Материал из BikesWiki — энциклопедия японских мотоциклов
Перейти к: навигация, поиск
Kawasaki KLE500
Ниже представлены прямые ссылки на скачку сервисной документации.
- Сервисный мануал (Service Manual) на Kawasaki KLE 500
Обзор модели
- Kawasaki KLE 500
Источник — «https://bikeswiki.ru/index.php?title=Kawasaki_KLE500:_мануалы&oldid=9632»
Категория:
- Сервисная документация
Перед вами файл pdf, где представлена инструкция (руководство) на русском для KAWASAKI KLE500 (2004). Вы можете скачать ее либо изучить в онлайн режиме.
Подробные сведения об инструкции:
Устройство из раздела: мотоцикл
Бренд-производитель: KAWASAKI
Наименование модели: KAWASAKI KLE500 (2004)
Инструкция на английском языке
Файл: pdf
Размер файла: 7,71 MB
Скачать инструкцию к HARPER HDT2-1110
ЗАГРУЗИТЬ
Просмотр инструкции онлайн

Руководство на английском языке по техническому обслуживанию и ремонту мотоциклов Kawasaki KLE500.
- Издательство: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Год издания: 2004
- Страниц: 401
- Формат: PDF
- Размер: 8,0 Mb

Руководство на английском языке по эксплуатации и техническому обслуживанию мотоциклов Kawasaki Versys.
- Издательство: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Год издания: 2009
- Страниц: 176
- Формат: PDF
- Размер: 1,7 Mb

Руководство на английском языке по техническому обслуживанию и ремонту мотоциклов Kawasaki Versys.
- Издательство: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Год издания: 2006
- Страниц: 627
- Формат: PDF
- Размер: 13,7 Mb

Руководство по эксплуатации и техническому обслуживанию мотоциклов Versys 1000.
- Издательство: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Год издания: 2011
- Страниц: 197
- Формат: PDF
- Размер: 5,7 Mb
- Главная
-
Kawasaki
-
Мотоциклы
-
KLE500
На этой странице вы найдёте полный список документов на Мотоциклы Kawasaki KLE500.
Выберите необходимый PDF файл.
-
Мотоциклы
Kawasaki KLE500 Инструкция по эксплуатации и обслуживаниюТип файла
PDFРазмер
6.3 MbКол-во страниц
401Просмотров
31793Download / Read online
- 1
Другие Kawasaki Мотоциклы
-
Kawasaki VN900 CLASSIC Руководство пользователя
PDF файлов
2Просмотров
93840 -
Kawasaki VN1600 MEAN STREAK — SERVICE Руководство пользователя
PDF файлов
2Просмотров
73720 -
Kawasaki Z750 ABS Инструкция по эксплуатации и обслуживанию
PDF файлов
1Просмотров
71152 -
Kawasaki KLE500 Инструкция по эксплуатации и обслуживанию
PDF файлов
1Просмотров
34772 -
Kawasaki Z1000 Инструкция по эксплуатации
PDF файлов
1Просмотров
33396 -
Kawasaki ZRX 1200/A/B/C Инструкция по эксплуатации
PDF файлов
1Просмотров
16820
Другие устройства Kawasaki
-
Автомобили
Kawasaki ZX-10R Инструкция по эксплуатацииPDF файлов
1Просмотров
85934 -
Вездеходы
Kawasaki Brute Force 750 4x4i Инструкция по эксплуатацииPDF файлов
1Просмотров
28148 -
Вездеходы
Kawasaki KVF 750 4×4 Инструкция по эксплуатацииPDF файлов
1Просмотров
22596 -
Автомобили
Kawasaki ZXR400 Инструкция по эксплуатацииPDF файлов
1Просмотров
19380 -
Велосипеды
Kawasaki ZZR1200 Инструкция по эксплуатацииPDF файлов
1Просмотров
14912 -
Компьютерное аппаратное обеспечение
Kawasaki 80C51 Инструкция по эксплуатацииPDF файлов
1Просмотров
14812
Вопросы
-
слабая батарея
Ноутбуки
Acer
1310
Alex 12.02.2016 17:26
Ранее вы смотрели
Производители
Aetrex
BIXOLON
Boca Research
Genelec
General Imaging (GIC)
Omega Juicers
Philco
Ricoh
Tangent Audio
Vanson
Типы устройств
Сонары
Автомобили
Виниловые проигрыватели
Цифровые ресиверы
Карточные игры
Аксессуары для вращательного оборудования
Транспортировка
Микрофокус и нанофоус
Двухдверные холодильники
Термостаты с сенсорным экраном
Устройства
Fujitsu MAB3045
Maytag UXT4230ADS
Midland Radio GMRS FRS Radio GXT-250
Miele NOVOTRONIC W 1986
National Geographic 264NE
Peavey Mark III 300 CHS
SurveyMonkey — 2011
THE SMITH AGENCY Espressione P-150A
freeuserguide.ru
About Us
Contacts
Disclamers
Privacy Policy
Эта страница полезна для вас? Поделитесь ссылкой:
Kawasaki
KLE500 Инструкция по эксплуатации и обслуживанию
Популярность:
33749 просмотры
Подсчет страниц:
401 страницы
Тип файла:
Размер файла:
6.3 Mb


Quick Reference Guide
This quick reference guide will assist you in locating a desired topic or procedure.
•Bend the pages back to match the black tab of the desired chapter number with the black tab on the edge at each table of contents page.
•Refer to the sectional table of contents for the exact pages to locate the specific topic required.
|
General Information |
1 |
j |
|
Periodic Maintenance |
2 |
j |
|
Fuel System |
3 |
j |
|
Cooling System |
4 |
j |
|
Engine Top End |
5 |
j |
|
Clutch |
6 |
j |
|
Engine Lubrication System |
7 |
j |
|
Engine Removal/Installation |
8 |
j |
|
Crankshaft/Transmission |
9 |
j |
|
Wheels/Tires |
10 |
j |
|
Final Drive |
11 |
j |
|
Brakes |
12 |
j |
|
Suspension |
13 |
j |
|
Steering |
14 |
j |
|
Frame |
15 |
j |
|
Electrical System |
16 |
j |
|
Appendix |
17 |
j |

KLE500
Motorcycle
Service Manual
All rights reserved. No parts of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic mechanical photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of Quality Division/Consumer Products & Machinery Company/Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Japan.
No liability can be accepted for any inaccuracies or omissions in this publication, although every possible care has been taken to make it as complete and accurate as possible.
The right is reserved to make changes at any time without prior notice and without incurring an obligation to make such changes to products manufactured previously. See your Motorcycle dealer for the latest information on product improvements incorporated after this publication.
All information contained in this publication is based on the latest product information available at the time of publication. Illustrations and photographs in this publication are intended for reference use only and may not depict actual model component parts.
|
© 2004 Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. |
First Edition (1): Dec. 10, 2004 (K) |
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
|
A |
ampere(s) |
lb |
pound(s) |
|
ABDC |
after bottom dead center |
m |
meter(s) |
|
AC |
alternating current |
min |
minute(s) |
|
ATDC |
after top dead center |
N |
newton(s) |
|
BBDC |
before bottom dead center |
Pa |
pascal(s) |
|
BDC |
bottom dead center |
PS |
horsepower |
|
BTDC |
before top dead center |
psi |
pound(s) per square inch |
|
°C |
degree(s) Celsius |
r |
revolution |
|
DC |
direct current |
rpm |
revolution(s) per minute |
|
F |
farad(s) |
TDC |
top dead center |
|
°F |
degree(s) Fahrenheit |
TIR |
total indicator reading |
|
ft |
foot, feet |
V |
volt(s) |
|
g |
gram(s) |
W |
watt(s) |
|
h |
hour(s) |
Ω |
ohm(s) |
|
L |
liter(s) |
Read OWNER’S MANUAL before operating.

Foreword
This manual is designed primarily for use by trained mechanics in a properly equipped shop. However, it contains enough detail and basic information to make it useful to the owner who desires to perform his own basic maintenance and repair work. A basic knowledge of mechanics, the proper use of tools, and workshop procedures must be understood in order to carry out maintenance and repair satisfactorily. Whenever the owner has insufficient experience or doubts his ability to do the work, all adjustments, maintenance, and repair should be carried out only by qualified mechanics.
In order to perform the work efficiently and to avoid costly mistakes, read the text, thoroughly familiarize yourself with the procedures before starting work, and then do the work carefully in a clean area. Whenever special tools or equipment are specified, do not use makeshift tools or equipment. Precision measurements can only be made if the proper instruments are used, and the use of substitute tools may adversely affect safe operation.
For the duration of the warranty period, we recommend that all repairs and scheduled maintenance be performed in accordance with this service manual. Any owner maintenance or repair procedure not performed in accordance with this manual may void the warranty.
To get the longest life out of your vehicle:
•Follow the Periodic Maintenance Chart in the Service Manual.
•Be alert for problems and non-scheduled maintenance.
•Use proper tools and genuine Kawasaki Motorcycle parts. Special tools, gauges, and testers that are necessary when servicing Kawasaki motorcycles are introduced by the Special Tool Catalog or Manual. Genuine parts provided as spare parts are listed in the Parts Catalog.
•Follow the procedures in this manual carefully. Don’t take shortcuts.
•Remember to keep complete records of maintenance and repair with dates and any new parts installed.
How to Use This Manual
In this manual, the product is divided into its major systems and these systems make up the manual’s chapters.
The Quick Reference Guide shows you all of the product’s system and assists in locating their chapters. Each chapter in turn has its own comprehensive Table of Contents.
For example, if you want ignition coil information, use the Quick Reference Guide to locate the Electrical System chapter. Then, use the Table of Contents on the first page of the chapter to find the ignition coil section.
Whenever you see these WARNING and CAUTION symbols, heed their instructions! Always follow safe operating and maintenance practices.

