 55…
-
Page 56
ADRESH. The program, however, will only use the top four MSbs in ADRESH. The ADNREG/ADPREG bits select the ADC reference, which may be either V or a separate reference voltage on V 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 56… -
Page 57
TABLE 3-21: AFTER SWAPF Registers After swapf WREG B’0011-1010’ ADRESH B’1010-0011’ FIGURE 3-3: SWAPF DIAGRAM 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 ADRESH WREG 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 57… -
Page 58
Here, the ADRESH register is shifted to the right by four spaces. For an unsigned vari- able, shifts are logical. For example: TABLE 3-22: ADRESH BEFORE SHIFT ADRESH – before shift Bit # MSb (7) LSb (0) value 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 58… -
Page 59
MSbs are being grabbed, meaning that there needs to be a great swing in voltage change to affect the topmost MSbs. As an added exercise, try using the lower nibble (bits 0 through 3) and assign them to LATC. The LEDs will change more frequently. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 59… -
Page 60: Introduction
The call is equivalent to adding functions in ‘C’. They are convenient since they allow the designer to create subroutines which can then be called from a main function. This improves the memory use efficiency and readability of your program. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 60…
-
Page 61
This is a quick test if a register is ‘0’ or not. Use this instruction on the PIC18 instead of the XORWF used on the PIC16, since this saves a few instructions. For example: 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 61… -
Page 62
ADC function is in program space and execute code. It will then return a single value and assign it to delay. A key note is that any function that is instantiated after the main function must have a prototype. unsigned char adc(void); //prototype 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 62… -
Page 63: Lesson 6: Debounce
The switch on the LPC Demo Board does not bounce much, but it is good practice to debounce all switches in the system. 3.7.2 Hardware Effects When the switch is held down, DS1 will be lit. When the switch is not held down, all LEDs are OFF. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 63…
-
Page 64: New Registers
Read-modify-write operations on the LATC register will read and write the latched output value for PORTC. 3.7.7 PIC18 Nothing new. 3.7.8 C Language Nothing new. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 64…
-
Page 65: Lesson 7: Reversible Variable Speed Rotate
Rotate LEDs to Left Get ADC Measurement Left Direction Check if ADC Result is ‘0’ Delay Using ADC Result Is Switch Down? Delay 5ms Is Switch Still Down? W as It Held Down Previously? Change Direction 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 65…
-
Page 66: New Registers
The PIC18 version is similar, but instead uses rlncf instead of lslf. 3.8.6.2 PIC18 The PIC18 always has to make sure that the carry bit is cleared once it is checked, otherwise more than one LED may become lit. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 66…
-
Page 67: C Language
Notice how the bytes, delay and direction, were declared inside of main. These cannot be modified anywhere outside of main. Also, notice how check_switch returns an unsigned char byte to the main loop. In ‘C’, only one variable can be returned. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 67…
-
Page 68: Lesson 8: Pulse-Width Modulation (Pwm)
It is recommended that the reader refer to the Capture/Compare/PWM section in the data sheet to learn about each register above. This lesson will briefly cover how to setup a single PWM. Figure 3-8 summarizes how the PWM waveform is setup: 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 68…
-
Page 69
PWM RESOLUTION 4 PRx Resolution —————————————- — bits 2 Two conditions must hold true for this lesson: 1. 10 bits of resolution 2. No flicker in LED 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 69… -
Page 70
Figure 3-9, and that the frequency did not change. FIGURE 3-10: GREATER PULSE WIDTH TABLE 3-29: Instruction English Purpose And a literal with WREG Masking values andlw 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 70… -