This warning symbol identifies special instructions or procedures which, if not correctly followed, could result in personal injury, or loss of life.
CAUTION
This caution symbol identifies special instructions or procedures which, if not strictly observed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment.
This manual contains four more symbols (in addition to WARNING and CAUTION) which will help you distinguish different types of information.
NOTE
○This note symbol indicates points of particular interest for more efficient and convenient operation.
•Indicatesdone. a procedural step or work to be ○Indicates a procedural sub-step or how to do the work of the procedural step it follows. It
also precedes the text of a NOTE.
In most chapters an exploded view illustration of the system components follows the Table of Contents. In these illustrations you will find the instructions indicating which parts require specified tightening torque, oil, grease or a locking agent during assembly.

GENERAL INFORMATION 1-1
General Information |
1 |
|
Table of Contents |
|
|
Before Servicing ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
1-2 |
|
Model Identification………………………………………………………………………………………………….. |
1-7 |
|
General Specifications……………………………………………………………………………………………… |
1-8 |
|
Unit Conversion Table ……………………………………………………………………………………………… |
1-11 |
1-2 GENERAL INFORMATION
Before Servicing
Before starting to perform an inspection service or carry out a disassembly and reassembly operation on a motorcycle, read the precautions given below. To facilitate actual operations, notes, illustrations, photographs, cautions, and detailed descriptions have been included in each chapter wherever necessary. This section explains the items that require particular attention during the removal and reinstallation or disassembly and reassembly of general parts.
Especially note the following:
Battery Ground
Before completing any service on the motorcycle, disconnect the battery wires from the battery to prevent the engine from accidentally turning over. Disconnect the negative wire
(–) first and then the positive (+). When completed with the service, first connect the positive (+) wire to the positive (+) terminal of the battery then the negative (–) wire to the negative terminal.
Edges of Parts
Lift large or heavy parts wearing gloves to prevent injury from possible sharp edges on the parts.
Solvent
Use a high flush point solvent when cleaning parts. High flush point solvent should be used according to directions of the solvent manufacturer.
Cleaning vehicle before disassembly
Clean the vehicle thoroughly before disassembly. Dirt or other foreign materials entering into sealed areas during vehicle disassembly can cause excessive wear and decrease performance of the vehicle.

GENERAL INFORMATION 1-3
Before Servicing
Arrangement and Cleaning of Removed Parts
Disassembled parts are easy to confuse. Arrange the parts according to the order the parts were disassembled and clean the parts in order prior to assembly.
Storage of Removed Parts
After all the parts including subassembly parts have been cleaned, store the parts in a clean area. Put a clean cloth or plastic sheet over the parts to protect from any foreign materials that may collect before re-assembly.
Inspection
Reuse of worn or damaged parts may lead to serious accident. Visually inspect removed parts for corrosion, discoloration, or other damage. Refer to the appropriate sections of this manual for service limits on individual parts. Replace the parts if any damage has been found or if the part is beyond its service limit.
Replacement Parts
Replacement Parts must be KAWASAKI genuine or recommended by KAWASAKI. Gaskets, O-rings, Oil seals, Grease seals, circlips or cotter pins must be replaced with new ones whenever disassembled.
Assembly Order
In most cases assembly order is the reverse of disassembly, however, if assembly order is provided in this Service Manual, follow the procedures given.

1-4 GENERAL INFORMATION
Before Servicing
Tightening Sequence
Generally, when installing a part with several bolts, nuts, or screws, start them all in their holes and tighten them to a snug fit. Then tighten them according to the specified sequence to prevent case warpage or deformation which can lead to malfunction. Conversely when loosening the bolts, nuts, or screws, first loosen all of them by about a quarter turn and them remove them. If the specified tightening sequence is not indicated, tighten the fasteners alternating diagonally.
Tightening Torque
Incorrect torque applied to a bolt, nut, or screw may lead to serious damage. Tighten fasteners to the specified torque using a good quality torque wrench.
Force
Use common sense during disassembly and assembly, excessive force can cause expensive or hard to repair damage. When necessary, remove screws that have a non -permanent locking agent applied using an impact driver. Use a plastic-faced mallet whenever tapping is necessary.
Gasket, O-ring
Hardening, shrinkage, or damage of both gaskets and O-rings after disassembly can reduce sealing performance. Remove old gaskets and clean the sealing surfaces thoroughly so that no gasket material or other material remains. Install new gaskets and replace used O-rings when re-assembling.
Liquid Gasket, Locking Agent
For applications that require Liquid Gasket or a Locking agent, clean the surfaces so that no oil residue remains before applying liquid gasket or locking agent. Do not apply them excessively. Excessive application can clog oil passages and cause serious damage.
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-5
Before Servicing
Press
For items such as bearings or oil seals that must be pressed into place, apply small amount of oil to the contact area. Be sure to maintain proper alignment and use smooth movements when installing.
Ball Bearing and Needle Bearing
Do not remove pressed ball or needle unless removal is absolutely necessary. Replace with new ones whenever removed. Press bearings with the manufacturer and size marks facing out. Press the bearing into place by putting pressure on the correct bearing race as shown.
Pressing the incorrect race can cause pressure between the inner and outer race and result in bearing damage.
Oil Seal, Grease Seal
Do not remove pressed oil or grease seals unless removal is necessary. Replace with new ones whenever removed. Press new oil seals with manufacture and size marks facing out. Make sure the seal is aligned properly when installing.
Apply specified grease to lip of seal before installing the seal.
Circlips, Cotter Pins
Replace circlips or cotter pins that were removed with new ones. Take care not to open the clip excessively when installing to prevent deformation.
1-6 GENERAL INFORMATION
Before Servicing
Lubrication
It is important to lubricate rotating or sliding parts during assembly to minimize wear during initial operation. Lubrication points are called out throughout this manual, apply the specific oil or grease as specified.
Direction of Engine Rotation
When rotating the crankshaft by hand, the free play amount of rotating direction will affect the adjustment. Rotate the crankshaft to positive direction (clockwise viewed from output side).
Electrical Wires
A two-color wire is identified first by the primary color and then the stripe color. Unless instructed otherwise, electrical wires must be connected to those of the same color.

GENERAL INFORMATION 1-7
Model Identification
KLE500-B1 Left Side View
KLE500-B1 Right Side View

1-8 GENERAL INFORMATION
General Specifications
|
Items |
KLE500-B1 |
|
Dimensions |
|
|
Overall Length |
2 215 mm (87.2 in.) |
|
Overall Width |
880 mm (34.6 in.) |
|
Overall Height |
1 270 mm (50.0 in.) |
|
Wheelbase |
1 500 mm (59.0 in.) |
|
Road Clearance |
180 mm (7.09 in.) |
|
Seat Height |
850 mm (33.5 in.) |
|
Dry Weight |
181 kg (399 lb.) |
|
Curb Weight: |
|
|
Front |
95 kg (209 lb.) |
|
Rear |
105 kg (232 lb.) |
|
Fuel tank Capacity |
15 L (4.0 US gal.) |
|
Performance |
|
|
Minimum Turning Radius |
2.4 m (7.9 ft.) |
|
Engine |
|
|
Type |
4-stroke, DOHC, 2-cylinder |
|
Cooling System |
Liquid-cooled |
|
Bore and Stroke |
74.0 × 58.0 mm (2.91 × 2.28 in.) |
|
Displacement |
498 mL (30.39 cu in.) |
|
Compression Ratio |
9.8:1 |
|
Maximum Horsepower |
33 kW (44.9 PS) @8 300 r/min (rpm) |
|
Maximum Torque |
41 N·m (4.2 kgf·m, 30 ft·lb) @7 500 r/min (rpm) |
|
Carburetion System |
Carburetors, Keihin CVK34 × 2 |
|
Starting System |
Electric starter |
|
Ignition System |
Battery and coil (transistorized) |
|
Timing Advance |
Electronically Advanced (digital) |
|
Ignition Timing |
From 10° BTDC @1 300 r/min (rpm) to 35° BTDC |
|
@5 000 r/min (rpm) |
|
|
Spark Plugs |
NGK DR9EA or ND X27ESR-U |
|
Cylinder Numbering Method |
Left to right, 1-2 |
|
Firing Order |
1-2 |
|
Valve Timing: |
|
|
Inlet |
|
|
Open |
27° BTDC |
|
Close |
47° ABDC |
|
Duration |
254° |
|
Exhaust |
|
|
Open |
52° BBDC |
|
Close |
22° ATDC |
|
Duration |
254° |
|
Lubrication System |
Forced lubrication |
|
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-9 |
|
|
General Specifications |
|
|
Items |
KLE500-B1 |
|
Engine Oil: |
|
|
Grade |
API SE, SF, SG or |
|
API SH or SJ with JASO MA |
|
|
Viscosity |
SAE10W-40 |
|
Capacity |
3.4 L (3.6 US qt) |
|
Drive Train |
|
|
Primary Reduction System: |
|
|
Type |
Chain |
|
Reduction Ratio |
2.652 (61/23) |
|
Clutch Type |
Wet multi disc |
|
Transmission: |
|
|
Type |
6-speed constant mesh, return shift |
|
Gear Ratios: |
|
|
1st |
2.571 (36/14) |
|
2nd |
1.722 (31/18) |
|
3rd |
1.333 (28/21) |
|
4th |
1.125 (27/24) |
|
5th |
0.961 (25/26) |
|
6th |
0.851 (23/27) |
|
Final Drive System: |
|
|
Type |
Chain drive |
|
Reduction Ratio |
2.588 (44/17) |
|
Overall Drive Ratio |
5.847 @Top gear |
|
Frame |
|
|
Type |
Tubular, double cradle |
|
Caster (rake angle) |
27° |
|
Trail |
105 mm (4.13 in.) |
|
Front Tire: |
|
|
Type |
Tubeless |
|
Size |
90/90-21 M/C 54S |
|
Rear Tire: |
|
|
Type |
Tubeless |
|
Size |
130/80-17 M/C 65S |
|
Front Suspension: |
|
|
Type |
Telescopic fork |
|
Wheel Travel |
220 mm (8.66 in.) |
|
Rear Suspension: |
|
|
Type |
Swingarm |
|
Wheel Travel |
200 mm (7.87 in.) |
|
Brake Type: |
|
|
Front |
Single disc |
|
Rear |
Single disc |

1-10 GENERAL INFORMATION
General Specifications
|
Items |
KLE500-B1 |
||
|
Electrical Equipment |
|||
|
Battery |
12 |
V 10 Ah |
|
|
Headlight: |
|||
|
Type |
Semi-sealed beam |
||
|
Bulb |
12 |
V 55/55 W (quartz-halogen) |
|
|
Tail/brake Light |
12 |
V 5/21 W |
|
|
Alternator: |
|||
|
Type |
Three-phase AC |
||
|
Rated output |
17 |
A × 14 V @6 000 r/min (rpm) |
Specifications subject to change without notice, and may not apply to every country.