Page 71: Assembly
A movwf or iorwf would not work, since it would not preserve the settings applied in the initialization. 3.9.5.2 PIC18 The PIC18 substitutes the rrncf instruction with the lsrf instruction above, although a rrcf would also work. 3.9.5.3 C LANGUAGE Nothing new. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 71…
-
Page 72: Lesson 9: Timer0
Using a counter provides a convenient method of measuring time or delay loops as it allows the processor to work on other tasks rather than counting instruction cycles. 3.10.4 New Registers 3.10.4.0.1 Enhanced Mid-range TABLE 3-30: ENHANCED MID-RANGE NEW REGISTER Register Purpose OPTION_REG Timer0 and pull-up/INT configuration 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 72…
-
Page 73: Assembly
Timers greatly simplify delay loops and are great for events that need precise timing. 3.10.5.2 PIC18 The only differences are that the initialization is slightly different and the relative branch uses “$-2”. 3.10.6 C Language Nothing new. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 73…
-
Page 74: Lesson 10: Interrupts And Pull-Ups
WREG, STATUS, and BSR registers. The FSR and PCLATH registers are saved only in the enhanced mid-range devices. The PIC18 requires a retfie, fast instruction execution to restore the context. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 74…
-
Page 75
PIC MCU. Since it is a weak pull-up, the designer can easily override this internal setting by using an external resistor, typically in the range of 1k-10k, to change the pin’s state. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 75… -
Page 76: New Registers
3.11.4.3.2 RCON The RCON register is used to detect what caused the PIC MCU to reset as well as enable/disable priority interrupts. This lesson shows how to use this register to disable priority interrupts. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 76…
-
Page 77: New Instructions
ISR can be successfully left. The retfie instruction exits the ISR by restoring the saved context, re-enables the GIE bit and returns to the instruction following the last instruction executed when the interrupt occurred. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 77…
-
Page 78: C Language
ISR(void) This is a special name and is reserved only for the ISR. The PIC18 can have two, but this lesson uses only one as shown above. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 78…
-
Page 79: Lesson 11: Indirect Addressing
– information in the data memory space can be addressed in several ways. For most instructions, the addressing mode is fixed. Other instructions may use up to three modes, depending on which operands are used and whether or not the extended instruction set is enabled. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 79…
-
Page 80
SFR space, but are not physically implemented. Reading or writing to a particular INDF register actually accesses its corresponding FSR register pair. A read from INDF1, for example, reads the data at the address indicated by FSR1H:FSR1L. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 80… -
Page 81: New Registers
New Instructions 3.12.5.1 BOTH TABLE 3-37: NEW INSTRUCTIONS FOR BOTH DEVICES Instruction English Purpose Increment Add a value of one incf 3.12.5.1.1 incf This increments a file register by a value of one. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 81…
-
Page 82: Assembly Language
FSR0 will point to the next byte in the Queue register. In this case, it is the second ADC reading. rrcf RunningSum,w ; divide by 2 and copy to a version we can corrupt A rotate or shift to the right is a quick method to divide by two. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 82…
-
Page 83: C Language
LED display. There is a great deal of information about pointers for the ‘C’ language on the web. It is recommended that the reader look there for additional information. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 83…
-
Page 84: Lesson 12: Look-Up Table
For the PIC18, the PC contains another register called PCU. This register contains the PIC18’s PC<20:16> bits; it is also not directly readable or writable. Updates to the PCU register are performed through the PCLATU register. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 84…
-
Page 85
The enhanced core assembly uses a $-1 to go back one valid program instruction in program memory. Likewise, the PIC18 uses a $-2. FIGURE 3-18: FIVE SITUATIONS FOR THE LOADING OF THE PC ON THE ENHANCED MID-RANGE CORE 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 85… -
Page 86: New Registers
3.13.5.2.2 TABLAT The Table Latch (TABLAT) is an 8-bit register mapped into the SFR space. The Table Latch register is used to hold 8-bit data during data transfers between program memory and data RAM. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 86…
-
Page 87: New Instructions
This instruction is used to read the contents of program memory. To address the program memory, a three-byte pointer called Table Pointer is used. All three bytes of Table Pointer must be setup before executing the * instruction. tblrd 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 87…
-
Page 88: Assembly Language
In addition, there are some nuances to be aware of, should the table cross a 256-word boundary. The Program Counter is 15 bits wide, but only the lower eight bits are repre- sented in PCL. The remaining five bits are stored in PCLATH. However, an overflow of 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 88…
-
Page 89
This method uses special SFRs that are used strictly for Flash program memory reads/writes. Writing to program memory is more complex and restrictive, but reading a single word from program memory is straightforward. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 89… -
Page 90
Table reads and table writes move data between these two memory spaces through an 8-bit register (TABLAT). The table read operation retrieves one byte of data directly from program memory and places it into the TABLAT register. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 90… -
Page 91: C Language
Like usual, the ‘C’ implementation is rather easy and much more readable. A look-up table is achieved by creating an array and declaring it as a constant, so that the compiler places it into program space and not data space. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 91…
-
Page 92
= adc(); //get the ADC value from the POT adc_value >> = 4; //save only the top 4 MSbs LATC = gray_code[adc_value]; //convert to Gray Code and display on the LEDs 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 92… -
Page 93: Lesson 13: Eeprom
Read EEPROM and move data onto LEDs Sleep Switch pressed/released Check if ADC result is ‘0’ Debounce Not down Still down Take ADC reading and move it onto LEDs Write ADC value to EEPROM 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 93…
-
Page 94: New Registers
Much like the previous lesson, EECON1/EEADRL/EEDAT is used throughout for all memory writes/reads. An EEPROM write requires that a unique sequence is written to the EECON2 virtual register. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 94…
-
Page 95: C Language
C Language 3.14.7.1 BOTH There are two functions that the XC8 compiler provides, which greatly simplify EEPROM reads and writes. EXAMPLE 3-56: eeprom_read(<addr>) eeprom_write(<addr>,<value>); Use this to read and write single bytes from EEPROM. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 95…
-
Page 96
PICkit™ 3 Starter Kit User’s Guide NOTES: 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 96… -
Page 97
PICkit™ 3 STARTER KIT USER’S GUIDE ® Appendix A. Block Diagram and MPLAB X Shortcuts FIGURE A-1: LOW PIN COUNT BOARD SCHEMATIC 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 95… -
Page 98
• Labels should be descriptive and should have a colon. • Do not hard code addresses. Use clbock/endc (non-linker) or #pragma udata sections (linker) to allow assembler or linker to assign variable addresses. 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 96… -
Page 99: Appendix A. Block Diagram And Mplab® X Shortcuts