GENERAL INFORMATION 1-11
Unit Conversion Table
Prefixes for Units: |
Units of Length: |
|
Prefix |
Symbol |
Power |
||
|
mega |
M |
× 1 000 |
000 |
|
|
kilo |
k |
× |
1 000 |
|
|
centi |
c |
× |
0.01 |
|
|
milli |
m |
× |
0.001 |
|
|
micro |
||||
|
µ |
× 0.000001 |
Units of Mass:
|
kg |
× |
2.205 |
= |
lb |
|
g |
× |
0.03527 |
= |
oz |
|
km |
× |
0.6214 |
= |
mile |
|
m |
× |
3.281 |
= |
ft |
|
mm |
× |
0.03937 |
= |
in |
Units of Torque:
|
N·m |
× |
0.1020 |
= |
kgf·m |
|
N·m |
× |
0.7376 |
= |
ft·lb |
|
N·m |
× |
8.851 |
= |
in·lb |
|
kgf·m |
× |
9.807 |
= |
N·m |
|
kgf·m |
× |
7.233 |
= |
ft·lb |
|
kgf·m |
× |
86.80 |
= |
in·lb |
Units of Volume: |
Units of Pressure: |
|||||||||
|
kPa |
× |
0.01020 |
= |
kgf/cm² |
||||||
|
L |
× |
0.2642 |
= |
gal (US) |
kPa |
× |
0.1450 |
= |
psi |
|
|
L |
× |
0.2200 |
= |
gal (imp) |
kPa |
× |
0.7501 |
= |
cm Hg |
|
|
L |
× |
1.057 |
= |
qt (US) |
kgf/cm² |
× |
98.07 |
= |
kPa |
|
|
L |
× |
0.8799 |
= |
qt (imp) |
kgf/cm² |
× |
14.22 |
= |
psi |
|
|
L |
× |
2.113 |
= |
pint (US) |
cm Hg |
× |
1.333 |
= |
kPa |
|
|
L |
× |
1.816 |
= |
pint (imp) |
||||||
|
mL |
× |
0.03381 |
= |
oz (US) |
Units of Speed: |
|||||
|
mL |
× |
0.02816 |
= |
oz (imp) |
km/h |
× |
0.6214 |
= |
mph |
|
|
mL |
× |
0.06102 |
= |
cu in |
||||||
Units of Force: |
Units of Power: |
|||||||||
|
kW |
× |
1.360 |
= |
PS |
||||||
|
N |
× |
0.1020 |
= |
kg |
kW |
× |
1.341 |
= |
HP |
|
|
N |
× |
0.2248 |
= |
lb |
||||||
|
PS |
× |
0.7355 |
= |
kW |
||||||
|
kg |
× |
9.807 |
= |
N |
PS |
× |
0.9863 |
= |
HP |
|
|
kg |
× |
2.205 |
= |
lb |
Units of Temperature:

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-1
Periodic Maintenance
|
Table of Contents |
2 |
||
|
Periodic Maintenance Chart ……………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-3 |
||
|
Torque and Locking Agent………………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-6 |
||
|
Specifications …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-11 |
||
|
Special Tools ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-13 |
||
|
Maintenance Procedure …………………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-14 |
||
|
Fuel System…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-14 |
||
|
Throttle Cable Inspection…………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-14 |
||
|
Idle Speed Inspection …………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-15 |
||
|
Carburetor Synchronization Inspection………………………………………………………………….. |
2-16 |
||
|
Coolant Filter Cleaning ……………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-17 |
||
|
Fuel Hoses and Connections Check……………………………………………………………………… |
2-17 |
||
|
Air Cleaner Element Cleaning and Inspection ………………………………………………………… |
2-17 |
||
|
Cooling System…………………………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-18 |
||
|
Coolant Level Inspection……………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-18 |
||
|
Radiator Hoses and Connections Inspection………………………………………………………….. |
2-19 |
||
|
Engine Top End ……………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-19 |
||
|
Air Suction Valve Inspection ………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-19 |
||
|
Valve Clearance Inspection …………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-19 |
||
|
Clutch………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-21 |
||
|
Clutch Operation Inspection…………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-21 |
||
|
Wheels/Tires………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-22 |
||
|
Air Pressure Inspection/Adjustment………………………………………………………………………. |
2-22 |
||
|
Tire Tread Wear Inspection………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-22 |
||
|
Wheel/Tire Damage Inspection…………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-23 |
||
|
Wheel Bearing Damage Inspection ………………………………………………………………………. |
2-24 |
||
|
Spoke Tightness and Rim Runout Inspection…………………………………………………………. |
2-24 |
||
|
Final Drive……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-25 |
||
|
Drive Chain Slack Inspection ……………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-25 |
||
|
Drive Chain Wear Inspection ……………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-26 |
||
|
Drive Chain Lubrication……………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-27 |
||
|
Brakes…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-27 |
||
|
Brake Fluid Leak (Brake Hose and Pipe) Inspection ……………………………………………….. |
2-27 |
||
|
Brake Hose Damage and Installation Condition Inspection………………………………………. |
2-28 |
||
|
Brake Operation Inspection …………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-28 |
||
|
Brake Fluid Level Inspection………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-28 |
||
|
Brake Pad Wear Inspection …………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-29 |
||
|
Brake Light Switch Operation Inspection ……………………………………………………………….. |
2-30 |
||
|
Suspension………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-30 |
||
|
Front Forks/Rear Shock Absorber Operation Inspection ………………………………………….. |
2-30 |
||
|
Front Fork Oil Leak Inspection……………………………………………………………………………… |
2-31 |
||
|
Rear Shock Absorber Oil Leak Inspection ……………………………………………………………… |
2-31 |
||
|
Rocker Arm Operation Inspection…………………………………………………………………………. |
2-31 |
||
|
Rocker Arm Bearings and Sleeves Lubrication ………………………………………………………. |
2-31 |
||
|
Tie-rod Operation Inspection ……………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-32 |
||
|
Swingarm Needle Bearing Lubrication…………………………………………………………………… |
2-32 |
||
|
Steering ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-32 |

2-2 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
|
Steering Play Inspection ……………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-32 |
|
Steering Stem Bearing Lubrication ……………………………………………………………………….. |
2-33 |
|
Electrical System ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-34 |
|
Spark Plug Gap Inspection ………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-34 |
|
Lights and Switches Operation Inspection……………………………………………………………… |
2-34 |
|
Headlight Aiming Inspection ………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-36 |
|
Side Stand Switch Operation Inspection………………………………………………………………… |
2-37 |
|
Engine Stop Switch Operation Inspection………………………………………………………………. |
2-38 |
|
Others…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-38 |
|
Chassis Parts Lubrication ……………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-38 |
|
Bolts, Nuts and Fastener Tightness Inspection ………………………………………………………. |
2-39 |
|
Replacement Parts ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-40 |
|
Fuel Hose Replacement ……………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-40 |
|
Air Cleaner Element Replacement………………………………………………………………………… |
2-41 |
|
Coolant Change…………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-41 |
|
Radiator Hoses and O-ring Replacement ………………………………………………………………. |
2-44 |
|
Engine Oil Change……………………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-44 |
|
Oil Filter Replacement ………………………………………………………………………………………… |
2-45 |
|
Brake Hose Replacement ……………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-45 |
|
Brake Fluid Change ……………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-46 |
|
Bleeding the Brake Line………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2-47 |
|
Caliper Rubber Parts Replacement ………………………………………………………………………. |
2-48 |
|
Master Cylinder Rubber Parts Replacement ………………………………………………………….. |
2-48 |
|
Spark Plug Replacement …………………………………………………………………………………….. |
2-49 |