Block Diagram and MPLAB® X Shortcuts EXAMPLE A-1: Bad: #define flowRate 0x20 flowRate equ 0x20 Good: Cblock 0x20 flowRate flowTotal endc 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 97…
-
Page 100
PICkit™ 3 Starter Kit User’s Guide NOTES: 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 98… -
Page 101
Thailand — Bangkok Tel: 86-29-8833-7252 Tel: 66-2-694-1351 Toronto Fax: 86-29-8833-7256 Fax: 66-2-694-1350 Mississauga, Ontario, Canada China — Xiamen Tel: 905-673-0699 Tel: 86-592-2388138 Fax: 905-673-6509 Fax: 86-592-2388130 China — Zhuhai Tel: 86-756-3210040 11/14/12 Fax: 86-756-3210049 2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS41628B-page 99… -
Page 102
Mouser Electronics Authorized Distributor Click to View Pricing, Inventory, Delivery & Lifecycle Information: Microchip DM164130-9…
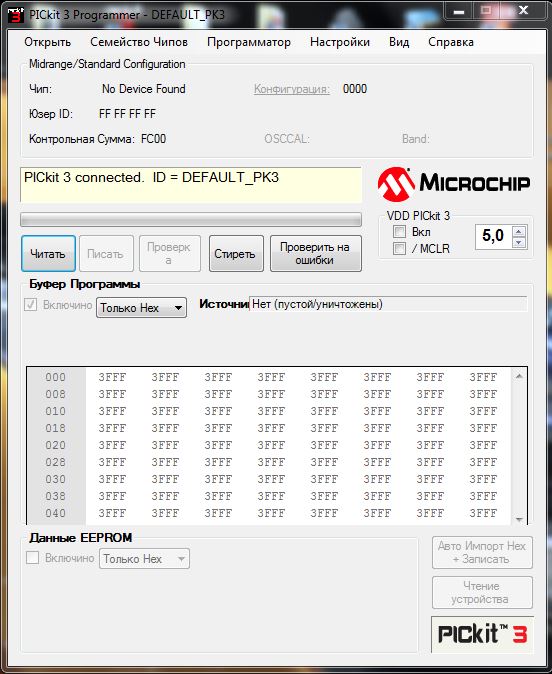
Утилита PICkit3 – специализированное программное обеспечение компании Microchip Technology Inc., предназначенное для работы с одноимённым программатором этой же марки. Приложение автоматически определяет подключенные к ПК на ОС Windows устройства, выбирает для них драйвера и выводит полную информацию. В списке техники, которая программируется с помощью PICkit3 и программатора – регуляторы напряжения, потенциометры, датчики температуры и контроля питания батарей, линейные и импульсные регуляторы напряжения, Ethernet и IrDA контроллеры.
Возможности программы
Получить утилиту можно вместе с программатором PICkit3, позволяющим устанавливать на контроллеры программы размером до 512 Кбайт. Владельцам старых версий устройства придётся скачать программу с сайта компании. Список её функций включает:
- проверку подключённого устройства на возможности чтения и записи, делать которую рекомендуется проводить для каждой новой техники;
- создание HEX-таблицы и считывание данных из энергонезависимой памяти EEPROM;
- просмотр всех данных и операций в окне приложения;
- отладку микросхем в режиме работы ICD;
- программирование микросхем PIC и dsPIC.
Ввод команд выполняется из командной строки Windows. Программа поддерживает большинство микроконтроллеров Microchip. При появлении новых микросхем можно получить возможность работы с ними, скачав обновления с ресурса разработчиков. А ещё утилита позволяет совместить программатор с различными автоматизированными системами и редакторами кода сторонних разработчиков.
Ключевые особенности
Список преимуществ утилиты включает:
- простой интерфейс – в верхней части главного окна отображаются сведения о модели подключённой микросхемы, команды и инструменты, внизу – окно для считывания EEPROM;
- минимальные требования к аппаратной части и операционным системам – программа запустится даже на ПК с ОС Windows XP с SP2, на котором установлено меньше 1 ГБ оперативной памяти;
- бесплатное распространение программы и её обновлений.
Среди минусов можно отметить отсутствие русскоязычного интерфейса – однако вся информация понятна и на английском языке. Особенно, пользователям, которые обладают достаточной квалификацией для программирования микросхем. Ещё один недостаток – не всегда стабильную работу программы, хотя все её версии не тестовые, а уже готовые к использованию.
Перед тем как скачать PICkit3 бесплатно на русском языке, прочитайте характеристики софта и требования к вашему устройству.
Похожие программы
Время на прочтение
3 мин
Количество просмотров 34K
Итак, без чего не обходится практически любое устройство на микроконтроллере? Правильно, без микроконтроллера! Но, увы, не получится его запрограммировать без программатора (если это конечно не Arduino).
Итак, рассмотрим внутрисхемный программатор-отладчик PicKit 3,
счастливым
обладателем коим являюсь я.
Описание функциональности данного девайса я описывать тут не буду, по скольку вы сами можете почитать вот тут http://pickit2.ru/doku.php/что.такое.pickit3 что вы собственно уже и сделали. А моей целью является — донести до вас информацию с точки зрения обыкновенного пользователя.
Заказывая сей девайс в интернет магазине я долго думал, размышлял PicKit2 или PicKit3. В то время я мало знал об этих программаторах, разве что то, что они работают через USB и являются внутрисхемными, плюс можно отлаживать программу непосредственно в микроконтроллере с помощью PicKit 2 и 3.