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-3
Periodic Maintenance Chart
The scheduled maintenance must be done in accordance with this chart to keep the motorcycle in good running condition.The initial maintenance is vitally important and must not be neglected.
|
FREQUENCY |
Whichever |
* ODOMETER READING |
|||||||||||||
|
× 1000 km |
|||||||||||||||
|
comes first |
See |
||||||||||||||
|
(× 1000 mile) |
|||||||||||||||
|
Page |
|||||||||||||||
|
1 |
6 |
12 |
18 |
24 |
30 |
36 |
|||||||||
|
OPERATION |
Every |
(0.6) |
(4) |
(7.5) |
(12) |
(15) |
(20) |
(24) |
|||||||
|
Fuel System |
|||||||||||||||
|
Throttle cable-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-14 |
|||||||||
|
Idle speed-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-15 |
||||||||||
|
Carburetor synchronization-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
2-16 |
|||||||||||
|
Coolant filter-clean |
year |
2-17 |
|||||||||||||
|
Air cleaner element-clean # |
• |
• |
• |
2-17 |
|||||||||||
|
Fuel hoses and connections-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-17 |
|||||||||
|
Cooling System |
|||||||||||||||
|
Coolant level-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-18 |
||||||||||
|
Radiator hose and connection-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-19 |
|||||||||
|
Engine Top End |
|||||||||||||||
|
Air suction valve-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
2-19 |
|||||||||||
|
Valve clearance-inspect |
• |
2-19 |
|||||||||||||
|
Clutch |
|||||||||||||||
|
Clutch operation (play, disengagement, |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-21 |
||||||||||
|
engagement)-inspect |
|||||||||||||||
|
Wheels and Tires |
|||||||||||||||
|
Tire air pressure-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-22 |
||||||||
|
Tire tread wear-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
2-22 |
|||||||||||
|
Wheel/tire damage-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
2-23 |
|||||||||||
|
Wheel bearing damage-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
2-24 |
||||||||||
|
Spoke tightness and rim runout-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-24 |
|||||||
|
Final Drive |
|||||||||||||||
|
Drive chain slack-inspect # |
Every 1 000 km (600 mile) |
2-25 |
|||||||||||||
|
Drive chain wear-inspect # |
Every 6 000 km (4 000 mile) |
2-26 |
|||||||||||||
|
Drive chain lubrication condition-inspect # |
Every 600 km (400 mile) |
2-27 |
|||||||||||||
|
Drive chain guide wear-inspect |
Every 12 000 km (7 500 mile) |
– |
|||||||||||||
|
Brake System |
|||||||||||||||
|
Brake fluid leak (brake hose and |
year |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-27 |
||||||
|
pipe)-inspect |
|||||||||||||||
|
Brake hose damage-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-28 |
||||||
|
Brake hose installation condition-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-28 |
||||||
|
Brake operation (effectiveness, play, no |
year |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-28 |
||||||
|
drag)-inspect |
|||||||||||||||
|
Brake fluid level-inspect |
6 months |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-28 |
||||||
|
Brake pad wear-inspect # |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-29 |
||||||||
|
Brake light switch operation-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-30 |

2-4 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Chart
|
FREQUENCY |
Whichever |
* ODOMETER READING |
||||||||||||
|
× 1000 km |
||||||||||||||
|
comes first |
See |
|||||||||||||
|
(× 1000 mile) |
||||||||||||||
|
Page |
||||||||||||||
|
1 |
6 |
12 |
18 |
24 |
30 |
36 |
||||||||
|
OPERATION |
Every |
(0.6) |
(4) |
(7.5) |
(12) |
(15) |
(20) |
(24) |
||||||
|
Suspensions |
||||||||||||||
|
Front forks/rear shock absorber operation |
• |
• |
• |
2-30 |
||||||||||
|
(damping and smooth stroke)-inspect |
||||||||||||||
|
Front forks/rear shock absorber oil |
year |
• |
• |
• |
2-31 |
|||||||||
|
leak-inspect |
||||||||||||||
|
Rocker arm operation-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
2-31 |
||||||||||
|
Rocker arm bearings and sleeves |
• |
2-31 |
||||||||||||
|
-lubricate |
||||||||||||||
|
Tie-rods operation-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
2-32 |
||||||||||
|
Swingarm pivot-lubricate |
• |
2-32 |
||||||||||||
|
Steering System |
||||||||||||||
|
Steering play-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-32 |
||||||||
|
Steering stem bearings-lubricate |
2 years |
• |
2-33 |
|||||||||||
|
Electrical System |
||||||||||||||
|
Spark plug condition-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
2-34 |
||||||||||
|
Lights and switches operation-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
2-34 |
|||||||||
|
Headlight aiming-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
2-36 |
|||||||||
|
Side stand switch operation-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
2-37 |
|||||||||
|
Engine stop switch operation-inspect |
year |
• |
• |
• |
2-38 |
|||||||||
|
Others |
||||||||||||||
|
Chassis parts-lubricate |
year |
• |
• |
• |
2-38 |
|||||||||
|
Bolts, nuts and fasteners tightness-inspect |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-39 |
#: Service more frequently when operating in severe conditions; dusty, wet, muddy, high speed or frequent starting/stopping.
*: For higher odometer readings, repeat at the frequency interval established here.

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-5
Periodic Maintenance Chart
Periodic Replacement Parts
|
FREQUENCY |
Whichever |
* ODOMETER READING |
||||||||||
|
come |
× 1000 km |
See |
||||||||||
|
first |
(× 1000 mile) |
|||||||||||
|
Page |
||||||||||||
|
1 |
12 |
18 |
24 |
36 |
48 |
|||||||
|
CHANGE/REPLACEMENT |
Every |
(0.6) |
(7.5) |
(12) |
(15) |
(24) |
(30) |
|||||
|
Fuel hose |
4 years |
• |
2-40 |
|||||||||
|
Air cleaner element |
2 years |
2-40 |
||||||||||
|
Coolant |
3 years |
• |
2-40 |
|||||||||
|
Radiator hose and O-ring |
3 years |
• |
2-43 |
|||||||||
|
Engine oil # |
year |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-43 |
|||||
|
Oil filter |
year |
• |
• |
• |
• |
• |
2-44 |
|||||
|
Brake hose |
4 years |
• |
2-44 |
|||||||||
|
Brake fluid |
2 years |
• |
• |
2-45 |
||||||||
|
Master Cylinder/Caliper Rubber Parts |
4 years |
• |
2-47 |
#: Service more frequently when operating in severe conditions; dusty, wet, muddy, high speed or frequent starting/stopping.
*: For higher odometer readings, repeat at the frequency interval established here.

2-6 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Torque and Locking Agent
Tighten all bolts and nuts to the proper torque using an accurate torque wrench. An insufficiently tightened bolt or nut may become damaged or fall off, possibly resulting in damage to the motorcycle and injury to the rider. A bolt or nut which is overtightened may become damaged, strip an internal thread, or break and then fall out. The following table lists the tightening torque for the major bolts and nuts, and the parts requiring use of a non-permanent locking agent or liquid gasket.
When checking the tightening torque of the bolts and nuts, first loosen the bolt or nut by half a turn and then tighten it to the specified torque.
Letters used in the «Remarks» column mean:
EO: Apply engine oil to the threads and seating surface.
L:Apply a non-permanent locking agent to the threads. LG: Apply liquid gasket to the threads.
Lh: Left-hand threads.
M:Apply molybdenum disulfide grease.
MO: Apply molybdenum disulfide oil (mixture of the engine oil and molybdenum disulfide grease in a weight ratio 10 : 1)
R:Replacement parts.
S:Tighten the fasteners following the specified sequence.
SS:Apply silicone sealant to the threads.
St: Stake the fasteners to prevent loosening.
|
Fastener |
Torque |
Remarks |
||||
|
N·m |
kgf·m |
ft·lb |
||||
|
Fuel System |
||||||
|
Fuel Tap Cover Screws |
0.8 |
0.08 |
7 in·lb |
|||
|
Fuel Tap Mounting Bolts |
5.0 |
0.51 |
44 |
in·lb |
||
|
Air Cut Valve Cover Screws |
1.0 |
0.10 |
9 in·lb |
|||
|
Cooling System |
||||||
|
Radiator Hose Clamp Screws |
2.5 |
0.25 |
22 in·lb |
|||
|
Radiator Fan Switch |
18 |
1.8 |
13 |
|||
|
Thermostat Housing Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Water Temperature Sensor |
7.8 |
0.8 |
69 in·lb |
SS |
||
|
Water Pump Cover Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 in·lb |
|||
|
Water Pump Shaft |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
Lh |
||
|
Water Pump Impeller |
9.8 |
1.0 |
87 |
in·lb |
Lh |
|
|
Water Pipe Bolts |
9.8 |
1.0 |
87 |
in·lb |
L |
|
|
Cylinder Head Jacket Plug |
9.8 |
1.0 |
87 |
in·lb |
L |
|
|
Radiator Cap Holder Mounting Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Coolant Drain Plug |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Engine Top End |
||||||
|
Air Suction Valve Cover Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Cylinder Head Cover Bolts |
9.8 |
1.0 |
87 |
in·lb |
S |
|
|
Camshaft Cap Bolts |
12 |
1.2 |
104 in·lb |
S |
||
|
Rocker Shafts |
39 |
4.0 |
29 |
EO |
||
|
Valve Adjuster Locknuts |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
|||
|
Camshaft Sprocket Bolts |
15 |
1.5 |
11 |
L |
||
|
Cylinder Head Bolts (10 mm) |
51 |
5.2 |
38 |
S |
||
|
Cylinder Head Bolts (6 mm) |
9.8 |
1.0 |
87 |
in·lb |
S |
|
|
Camshaft Chain Tensioner Mounting Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Camshaft Chain Tensioner Cap Bolt |
13 |
1.3 |
9.5 |

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-7
Torque and Locking Agent
|
Fastener |
Torque |
Remarks |
||||
|
N·m |
kgf·m |
ft·lb |
||||
|
Main Oil Pipe Upper Banjo Bolts M8 |
12 |
1.2 |
104 in·lb |
|||
|
Main Oil Pipe Lower Banjo Bolt M10 |
20 |
2.0 |
14.5 |
|||
|
Water Jacket Plug |
9.8 |
1.0 |
87 |
in·lb |
L |
|
|
Oil Pipe Bolts (in the cylinder head) |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Main Oil Pipe Mounting Bolt |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Clutch |
||||||
|
Oil Filler Plug |
1.5 |
0.15 |
13 |
in·lb |
||
|
Clutch Hub Nut |
132 |
13.5 |
98 |
|||
|
Clutch Spring Bolts |
9.3 |
0.95 |
82 |
in·lb |
||
|
Clutch Cable Holder Bolt |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Clutch Cover Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Engine Lubrication System |
||||||
|
Oil Filler Plug |
1.5 |
0.15 |
13 |
in·lb |
||
|
Oil Passage Plug |
18 |
1.8 |
13 |
|||
|
Oil Filter Mounting Stud |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
L |
||
|
(Planted |
||||||
|
side) |
||||||
|
Oil Filter (Cartridge Type) |
||||||
|
17 |
1.7 |
12.5 |
||||
|
Oil Pipe for Balancer Shaft Banjo Bolt |
20 |
2.0 |
14.5 |
|||
|
Oil Pipe for Drive Shaft Upper Banjo Bolt M6 |
7.8 |
0.8 |
69 |
in·lb |
||
|
Oil Pipe for Drive Shaft Lower Banjo Bolt M8 |
12 |
1.2 |
104 in·lb |
|||
|
Oil Pipe for Output Shaft Upper Banjo Bolt M6 |
7.8 |
0.8 |
69 |
in·lb |
||
|
Oil Pipe for Output Shaft Lower Banjo Bolt M8 |
12 |
1.2 |
104 in·lb |
|||
|
Oil Pipe for Output Shaft Mounting Bolt |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
L |
|
|
Oil Pump Outer Oil Pipe Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
L |
|
|
Relief Valve |
15 |
1.5 |
11 |
L |
||
|
Oil Pressure Switch Terminal Bolt |
1.5 |
0.15 |
13 |
in·lb |
||
|
Oil Pressure Switch |
15 |
1.5 |
11 |
SS |
||
|
Main Oil Pipe Mounting Bolt |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Main Oil Pipe Upper Banjo Bolts |
12 |
1.2 |
104 in·lb |
|||
|
Main Oil Pipe Lower Banjo Bolt |
20 |
2.0 |
14.5 |
|||
|
Rocker Shafts |
39 |
4.0 |
29 |
|||
|
Engine Oil Drain Plug |
29 |
3.0 |
22 |
|||
|
Oil Pan Mounting Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Oil Pump Mounting Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Engine Removal/Installation |
||||||
|
Downtube Bolts |
44 |
4.5 |
33 |
|||
|
Engine Mounting Bolts and Nuts |
44 |
4.5 |
33 |
|||
|
Engine Mounting Bracket Bolts |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
|||
|
Crankshaft/Transmission |
||||||
|
Breather Body Bolt |
5.9 |
0.6 |
52 |
in·lb |
||
|
Crankcase Bolts (8 mm) |
27 |
2.8 |
20 |
S |
||
|
Crankcase Bolts (6 mm) |
12 |
1.2 |
104 in·lb |
S |

2-8 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Torque and Locking Agent
|
Fastener |
Torque |
Remarks |
|||||
|
N·m |
kgf·m |
ft·lb |
|||||
|
Upper Primary Chain Guide Mounting Bolt |
11 |
1.1 |
95 in·lb |
L |
|||
|
Lower Primary Chain Guide Mounting Bolt |
11 |
1.1 |
95 in·lb |
L |
|||
|
Connecting Rod Big End Nuts |
|||||||
|
36 |
3.7 |
27 |
|||||
|
Return Spring Pin |
20 |
2.0 |
14.5 |
L |
|||
|
Gear Positioning Lever Pivot Stud |
– |
– |
– |
L |
|||
|
(planted |
|||||||
|
side) |
|||||||
|
Gear Positioning Lever Nut |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
|||
|
Shift Pedal Link Lever Mounting Bolt |
12 |
1.2 |
104 in·lb |
||||
|
Shift Drum Bearing Holder Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
L |
||
|
Shift Drum Cam Pin Plate Screw |
– |
– |
– |
L |
|||
|
Engine Sprocket Nut |
127 |
13 |
94 |
EO |
|||
|
External Shift Mechanism Cover Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
|||
|
Neutral Switch |
15 |
1.5 |
11 |
||||
|
Wheels/Tires |
|||||||
|
Spoke Nipple |
2.0 3.9 |
0.2 0.4 |
17 |
35 in·lb |
|||
|
Front Axle Nut |
88 |
9.0 |
65 |
||||
|
Rear Sprocket Nut |
33 |
3.4 |
24 |
||||
|
Rear Axle Nut |
108 |
11 |
80 |
||||
|
Final Drive |
|||||||
|
Engine Sprocket Nut |
127 |
13 |
94 |
EO |
|||
|
Rear Sprocket Nuts |
33 |
3.4 |
24 |
||||
|
Rear Coupling Studs |
– |
– |
– |
L |
|||
|
(planted |
|||||||
|
side) |
|||||||
|
Rear Axle Nut |
108 |
11 |
80 |
||||
|
Drive Chain Guide Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
|||
|
Brakes |
|||||||
|
Brake Hose Banjo Bolts |
34 |
3.5 |
25 |
||||
|
Front Reservoir Cap Screws |
1.5 |
0.15 |
13 |
in·lb |
|||
|
Brake Lever Pivot Bolt |
1.0 |
0.10 |
9 in·lb |
||||
|
Brake Lever Pivot Locknut |
5.9 |
0.60 |
52 |
in·lb |
|||
|
Front Master Cylinder Clamp Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
S |
||
|
Front Brake Light Switch Mounting Screw |
1.2 |
0.12 |
10 |
in·lb |
|||
|
Front Caliper Mounting Bolts |
34 |
3.5 |
25 |
||||
|
Rear Caliper Mounting Bolts |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
||||
|
Caliper Bleed Valves |
7.8 |
0.8 |
69 |
in·lb |
|||
|
Brake Disc Mounting Bolts |
23 |
2.3 |
16.5 |
L |
|||
|
Brake Pedal Bolt |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
||||
|
Rear Reservoir Mounting Bolt |
5.9 |
0.60 |
52 |
in·lb |
|||
|
Rear Master Cylinder Mounting Bolts |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
||||
|
Suspension |
|||||||
|
Front Fork Upper Clamp Allen Bolts |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
S |
|||
|
Front Fork Lower Clamp Bolts |
23 |
2.3 |
16.5 |
S |

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-9
Torque and Locking Agent
|
Fastener |
Torque |
Remarks |
||||
|
N·m |
kgf·m |
ft·lb |
||||
|
Front Fork Top Bolts |
30 |
3.1 |
22 |
|||
|
Front Fork Bottom Allen Bolt |
30 |
3.1 |
22 |
L |
||
|
Rear Shock Absorber Upper Mounting Nut |
59 |
6.0 |
43 |
|||
|
Rear Shock Absorber Lower Mounting Nut |
98 |
10 |
72 |
|||
|
Swingarm Pivot Nut |
118 |
12 |
87 |
|||
|
Rocker Arm Pivot Nut |
98 |
10 |
72 |
|||
|
Tie-Rod Mounting Nuts |
98 |
10 |
72 |
|||
|
Steering |
||||||
|
Handlebar Clamp Bolts |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
S |
||
|
Handlebar Weight Allen Bolts |
– |
– |
– |
L |
||
|
Front Fork Upper Clamp Allen Bolts |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
S |
||
|
Front Fork Lower Clamp Bolts |
23 |
2.3 |
16.5 |
S |
||
|
Steering Stem Head Nut |
39 |
4.0 |
29 |
|||
|
Steering Stem Locknut |
Hand |
Hand |
Hand |
|||
|
-Tighten |
-Tighten |
-Tighten |
||||
|
(about 4.9) |
(about 0.5) |
(about 43 |
||||
|
in·lb) |
||||||
|
Frame |
||||||
|
Tail Grip Bolts |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
|||
|
Front Footpeg Bracket Bolts |
34 |
3.5 |
25 |
|||
|
Sidestand Bolt and Nut |
44 |
4.5 |
33 |
|||
|
Rear Footpeg Bracket Bolts |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
|||
|
Carrier Stay Mounting Bolts |
25 |
2.5 |
18 |
|||
|
Electrical System |
||||||
|
Crankshaft Sensor Mounting Screws |
8.3 |
0.85 |
74 in·lb |
L |
||
|
Timing Inspection Plug |
2.5 |
0.25 |
22 |
in·lb |
||
|
Alternator Rotor Bolt Plug |
1.5 |
0.15 |
13 |
in·lb |
||
|
Alternator Cover Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Alternator Lead Clamp Screws |
2.9 |
0.30 |
26 |
in·lb |
||
|
Spark Plug |
14 |
1.4 |
10 |
|||
|
Alternator Stator Allen Bolts |
12 |
1.2 |
104 in·lb |
|||
|
Alternator Rotor Bolt |
69 |
7.0 |
51 |
Lh |
||
|
Starter Motor Mounting Bolts |
11 |
1.1 |
95 |
in·lb |
||
|
Starter Chain Guide Bolts |
4.9 |
0.5 |
43 |
in·lb |
L |
|
|
Starter Motor Through Bolts |
6.9 |
0.7 |
65 |
in·lb |
||
|
Starter Motor Terminal Nut |
in·lb |
|||||
|
4.9 |
0.5 |
43 |
||||
|
Starter Motor Lead Clamp Nut |
4.9 |
0.5 |
43 |
in·lb |
||
|
Starter Clutch Allen Bolts |
34 |
3.5 |
25 |
L |
||
|
Sidestand Switch Mounting Screw |
3.9 |
0.4 |
35 |
in·lb |
L |
|
|
Sidestand Bolt and Nut |
44 |
4.5 |
33 |
|||
|
Radiator Fan Switch |
18 |
1.8 |
13 |
|||
|
Water Temperature Switch |
7.8 |
0.80 |
69 in·lb |
SS |
||
|
Oil Pressure Switch Terminal Bolt |
1.5 |
0.15 |
13 |
in·lb |