Внутрисхемным программированием ICSP (In-circuit serial programming) прямо на конечном устройстве, который мы собираем на PIC контроллере. И нам не придётся вытаскивать его из программатора запрограммированный микроконтроллер и втыкать его обратно в конечную схему. А отлаживать его было бы как сложно в таких условиях? Так что ICSP вещь очень удобная и практичная. Единственно нужно только предусмотреть разъём ICSP/ICD на конечном устройстве для подключения программатора.
Об отличиях PicKit 3 от Pickit2 я знал мало, но рассуждал логически так. PicKit 2 проверенный временем и людьми, надёжный и удобный. А PicKit 3 должно быть следующая версия, более доработанный, более мощный, современный и функциональный чем PicKit 2. К тому же PicKit 3 стоил не сильно дороже чем программатор предыдущей версии. И хотя функциональности Пиккит 2 мне полностью было предостаточно в итоге было решено купить PicKit 3 с расчётом на будущее, так сказать «на вырост».
Вот прислали почтой мне эту красивую коробочку. Внутри сам непосредственно программатор, Провод USB-miniUSB. Пара каких то бумажек, среди которых плакат с объяснением как и куда подключать программатор и диск с MPLAB 8.36 и примерами. Естественно всё на английском.
Достаём, подключаем к компу через прилагаемый шнурок. Компьютер определяет подключенное HID совместимое устройство. Это означает, что дтов для программатора не нужно. Загораются 3 огонька — вроде работает.
Далее, устанавливаем MPLAB IDE 8.38. С более новыми версиями возникнут определённые проблемы, до тех пор, пока в новых версиях не устранят баг. О проблемах и их решении в новых версиях я расскажу чуть позже.
Установили, запускаем! Лезем в меню Programmer — Select Programmer — Pickit 3. Мплаб должен определить программатор, но если он не подключен к контроллеру, или на контроллер не подано питание то он ругнётся об этом. При первом подключении Мплаб сказал что нашёл в инете более новую прошивку для программатора и предложил её загрузить и закачать — соглашаемся!
Хотелось бы отдельно заострить внимание на питании микроконтроллера. Тут возможны 2 варианта:
1. питание от внешнего источника;
2. питание от программатора.
Если внешнего источника питания у вас нет, то выбираем в настройках Programmer — Settings… и идём на вкладку Power. Ставим галочку и меняем значение величины напряжения если требуется.
Большинству контроллеров PIC нормально будет 5В., но в некоторых случаях контроллеры могут питаться от более низкого напряжения и установив на него 5В можно его повредить. Если не уверены — лучше всего ознакомиться со спецификацией контроллера.
Если вы решите питать схему от внешнего источника, и при этом подключите напряжение от пиккита, то ничего страшного не произойдёт — программатор замерит напряжение и если на нём будет +5в. то он не даст пропустить напряжение через себя и не подаст дополнительного питания на контроллер, не смотря на установленную настройку в МПлабе. По крайне мере так написано в даташите, но у меня, на всякий случай питание внешнее и питание от программатора расключены фиксируемой кнопкой.
Теперь о бочке дёгтя в ложке мёда. Недостатков, пока что, у PicKit3 больше чем достоинств по сравнению с PicKit2. Начнём с того, что для второго пиккита есть русская документация, а для третьего я не нашёл. Кроме того, программировать через PICkit 3 можно только в среде MPLAB IDE, а для второго пиккита кромеMPLAB IDE есть специальная компактная и удобная утилита PICkit 2 Programmer. И в завершении хочу сказать что в Linux (не всем же под виндой сидеть) я не нашёл вооообще программ, для программирования через PICkit 3, а для PICkit 2 есть. И хотя в будущем эти проблемы решаемы, но сейчас пока по моему скромному мнению этот программатор не стоит своих денег и по этому лучше, надёжней и дешевле будет приобрести PICkit 2.