2-10 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Torque and Locking Agent
|
Fastener |
Torque |
Remarks |
|||
|
N·m |
kgf·m |
ft·lb |
|||
|
Oil Pressure Switch |
15 |
1.5 |
11 |
SS |
|
|
Neutral Switch |
15 |
1.5 |
11 |
||
|
Tail Light Mounting Nut |
5.9 |
0.6 |
52 in·lb |
The table relating tightening torque to thread diameter, lists the basic torque for the bolts and nuts. Use this table for only the bolts and nuts which do not require a specific torque value. All of the values are for use with dry solvent-cleaned threads.
Basic Torque for General Fasteners
|
Threads |
Torque |
||||||||
|
dia. (mm) |
N·m |
kgf·m |
ft·lb |
||||||
|
5 |
3.4 |
4.9 |
0.35 |
0.50 |
30 |
43 in·lb |
|||
|
6 |
5.9 |
7.8 |
0.60 |
0.80 |
52 |
69 in·lb |
|||
|
8 |
14 19 |
1.4 1.9 |
10.0 |
13.5 |
|||||
|
34 |
2.6 |
3.5 |
19.0 |
25 |
|||||
|
10 |
25 |
||||||||
|
12 |
44 |
61 |
4.5 |
6.2 |
33 |
45 |
|||
|
14 |
73 |
98 |
7.4 |
10.0 |
54 |
72 |
|||
|
16 |
115 |
155 |
11.5 |
16.0 |
83 |
115 |
|||
|
18 |
165 |
225 |
17.0 |
23.0 |
125 |
165 |
|||
|
20 |
225 |
325 |
23 |
33 |
165 |
240 |

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-11
Specifications
|
Item |
Standard |
Service Limit |
|||
|
Fuel System |
|||||
|
Throttle Grip Free Play |
2 3 mm (0.08 0.12 in.) |
– – – |
|||
|
Idle Speed |
1 200 ±50 r/min (rpm) |
– – – |
|||
|
Engine Top End |
|||||
|
Valve Clearance |
|||||
|
Inlet |
0.13 |
0.18 mm (0.0051 |
0.0071 in.) |
– – – |
|
|
Exhaust |
0.18 |
0.23 mm (0.0070 |
0.0090 in.) |
– – – |
|
|
Clutch |
|||||
|
Clutch Lever Free Play |
2 3 mm (0.08 0.12 in.) |
– – – |
|||
|
Wheels/Tires |
|||||
|
Air Pressure |
|||||
|
Front |
150 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm², 21 psi) |
– – – |
|||
|
Rear |
225 kPa (2.25 kgf/cm², 32 psi) |
– – – |
|||
|
Tread Depth |
|||||
|
Front |
|||||
|
Dunlop |
6.9 mm (0.27 in.) |
1 mm (0.04 in.) |
|||
|
Bridgestone |
6.0 mm (0.24 in.) |
||||
|
Rear |
|||||
|
Dunlop |
|||||
|
8.8 mm (0.35 in.) |
2 mm (0.08 in.) |
||||
|
(Up to 130 km/h |
|||||
|
(80 mph)) |
|||||
|
Bridgestone |
8.5 mm (0.33 in.) |
3 mm (0.12 in.) |
|||
|
(Over to 130 km/h |
|||||
|
(80 mph)) |
|||||
|
Rim Runout |
|||||
|
Axial |
0.5 mm (0.02 in.) |
1.5 mm (0.06 in.) |
|||
|
Radial |
0.8 mm (0.03 in.) |
1.5 mm (0.06 in.) |
|||
|
Final Drive |
|||||
|
Drive Chain Slack |
2 12 mm (0.08 0.47 in.) |
– – – |
|||
|
Drive Chain Wear (20-link length) |
317.5 |
318.2 mm (12.50 |
12.53 in.) |
323 mm (12.7 in.) |
|
|
Brakes |
|||||
|
Brake Fluid Grade |
DOT4 |
– – – |
|||
|
Pad Lining Thickness |
5.5 mm (0.203 in.) |
1 mm (0.04 in.) |
|||
|
Brake Light Timing |
|||||
|
Front |
ON after 10 mm (0.39 in.) lever travel |
– – – |
|||
|
Rear |
ON after 15 mm (0.59 in.) pedal travel |
– – – |
|||
|
Electrical System |
|||||
|
Spark Plug Gap |
0.6 0.7 mm (0.024 0.028 in.) |
– – – |
|||
|
Replacement Parts |
|||||
|
Coolant Capacity |
1.7 L (1.8 US qt) |
– – – |
|||
|
Engine Oil |
|||||
|
Grade |
API SE, SF, SG or |
– – – |
|||
|
API SH or SJ with JASO MA |
|||||
|
Viscosity |
SAE10W-40 |
– – – |
|||

2-12 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Specifications
|
Item |
Standard |
Service Limit |
|
Capacity |
||
|
when filter is not removed |
2.8 L (3.0 US qt) |
– – – |
|
when filter is removed |
3.0 L (3.2 US qt) |
– – – |
|
when engine is completely dry |
3.4 L (3.6 US qt) |
– – – |

|
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-13 |
||
|
Special Tools |
||
Steering Stem Nut Wrench: |
Oil Filter Wrench: |
|
|
57001-1100 |
57001-1249 |
|
|
Jack: |
Vacuum Gauge: |
|
|
57001-1238 |
57001-1369 |
|
|
Pilot Screw Adjuster, A: |
Filler Cap Driver: |
|
|
57001-1239 |
57001-1454 |
|

2-14 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Procedure
Fuel System
Throttle Cable Inspection
Throttle Grip Free Play Inspection
•Check throttle grip play [A] by lightly turning the throttle grip back and forth.

Throttle Grip Free Play
Standard: 2 3 mm (0.08 0.12 in.)
•Check that the throttle grip moves smoothly from full open to close, and the throttle closes quickly and completely in all steering positions by the return spring.

•Run the engine at the idle speed, and turn the handlebar all the way to the right and left to ensure that the idle speed does not change.

Throttle Grip Free Play Adjustment

•Tighten the locknut against the adjuster securely.
•Check that the throttle pulley [A] stops against the idle adjusting screw [B] with the throttle grip closed.

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-15
Maintenance Procedure

•Screw in the adjuster fully at the throttle grip and tighten the locknut.
•Remove the fuel tank (see Fuel Tank Removal in the Fuel System chapter).
○Make the necessary free play adjustment at the lower cable end.
•Check that the throttle pulley stops [A] against the idle adjusting screw [B], with the throttle grip released and stops against the carburetor stopper with the throttle grip opened.
•Turngine. the handlebar from side to side while idling the en-


Operation with an improperly adjusted, incorrectly routed, or damaged cable could result in an unsafe riding condition.
Throttle Cable Inspection
•Remove both ends of the throttle cables.
•With the throttle cable disconnected at both ends, the cable should move freely [A] within the cable housing.
○If cable movement is not free after lubricating, if the cable is frayed [B], or if the cable housing is kinked [C], replace the cable.
Idle Speed Inspection
Idle Speed Inspection
•Start the engine and warm it up thoroughly.
•With the engine idling, turn the handlebar to both sides. 

Operation with improperly adjusted, incorrectly routed, or damaged cables could result in an unsafe riding condition.
•Check idle speed.

Idle Speed
1 200 ±50 r/min (rpm)

2-16 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Procedure
Idle Speed Adjustment
•Start the engine and warm it up thoroughly.
•Turn the adjusting screw [A] until idle speed is correct. ○Open and close the throttle a few times to make sure that the idle speed is within the specified range. Readjust if
necessary.
Carburetor Synchronization Inspection
Synchronization Inspection
•Situateground.the motorcycle so that it is perpendicular to the
•Remove the fuel tank and connect the auxiliary fuel tank to supply the fuel.
•Warm up the engine.
•Check idle speed and adjust if necessary.
•Pull the vacuum hoses off, and attach vacuum gauge [A] to the vacuum hose fittings on the carburetors.
Special Tool — Vacuum Gauge: 57001-1369
Synchronization Adjustment
○The pilot screw is set at the factory and should not be removed. But if necessary, check the pilot screw opening as follows.
•Turn in the pilot screw and count the number of turns until it seats fully but not tightly, and then remove the screw. This is to set the screw to its original (correct) position when assembling.
Special Tool — Pilot Screw Adjuster, C [A]: 57001-1239
NOTE
○Each carburetor has different opening of the pilot screw. When setting the pilot screw, do not refer to the specifications which show mean opening of the pilot screws.

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-17
Maintenance Procedure
Coolant Filter Cleaning
○Before winter season starts, clean the coolant filter [A] in the carburetor system.
•Drain the coolant (see Coolant Draining).
•Remove the coolant filter from the cooling hoses in the carburetor system.
•Blow dirt and sediment off the filter with compressed air.
Fuel Hoses and Connections Check
○The fuel hoses are designed to be used throughout the motorcycle’s life without any maintenance, however, if the motorcycle is not properly handled, the high pressure inside the fuel line can cause fuel to leak [A] or the hose to burst. Remove the fuel tank (see Fuel Tank Removal in the Fuel System chapter) and check the fuel hose.

[C] are noticed.
•Check that the hoses are securely connected and clamps are tightened correctly.
•When installing, route the hoses according to Cable, Wire, and Hose Routing section in the General Information chapter.
•When installing the fuel hoses, avoid sharp bending, kinking, flattening or twisting, and route the fuel hoses with a minimum of bending so that the fuel flow will not be obstructed.
Replace the hose if it has been sharply bent or kinked.
Air Cleaner Element Cleaning and Inspection
NOTE
○In dusty areas, the element should be cleaned more frequently than the recommended interval.
○After riding through rain or on muddy roads, the element should be cleaned immediately.

Clean the element in a well-ventilated area, and make sure that there are no sparks or flame anywhere near the working area. Because of the danger of highly flammable liquids, do not use gasoline or a low-flash point solvent to clean the element.

2-18 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Procedure
•Remove the element assembly from the air cleaner housing (see Air Cleaner Element Removal in the Fuel System chapter).
•Separate the element [A] from the element holders [B].
•Clean the element in a bath of high-flash point solvent, and then dry it with compressed air or by shaking it.
•Visually check the element for tear or breaks.

•After cleaning of the element, saturate it with high quality form air filter oil and squeeze out excess oil.
•Wrap the element [A] in a clean rag [B] and squeeze it as dry as possible.
•Assemble the element with the holders, and install them into the air cleaner housing.
Cooling System
Coolant Level Inspection
•Situateground.the motorcycle so that it is perpendicular to the
•Check the level through the coolant level gauge on the reservoir tank [C]. The coolant level should be between the «H» (High) [A] and the «L» (Low) [B] level lines.
NOTE
○Check the level when the engine is cold (room or ambient temperature).

CAUTION
For refilling, add the specified mixture of coolant and soft water. Adding water alone dilutes the coolant and degrades its anticorrosion properties. The diluted coolant can attack the aluminum engine parts. In an emergency, soft water alone can be added. But the diluted coolant must be returned to the correct mixture ratio within a few days. If coolant must be added often, or the reserve tank has run completely dry, there is probably leakage in the cooling system. Check the system for leaks (see Visual Leak Inspection, and Cooling System Pressure Testing).

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-19
Maintenance Procedure
Radiator Hoses and Connections Inspection
○The high pressure inside the radiator hose can cause coolant to leak [A] or the hose to burst if the line is not properly maintained. Visually inspect the hoses for signs of deterioration. Squeeze the hoses. A hose should not be hard and brittle, nor should it be soft or swollen.

•Check that the hoses are securely connected and clamps are tightened correctly.
Torque — Radiator Hose Clamp Screws: 2.5 N·m (0.25 kgf·m, 22 in·lb)
Engine Top End
Air Suction Valve Inspection
The air suction valve is essentially a check valve which allows fresh air to flow from the air cleaner into the exhaust port. Any air that has passed the air suction valve is prevented from returning to the air cleaner.
•Remove the air suction valves.
•Visually inspect the reeds [A] for cracks, folds, warps, heat damage, or other damage.

•Check the reed contact areas [B] of the valve holder for grooves, scratches, any signs of separation from the holder, or heat damage.

•If any carbon or other foreign particles have accumulated between the reed and the reed contact area, wash the valve assembly clean with a high flash-point solvent.
CAUTION
Do not scrape off the deposits with a scraper as this could damage the rubber, requiring replacement of the suction valve assembly.
Valve Clearance Inspection
Valve Clearance Inspection
NOTE
○Valve clearance must be checked and adjusted when the engine is cold (room temperature).
•Remove the cylinder head cover (see Cylinder Head Cover Removal in the Engine Top End chapter).
•Remove the cylinder head oil pipes (see Cylinder Head Oil Pipe Removal in the Engine Top End chapter).

2-20 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Procedure
•Unscrew the upper [A] and lower [B] caps on the alternator cover.
Special Tool — Filler Cap Driver: 57001-1454
•Check the valve clearance when the pistons are at TDC. ○The pistons are numbered beginning with the engine left
side.
•Using a wrench on the crankshaft rotation bolt [A], turn the crankshaft clockwise [B] until the «C» mark [C] on the rotor is aligned with the notch [D] in the edge of the upper hole in the alternator cover for #2 piston and «T» mark for #1 piston.
○Measure the valve clearance of the valves for which the cam lobe is pointing away from the rocker arm.
•Each piston has two inlet and two exhaust valves. Measure these two inlet or exhaust valves at the same crankshaft position.
Valve Clearance Measuring Position
#2 Piston TDC at End of Compression Stroke → Inlet valve clearances of #2 piston, and Exhaust valve clearances of #2 piston
NOTE
○Check the valve clearance using this method only. Checking the clearance at any other cam position may result in improper valve clearance.
Valve Clearance Measuring Position
#1 Piston TDC at End of Compression Stroke → Inlet valve clearances of #1 piston, and Exhaust valve clearances of #1 piston

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-21
Maintenance Procedure
•Measure the clearance of each valve by inserting a thickness gauge [A] between the adjusting screw [B] and the valve stem.
Valve Clearance (when cold) |
|||
|
Inlet |
0.13 |
0.18 mm (0.0051 |
0.0071 in.) |
|
Exhaust |
0.18 |
0.23 mm (0.0070 |
0.0090 in.) |
Valve Clearance Adjustment

•Tighten the locknut.
Torque — Valve Adjuster Locknuts: 25 N·m (2.5 kgf·m, 18 ft·lb)
•Install the two caps on the alternator cover.
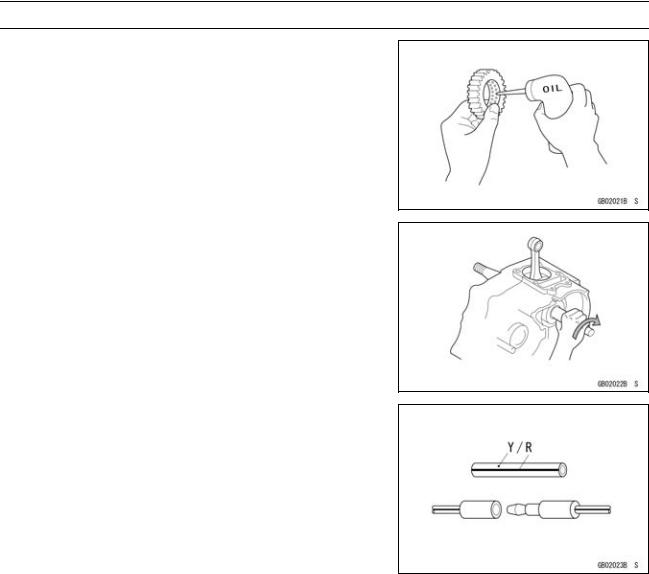
Clutch

To avoid a serious burn, never touch the engine or exhaust pipe during clutch adjustment.
Clutch Operation Inspection
Clutch Operation Inspection
•With the engine idling, make sure that there is no noise or abnormally heavy feeling when pulling [A] in the clutch lever fully. Also, make sure that the shift lever operates smoothly.
•When moving off the motorcycle by releasing the clutch lever gradually, make sure that the clutch does not slip
and that the clutch engages smoothly.


When inspecting by running the vehicle, note a surrounding traffic situation enough in the place of safety.
Clutch Lever Free Play Inspection
•Pull[A]. the clutch lever just enough to take up the free play
•Measure the gap between the lever and the lever holder. 
Clutch Lever Free Play
Standard: 2 3 mm (0.08 0.12 in.)

2-22 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Procedure
Clutch Lever Free Play Adjustment
•Slide back the dust cover [A].
•Loosen both adjuster nuts [B] at the right hand crankcase as far as they will go.
•Loosen the knurled locknut [A] at the clutch lever.
•Turn the adjuster [B] so that 5 6 mm (0.20 0.24 in.) [C] of threads are visible.

Be sure that the outer cable end at the clutch lever is fully seated in the adjuster at the clutch lever, or it could slip into the place later, creating enough cable play to prevent clutch disengagement.
•After the adjustment is made, start the engine and check that the clutch does not slip and that it releases properly.
Wheels/Tires
Air Pressure Inspection/Adjustment
•Measure the tire air pressure with an air pressure gauge [A] when the tires are cold (that is, when the motorcycle has not been ridden more than a mile during the past 3
hours).

Air Pressure (when cold)
|
Front |
150 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm², 21 psi) |
|
Rear |
225 kPa (2.25 kgf/cm², 32 psi) |
Tire Tread Wear Inspection
As the tire tread wears down, the tire becomes more susceptible to puncture and failure. An accepted estimate is that 90% of all tire failures occur during the last 10% of tread life (90% worn). So it is false economy and unsafe to use the tires until they are bald.
•Measure the tread depth at the center of the tread with a depth gauge [A]. Since the tire may wear unevenly, take measurement at several places.

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-23
Maintenance Procedure
Wear Indicator [A]
Wear Indicator Position Mark [B]

Tread Depth
|
Front |
DUNLOP |
BRIDGESTONE |
|
Standard |
6.9 mm (0.27 in.) |
6.0 mm (0.24 in.) |
|
Service Limit |
1 mm (0.04 in.) |
|
|
Rear |
DUNLOP |
BRIDGESTONE |
|
Standard |
8.8 mm (0.35 in.) |
8.5 mm (0.33 in.) |
|
Service Limit |
2 mm (0.08 in.)(Up to 130 km/h (80 mph)) |
|
|
3 mm (0.12 in.)(Over 130 km/h (80 mph)) |

To ensure safe handling and stability, use only the recommended standard tires for replacement, inflated to the standard pressure.
Use the same manufacturer’s tires on both front and rear wheels.
NOTE
○Check and balance the wheel when a tire is replaced with a new one.
Wheel/Tire Damage Inspection
•Remove any imbedded stones [D], nail [C] or other foreign particles from the tread.
Wear Indicator [E]
•Visually inspect the tire for cracks [A] and cuts [B], and replace the tire if necessary. Swelling or high spots indicate internal damage, requiring tire replacement.
•Visuallyage. inspect the wheel for cracks, cuts and dents dam-


2-24 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Procedure
Wheel Bearing Damage Inspection
•Using a jack and attachment, raise the front wheel off the ground (see Wheels/Tires chapter).
•Turn the handlebar all the way to the right or left.
•Inspect the roughness of the front wheel bearing by pushing and pulling [A] the wheel.
•Spin [B] the front wheel lightly, and check for smoothly turn, roughness, binding or noise.

Spoke Tightness and Rim Runout Inspection
Spoke Tightness Inspection
•Check whether all the spokes are uniformly tightened.

Torque — Spoke Nipple: 3.0 N·m (0.3 kgf·m, 26 in·lb)
(On and after EJ650-A3/C3): 5.1 N·m (0.52 kgf·m,
45in·lb)
•Inspect the rims.
WARNING
If any spoke brakes, it should be replaced immediately. A missing spoke places an additional load on the other spokes, which will eventually cause other spokes to break.
Rim Runout Inspection
•Raise the front/rear wheel of the ground.
Special Tool — Jack: 57001-1238
•Check the rim for damage or warpage.
If there is any damage to the rim, replace the rim.
•Measure the radial [A] and axial [B] rim runout by placing a dial gauge against the sides and the outer circumference of the rim, and slowly rotating the wheel.
Rim Runout (with tire installed)
|
Standard: |
|
|
Axial Runout |
0.5 mm (0.02 in.) |
|
Radial Runout |
0.8 mm (0.03 in.) |
|
Service Limit: |
|
|
Axial Runout |
1.5 mm (0.06 in.) |
|
Radial Runout |
1.5 mm (0.06 in.) |


Never attempt to repair a damaged wheel part. If the wheel part is damaged, it must be replaced with a new part.

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-25
Maintenance Procedure
Final Drive
Drive Chain Slack Inspection
Drive Chain Slack Inspection
NOTE
○Check the slack with the motorcycle setting on its side stand.
○Clean the chain if it is dirty, and lubricate it if it appears dry.
•Check the wheel alignment (see Wheel Alignment Inspection/Adjustment).
•Rotate the rear wheel to find the position where the chain is tightest.
•Measure the vertical movement (chain slack) [A] midway between the sprockets.

Chain Slack |
35 45 mm (1.4 1.8 in.) |
|
Standard: |
Drive Chain Slack Adjustment
•Remove: Cotter Pin [A]
•Loosen: Axle Nut [B]
Chain Adjuster Locknuts [F] (both sides)
•Turn the chain adjusting nuts [C] forward or rearward until the drive chain has the correct amount of chain slack. To keep the chain and wheel properly aligned, the left adjuster mark [D] position should align with the same graduation that the right adjuster mark [E] position aligns with.

Misalignment of the wheel will result in abnormal wear and may result in an unsafe riding condition.
•Tighten both chain adjuster locknuts securely.
•Tighten the axle nut (see Front/Rear Wheel Installation in the Wheels/Tires chapter).
Torque — Rear Axle Nut: 108 N·m (11 kgf·m, 80 ft·lb)
•Insert a the new cotter pin [A].
NOTE
○When inserting the cotter pin, if the slots in the nut do not align with the cotter pin hole in the axle shaft, tighten the nut clockwise [A] up to next alignment.
○It should be within 30 degree.
○Loosen once and tighten again when the slot goes past the nearest hole.

2-26 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Procedure
•Bend the cotter pin [A] over the nut.
•Turn the wheel, measure the chain slack again at the tightest position, and readjust if necessary.
•Check the rear brake.
Wheel Alignment Inspection/Adjustment
•Check that the left adjuster mark [A] position should align with the same graduation [B] that the right adjuster mark
position aligns with.

NOTE
○Wheel alignment can also be checked using the straightedge or string method.

Misalignment of the wheel will result in abnormal wear, and may result in an unsafe riding condition.
Drive Chain Wear Inspection
•Remove: Chain Cover
•Rotate the rear wheel to inspect the drive chain for damaged rollers, loose pins and links.

•Stretch the chain taut by hanging a 98 N (10 kg, 20 lb) weight [A] on the chain.
•Measure the length of 20 links [B] on the straight part [C] of the chain from the pin center of the 1st pin to the pin center of the 21st pin. Since the chain may wear unevenly, take measurements at several places.

Drive Chain 20-link Length
|
Standard: |
317.5 318.2 mm (12.50 12.53 in.) |
|
Service Limit: |
323 mm (12.7 in.) |

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-27
Maintenance Procedure

If the drive chain wear exceeds the service limit, replace the chain or an unsafe riding condition may result. A chain that breaks or jumps off the sprockets could snag on the engine sprocket or lock the rear wheel, severely damaging the motorcycle and causing it to go out of control.
For safely, use only the standard chain. It is an endless type and should not be cut for installation.
Drive Chain Lubrication
•If a special lubricant is not available, a heavy oil such as SAE 90 is preferred to a lighter oil because it will stay on the chain longer and provide better lubrication.
•If the chain appears especially dirty, clean it before lubrication.
[A]Apply oil
CAUTION
The O-rings between the side plates seal in the lubricant between the pin and the bushing. To avoid damaging the O-rings and resultant loss of lubricant, observe the following rules:
Use only kerosene or diesel oil for cleaning an O -ring drive chain.
Any other cleaning solution such as gasoline or trichloroethylene will cause deterioration and swelling of the O-ring.
Blow the chain dry with compressed air immediately after cleaning.
Complete cleaning and drying the chain within 10 minutes.
•Apply oil to the sides of the rollers so that oil will penetrate to the rollers and bushings. Apply the oil to the O-rings so that the O-rings will be coated with oil.
•Wipe off any excess oil.
Brakes
Brake Fluid Leak (Brake Hose and Pipe) Inspection
•Apply the brake lever or pedal and inspect the brake fluid leak from the brake hoses [A] and fittings.


2-28 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Procedure
Brake Hose Damage and Installation Condition Inspection
•Inspect the brake hose and fittings for deterioration, cracks and signs of leakage.
○The high pressure inside the brake line can cause fluid to leak [A] or the hose to burst if the line is not properly maintained. Bend and twist the rubber hose while examining it.


Torque — Brake Hose Banjo Bolts: 34 N·m (3.5 kgf·m, 25 ft·lb)
•Inspect the brake hose routing.

Brake Operation Inspection
•Inspect the operation of the front and rear brake by running the vehicle on the dry road.


When inspecting by running the vehicle, note a surrounding traffic situation enough in the place of safety.
Brake Fluid Level Inspection
•Check that the brake fluid level in the front/rear brake reservoirs [A] is above the lower level line [B].
NOTE
○Hold the reservoirs horizontal by raising the motorcycle perpendicular to the ground when checking brake fluid level.
Special Tool — Jack: 57001-1238
•Remove the right side cover.

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-29
Maintenance Procedure


Change the brake fluid in the brake line completely if the brake fluid must be refilled but the type and brand of the brake fluid that is already in the reservoir are unidentified. After changing the fluid, use only the same type and brand of fluid thereafter.
Recommended Disc Brake Fluid
Grade: DOT4

○First, tighten the brake fluid reservoir cap [B] clockwise [C] by hand until the resistance is felt fully; then, tighten the cap an additional 1/6 turn [D] while holding the brake fluid reservoir [A] body.
Brake Pad Wear Inspection
In accordance with the Periodic Maintenance Chart, in-
|
spect the brake pads for wear. |
|
|
•Remove the pads. |
|
|
•Check the lining thickness [A] of the pads in the caliper. |
|
|
If the lining thickness of either pad is less than the service |
|
|
limit [B], replace both pads in the caliper as a set. |
|
|
Stepped Portion [C] |
|
Pad Lining Thickness |
|
|
Standard: |
5.15 mm (0.203 in.) |
|
Service Limit: |
1 mm (0.04 in.) |

2-30 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Procedure
Brake Light Switch Operation Inspection
Front Brake Light Timing Inspection
•Turn on the ignition switch.
•The brake light should go on when the brake lever is applied or after the tip of brake lever moves about 10 mm (0.39 in.) [A].
Rear Brake Light Timing Inspection
•Turn on the ignition switch.
•Check the operation of the rear brake light switch by depressing the brake pedal. The brake light should go on as specified.

Brake Light Timing
Standard: On after about 15 mm (0.59 in.) pedal travel [A]
Rear Brake Light Timing Adjustment
Brake light timing is adjusted by changing the position of the rear brake light switch [A].
•Adjust the position of the switch so that the brake light goes on after the specified pedal travel by turning the adjusting nut [B].
[C]Lights sooner.
[D]Lights later.
CAUTION
To avoid damaging the electrical connections inside the switch, be sure that the switch body does not turn during adjustment.
Suspension
Front Forks/Rear Shock Absorber Operation
Inspection
•Pump the forks down and up [A] 4 or 5 times, and inspect the smooth stroke.



Руководство на английском языке по техническому обслуживанию и ремонту мотоциклов Kawasaki KLE500.
- Издательство: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Год издания: 2004
- Страниц: 401
- Формат: PDF
- Размер: 8,0 Mb

Руководство на английском языке по эксплуатации и техническому обслуживанию мотоциклов Kawasaki Versys.
- Издательство: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Год издания: 2009
- Страниц: 176
- Формат: PDF
- Размер: 1,7 Mb

Руководство на английском языке по техническому обслуживанию и ремонту мотоциклов Kawasaki Versys.
- Издательство: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Год издания: 2006
- Страниц: 627
- Формат: PDF
- Размер: 13,7 Mb

Руководство по эксплуатации и техническому обслуживанию мотоциклов Versys 1000.
- Издательство: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Год издания: 2011
- Страниц: 197
- Формат: PDF
- Размер: 5,7 Mb